Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Human Resource
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
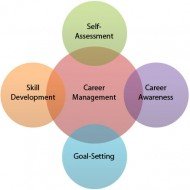
Career Management How to go about Career Management? Career Management is very essential which facilitates smooth transitions from one level to the next higher level in a profession. You cannot decide what to do unless you know what you are going to do or where you want to be tomorrow. Long term personal goals and professional goals are elemental in setting overall targets. According to Stephen P.Robbins, career is “a sequence of life positions occupied by a person during the course of a lifetime. Setting Goals for an Effective Career Your goals may be Long term Short term Personal or Professional Consider if you are goals are Realistic Whether you possess the skill set Achievable within the set time limit (duration) Based on these goals it is important to make long term and short term career plans. Also write down your Experience Skills and Qualification All these basic but vital things will give you a clear picture as to where you stand and what has to be done to improve your skills. Pic Courtesy: Cupcakes and Cashmere EYE Openers While Setting Personal Career Targets A. What do you want to accomplish from two or three years from now? B. What developments and knowledge can make this possible? C. How do you want to prepare yourself to achieve these targets or in what way you want to improve your skills? D. Is there a necessity for check points in the middle of the progress to make the necessary revisions? Tips to Manage Diversifying Careers Adaptability and flexibility are vital to reduce the stress of redundancy. Anticipate the changes and be prepared for anything at any time Look at the ‘Job Loss’ as an opportunity to pursue a new career that interests you. Career Planning A career will be satisfactory only when it interests the person and provides challenge and not by mere compensation or reward. Each organization should plan and help the individual, but every individual should take interest in his career. Career planning entails evaluating abilities and interests and considering alternative career development activities. The process results in Decisions to enter a certain occupation Join a particular organization Accept or decline new job opportunities{relocations, promotions or transfers} Leave an organization for another job or recruitment. Effects of Career Planning In corporate companies, a typical career planning program might include 1. Career counseling by members of the HR department 2. Workshops to help employees evaluate their skills, abilities, and interests to decide on their career development plans 3. Self directed programs to help the workforce guide their own careers through self-assessment and 4. Communication of job opportunities through job postings, videotapes and publications. One has to remember that career counseling may increase the pressure for managers and in turn the organization, as employees either become anxious about their present level of performance and chances for career advancement or they might use the opportunity to demand more from the firm in terms of pay, promotions etc., Key Career Issues of Employees Dual-career couples: When both husband and wife work, their earnings and stress are in surplus Stressors: Children under the age of six need parental care , but the amount of quality time of parents with that of the children is not at all balanced and this causes a heavy stress for both sides emotionally. Work schedule stressors: This increases as a person rises in an organization, job demands increase, with long hours of work and travel, but little time for family and vacation. Relocation: The increase in the number of dual career couple poses problems for many companies when they try to relocate...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments

An Open Frame of Mind: Line and staff authority should be open with each other and come out of their compartmentalized state of mind. Rationale thinking and logical action is what is required to understand and resolve conflicts.Be a Manager rather than a Technocrat: Specialization has made people to stick to their line of action and they act merely like tech wizards and conveniently forget the human element of flexible mental purview and compromise. Development of each individual’s managerial qualities will minimize conflicts. A manager has to harmonize functions of diverse natures and bring about co-ordination.Think as an Entrepreneur: Thinking about the strength, weaknesses, opportunities and threats an organization faces makes each individual realize that he or she is part of the organization and whatever happens to the firm directly affects his/her stability and security.Make others feel a Sense of Achievement: It is the job of a manager to appreciate and encourage the achievements of his sub ordinates that bring greater joy in the minds of individuals and motivate them to work for the cause.Interaction among Functions: Cross functional interactions on a continuous basis are found to be useful in preventing and resolving conflicts. Informal groups serve as the best example of a committee consisting of members from different functional groups but with a common interest. These groups can be best identified and utilized by the management to resolve conflicts by seeking the help of the key person in the group.Roles, Responsibilities and the Scope of other Functions: The basic requirement is to first clearly define the objectives and sub objectives, the process, the roles of each function as a tool and their rights and responsibilities. One should know the roles and responsibilities of all functions having common interface: their position in the firm as well as their relevance and contribution towards the organizational goals.Communication and Information Sharing: The informal communication system helps in achieving group dynamics and cohesion while the formal channels take care of organizational directives. A quick and effective means of communication can considerably reduce the conflict level that arises out of communication disorders.Adequate Planning and Co-ordinations: At each operational level, hasty actions must be avoided to stop conflicts from arising. Planning and Co-ordination go hand in hand: Say, if a new product launch is aimed at without proper promotion, what would happen to the success of the project?Evaluation of Functional Performance: A standard mechanism must be set to evaluate managerial performance in terms of their ability to achieve an integrated set of objectives in a balanced manner.Necessity of Transparency: Transparency is needed at all functional levels or the initiator appears to be tainted with the accusation of having an ulterior motive. In case of big corporate firms all the policy decisions are taken by the board and not by a single person to avoid conflicts. Conflict need not necessarily be viewed as an evil but a disorder to be curbed. Sometimes a conflict might showcase the inherent inflexibility and malfunctions in the firm to be corrected paving way for innovations. Sometimes it causes frustration for the management by preventing synergy amongst the sub-systems. All said and done, conflict once identified have to be immediately dealt with and resolved by the management in order to facilitate smooth functioning of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
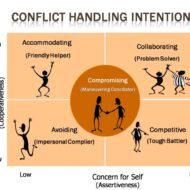
Conflict Management What is a conflict? An organization is a network consisting of human element as the major functional source and as such is prone to weaker vulnerable aspects of human psychology. Conflict is, of course, one such weak point. The diverse functional groups in the organization get into conflicts while setting up objectives and goals; in prioritizing and weighing the objectives, the methods of their achievement and their evaluation. Though there are numerous kinds of conflicts, this is the major one affecting the functioning of the firm. Certain examples of conflicts: The objective of a project manager to construct a building might go against the objective of minimizing the project cost. For work force, their personal goals come before the organizational goals. The objective of the production department to increase productivity may go against the objective of maintaining the product quality The objectives of the marketing department to increase the sales through promotions may not be welcome by the finance department whose objective will be to cut the cost’ Reasons for conflicts: 1. Lack of clarity as to the scope and relevance of functions in achieving the corporate objectives. 2. Clash between line and staff authorities. 3. Ignorance or lack of knowledge needed for decision making in the part of chief executives 4. Different sets of beliefs and views, along with one’s personal interest and ego. 5. Different kinds of attitudes of members of the organization 6. Absence of clarity in organizational policy, procedures, rules and guidelines. The Results of Conflict: The most affected element in a group conflict is “Employee Morale.” Conflicts undermine professionalism and lead to under utilization of organizational capacity. Loss of Importance: A particular group of employees feel that their importance is being undermined. When a manager is being inducted from an outside source, the prospective employees of the firm feel that they have been let down by the management. Frustration: There are certain rules and regulations to be stuck to when issues arise. If the finance department is not consulted regarding issues related to insurance claims, there are chances that the company might lose a good deal. In such cases frustration arises which is not good for the health of the firm. Feeling of Insecurity: This affects severely the morale of an employee. A clerical staff feels insecure if new technological system is introduced in the company where he is a novice. When one’s importance is persistently reduced, he may start feeling redundant. Blocked Personal Growth: Persons who experience reduced importance may apprehend a situation where they don’t expect much by way of personal growth through increments and...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Interview Questions, Principles of Management
on Feb 27th, 2014 | 0 comments

Interview Interesting Aspects An interview can be explained as a mutual conversation or a one to one meeting that gets stretched into a “recruitment process or promotion.” In French, from which it originates interview means ‘inter-sight’ and in Latin, it is interpreted as ‘seeing each other.’ Nowadays interview is a powerful tool in psychology, in the healthcare profession as well as in business. Too many approaches in the interviewing process may be successful as fact finding tools but without looking at the dynamics existing between an interviewer and interviewee; such meetings then become lifeless. The notion of an interview should not only aim at collecting scientific data but also look into the human aspect to capture the essence of a person. Only a trained interviewer must be allowed to evaluate the interviewee’s motivation, personality component and the influence of environmental/ emotional problems on him/her. The two common pitfalls in an interview are the ‘stereotyping’ of the individual and the unconscious exercise of personal bias. Is it wise to judge a person based on similarities to some other person/ trait? ‘Halo Effect’ is the tendency to judge a person based on one of a few specific characteristics- the traits liked or disliked by the interviewer need not be superimposed on the interviewee to decide if he is suitable for the job. All depends on the interviewer and his characteristics which help or hinder an interview from the interviewee’s view point. Care must be taken on the part of the interviewer not to conclude the interview in an abrupt manner and it is also necessary for him to create a favorable image for the company in the mind of the interviewee. The interview is not to be considered merely as a selection technique, but as a means of in- depth analysis that facilitates closer and enhanced communication. This approach is very much necessary for psychologists, teachers, managers, leaders and the like. Definition: The interview is a conversation with a purpose. There are three purposes. 1. Obtaining information– Collecting relevant data about the candidate’s background, training, education, experience and interests. 2. Giving information– Apprising the interviewee with the present position of the company, the future plans, specific job and the personnel. 3. Motivation– Instigating the candidate to join the company Advantages of Interview: Interviews prove as a better means to measure the ability and traits of a personality rather than through written tests or other techniques. It is easy to determine how a person reacts in a conversation and whether he is good looking (here it means if he/ she is presentable, looks are equally important). A skilled interviewer can easily determine the personality traits such as loyalty and responsibility that can be expected from the candidate during this personal meeting. Limitations of Interview: · Stereo typing · Halo Effect · Personal bias Interviewing Techniques: A. Patterned Interview: This was developed by Mc. Murry. Senior recruitment, promotion and appraisal interviews fall under this category. This patterned interview contains no questions related to ‘job skills’. Basically it is conducted to appraise personality, motivation and interests. Reference checks and academic records determine knowledge and job competencies. The following personality traits could be measured through patterned interview according to Mc. Murry: i. Stability ii. Ability to get along with others iii. Self-reliance iv. Willingness to accept responsibility v. Freedom from emotional immaturity vi. Motivation B. Directive Style: This type of interview is appropriate when the interviewer seeks factual information only where the interviewee is not given much freedom of expression and so becomes defensive. There are also chances that the relationship between the interviewer and the interviewee might be impaired. C. Non-Directive Style: This requires more time, and suitable for exploring sensitive matters, understanding feelings and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments

Following are some of the intrinsic motivational techniques employed by the organisations to boost the morale of the employees and thus the productivity. Intrinsic motivation 1. Job Design Arranging work elements to form tasks and a combination of such tasks to form a job is called as job design. Here the focus is on the job. 2. Job Redesign Here the work elements are rearranged into meaningful tasks and combining such tasks to form work modules is the principle behind job redesigning. Each work module is assigned to the respective worker who is capable of performing it efficiently and number of such modules can be combined to form a whole job which is assigned to a group to improve their intrinsic motivation. Here the focus is on the individual workers. 3. Work Modules Work module can be defined as one that is being completed approximately in two hours time. In an eight hours shift there will be four such work modules. Employees are motivated not merely by pay and perks; there should be something more to the job , more challenging and meaningful. The following are some of the methods of job redesign that provide the expected challenge and meaning. Types of Job Redesigning A. Job Rotation Monotonous work makes an employee dull and in order to motivate the employees, the management can think of what is called Job Rotation. To rotate the person or persons from job to job, from time to time. The job to which he is rotated should match his attributes, level of hierarchical position in the organization and compatible with his competence and experience. BENEFITS OF JOB ROTATION: Reduces boredomIncreases motivationIncreases Employment flexibilityAdds experience to a worker’s careerIncreases training motivation LIMITATIONS OF JOB ROTATION Lot of time is consumed as workers need to be trained to suit the new jobAs well increases training costIf the worker does not fit in the new job, he has to continue his routine work which can create a sense of inferiority and loss of moraleReduced productivity during transition periodDemotivates ambitious employees who seek steady employmentIt is generally believed that job rotation reduces turnover of employees in an organization. B. Job Enlargement When a job is expanded horizontally, job enlargement occurs. For example, when an accountant is entrusted with additional responsibilities of following up of orders, dispatch and payments, his job is said to be enlarged. He has to take up variety of tasks and job activities other than book keeping. BENEFITS OF JOB ENLARGEMENT Increases one’s area of responsibilityAids in growth and versatilityFlexibility in deployment LIMITATIONS OF JOB ENLARGEMENT The criticism is, whether there is improvement in the quality of work is a question mark; the workers line of thinking may be like this” Instead of one lousy job, now I have many”!Does not add challenging or meaningful work. C. Job Enrichment When the job expands vertically, it is called job enrichment. If a person is made to involve in quality work, in other words management functions like planning, co-ordinating, controlling and decision-making, it is said to enrich him in terms of experience and expertise. Guidelines for Job Enrichment: Combine tasks When certain tasks are combined to form work modules, it increases skill variety and task identity. ERP or ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING is a job entity that combines production, marketing, finance, human resource and logistics departments in one go. The software connects all the departments in such a fashion that when an order is placed by a customer, the stock existence, current price of the product, credibility of the customer, delivery schedule are available for the executives of the concerned department in their systems simultaneously so that decisions could be quickly made. Time is saved as the order need not be passed on from department to department thanks to the availability of common information to all the departments at...










