Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Apr 10th, 2014 | 0 comments
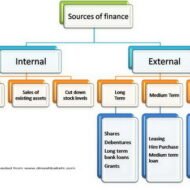
Unsecured and Secured Short Term Sources Unsecured Non-Bank Short Term Sources Commercial Paper: Short-term, unsecured promissory notes, generally issued by large corporations, with maturities of a few days to 270 days. Usually issued in multiples of $100,000 or more. Commercial paper market is composed of the (1) dealer and (2) direct-placement markets. Advantage: Cheaper than a short-term business loan from a commercial bank. Dealers require a line of credit to ensure that the commercial paper is paid off. Private Loans: A short term unsecured loan may be taken from a wealthy shareholder, a major supplier, or other parties interested in assisting the firm through a short term difficulty. Cash Advances for Customers: A customer may pay for all or a portion of future purchases before receiving the goods. This aids the firm to purchase raw materials and produce the final goods. This form of financing is a special arrangement for expensive or custom-made items that would strain the financial resources of the manufacturing company. Secured Short-term Sources: Security (collateral) — Asset (s) is pledged by a borrower to ensure repayment of a loan. If the borrower defaults, the lender may sell the security to pay off the loan. Collateral value depends on: Marketability Life Riskiness Types of Inventory Backed Loans: Field Warehouse Receipt — A receipt for goods segregated and stored on the borrower’s premises (but under the control of an independent warehousing company) that a lender holds as collateral for a loan. Terminal Warehouse Receipt — A receipt for the deposit of goods in a public warehouse that a lender holds as collateral for a loan. Trust Receipt – This loan is secured by specific and easily identified collateral that remains in the control or physical possession of the borrower. A security device acknowledging that the borrower holds specifically identified inventory and proceeds from its sale in trust for the lender. Example: When automobile dealers use this kind of financing for the cars in their showrooms or in stock, it is called floor planning. As implied by the name, this kind of loan requires a considerable degree of trust in the honesty and integrity of the borrower. Once the inventory is sold or the receivable is collected, payment must be remitted to the lender. If there is a default, the loan is said to be secured by bogus collateral. These loans are common when the collateral is easily identified by description or serial number and then each item of collateral has relatively large dollar value. Floating Lien — A general, or blanket, lien against a group of assets, such as inventory or receivables, without the assets being specifically identified Chattel Mortgage — A lien on specifically identified personal property (assets other than real estate) backing a loan. Financial Institutions: Primary sources of secured short term financing are banks and financial institutions, including insurance companies, finance companies, and the financial subsidiaries of major corporations. The best mix of short-term financing depends on: Cost of the financing method Availability of funds Timing Flexibility Degree to which the assets are encumbered It is always better to go for bank loans or loans from established and long standing private institutions because there is a leverage for the debtors to sit for discussions to sort out issued in case of defaults. All banks in India are trying to close accounts labeled under NPA- Non Performing assets either by recovering the money through one time settlement (OTS) or by auctioning the collaterals pledged during the time of loan sanctioning. If you happen to take loans from individuals or third-parties, you cannot enjoy this comfort or breather. Some Finance Quotes and Sayings for You: A...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Decision Making, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 30th, 2014 | 0 comments
TURNOVER RATIO OR ACTIVITY RATIO or ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIO Turnover ratios are also known as activity ratios or efficiency ratios with which a firm manages its current assets. The following turnover ratios can be calculated to judge the effectiveness of asset use. Inventory Turnover Ratio Debtor Turnover Ratio Creditor Turnover Ratio Assets Turnover Ratio 1. INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO This ratio indicates whether investment in stock is efficiently used or not, in other words, the number of times the inventory has been converted into sales during the period. Thus it evaluates the efficiency of the firm in managing its inventory. It helps the financial manager to evaluate the inventory policy. It is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by average inventory. Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of goods sold / Average Inventory (or) Net Sales / Average Stock Cost of goods sold = Sales-Gross profit Average Stock =Opening stock + Closing stock/2 2. DEBTOR TURNOVER RATIO Debtors play a vital role in current assets and to a great extent determines the liquidity of a firm. This indicates the number of times average debtors have been converted into cash during a year. It is determined by dividing the net credit sales by average debtors. Debtor Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Trade Debtors (or) Net Credit Sales / Average Debtors – Average Bills Receivable Net credit sales = Total sales – (Cash sales + Sales return) Total debtors = [ Op.Dr. + Cl.Dr. / 2 + Op.B/R + Cl. B/R / 2] When the information about credit sales, opening and closing balances of trade debtors is not available then the ratio can be calculated by dividing total sales by closing balances of trade debtor Debtor Turnover Ratio = Total Sales / Trade Debtors Note: Bad and doubtful doubts and their provisions are not deducted from the total debtors. The higher ratio indicates that debts are being collected promptly. 3. CREDITOR TURNOVER RATIO This is also known as “Creditors Velocity”. It indicates the number of times sundry creditors have been paid during a year. It is calculated to judge the requirements of cash for paying sundry creditors. It is calculated by dividing the net credit purchases by average creditors. Creditor Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Purchases / Average Trade Creditor (or) Net Credit Purchases / Average Creditors + Average Bills Payable Net credit purchases = Total purchases – (Cash purchase + Purchase return) Total Creditors = [Op.Cr. + Cl.Cr. / 2 + Op. B/P + Cl. B/P / 2] The higher ratio should indicate that the payments are made promptly. Net credit purchases consist of gross credit purchases minus purchase return. When the information about credit purchases, opening and closing balances of trade creditors is not available then the ratio is calculated by dividing total purchases by the closing balance of trade creditors. Creditor Turnover Ratio = Total purchases / Total Trade Creditors 4. ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO The relationship between assets and sales is known as assets turnover ratio. Several assets turnover ratios can be calculated depending upon the groups of assets, which are related to sales. a) Total asset turnover. b) Net asset turnover c) Fixed asset turnover d) Current asset turnover e) Net working capital turnover ratio a. TOTAL ASSET TURNOVER This ratio shows the firms ability to generate sales from all financial resources committed to total assets. It is calculated by dividing sales by total assets. Total asset turnover = Total Sales / Total Assets b. NET ASSET TURNOVER This is calculated by dividing sales by net assets. Net asset turnover =Total Sales / Net Assets Net assets represent total assets minus current liabilities. Intangible and fictitious assets like goodwill, patents, accumulated losses, deferred expenditure may be excluded for...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 30th, 2014 | 0 comments

SOLVENCY OR LEVERAGE RATIOS Long-term solvency ratios analyze the long-term financial position of the organization. Bankers and creditors are interested in the liquidity of the firm, whereas shareholders, debenture holders and financial institutions are concerned with the long term prosperity of the firm. There are thus two aspects of the long-term solvency of a firm. Ability to repay the principal amount when due Regular payment of the interest. The ratio is based on the relationship between borrowed funds and owner’s capital it is computed from the balance sheet, the second type is calculated from the profit and loss a/c. The various solvency ratios are Debt equity ratio Debt to total capital ratio Proprietary (Equity) ratio Fixed assets to net worth ratio Fixed assets to long term funds ratio Debt service (Interest coverage) ratio 1. DEBT EQUITY RATIO OR EXTERNAL – INTERNAL EQUITY RATIO Debt equity ratio shows the relative claims of creditors (Outsiders) and owners (Interest) against the assets of the firm. The relationship between borrowed fund and capital is shown in debt-equity ratio. It can be calculated by dividing outsider funds (Debt) by shareholder funds (Equity) Ebt equity ratio = Outsider Funds (Total Debts) / Shareholder Funds or Equity (or) Long-term Debts / Shareholders funds Shareholders fund = Preference capital + Equity capital + Reserves & Surplus – Goodwill & Preliminary expenses Outsiders funds = Current liabilities + Debentures + Loans The ideal ratio is 2:1. High ratio means, the claim of creditors is greater than owners and vice-versa 2. DEBT TO TOTAL CAPITAL RATIO Debt to total capital ratio = Total Debts / Total Assets 3. PROPRIETARY (EQUITY) RATIO This ratio indicates the proportion of total assets financed by owners. It is calculated by dividing proprietor (Shareholder) funds by total assets. Proprietary (equity) ratio = Shareholder funds / Total Tangible assets The ideal ratio is 1:3. A ratio below 50% may be alarming for creditors, because they incur loss during winding up. 4. FIXED ASSETS TO NET WORTH RATIO This ratio establishes the relationship between fixed assets and shareholder funds. It is calculated by dividing fixed assets by shareholder funds. Fixed assets to net worth ratio = Fixed Assets X 100 / Net Worth The shareholder funds include equity share capital, preference share capital, reserves and surplus including accumulated profits. However fictitious assets like accumulated deferred expenses etc should be deducted from the total of these items to shareholder funds. The shareholder funds so calculated are known as net worth of the business. 5. FIXED ASSETS TO LONG TERM FUNDS RATIO Fixed assets to long term funds ratio establishes the relationship between fixed assets and long-term funds and is calculated by dividing fixed assets by long term funds. Fixed assets to long term funds ratio = Fixed Assets X 100 / Long-term Funds 6. DEBT SERVICE (INTEREST COVERAGE) RATIO This shows the number of times the earnings of the firms are able to cover the fixed interest liability of the firm. This ratio therefore is also known as Interest coverage or time interest earned ratio. It is calculated by dividing the earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) by interest charges on loans. Debt Service Ratio = Earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) / Interest...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Project Management, Startups
on Mar 5th, 2014 | 0 comments

Small Business Startup Checklist Establishment of a small business and successfully running it is definitely by no means a small achievement. It is a commendable achievement as entrepreneurs are the backbones of a country’s economy and its growth. Proper planning and understanding the significance of critical factors and determinants affecting a small business paves way for the smooth functioning of your enterprise. What are the prerequisites for running a small business? Any plan or idea to be transformed into a product or a service needs to be categorically put into experimentation and subject to inquiries. Prepare a detailed project report With the help of an external expert consultant get it appraised Let the product be innovative which has hitherto not hit the market, for instance flying cars Plan your geographical area of operations Go for a detailed market survey through questionnaires and giving out free samples Try to gauge the pulse of your target customers Launch your product at the right time Plan your marketing strategy regarding price and promotions Fix up proper capitalization that would meet your financial requirements. Definitely you have to bring in initial working capital of your own and don’t rely solely on bankers for the entire funding. Asset management, fixed capital and working capital management must be absolutely preplanned. Man power requirements -Right person for the right job and the appropriate number of persons needed to complete a job has to be planned. Their recruitment, selection, training and development forms part of the package. Location and Layout Most important criterion is the location and layout of your manufacturing facility. It should facilitate easy movement of materials to bring the product out to the market in the shortest possible time. Avoid bottlenecks or try to resolve them for smooth production. As we all know technology feeds on itself and more the delay, more competitors and better products throng the market. Keep in mind the end product should always reach the buyer or the consumer at the right time. Plan your re order level, delivery schedule and lead times in accordance with the orders in hand. Picture Courtesy : Yourcityenterprise.com Production Inputs Smooth supply of production inputs, uninterrupted supply of power, copious water supply, the nature of the soil( if your product is agro based), proximity to the market and transportation facilities have to be given due importance. Your product has to be compliant in such a way that it should not pollute the environment. So a proper waste disposal management system should be designed right at the start of your operations. Book-Keeping Proper book keeping and maintaining your accounts will please the tax authorities by which you create goodwill for your company and also keep your credit management under controllable limits. Any product centered around the consumer will be a hit and that is “marketing”. If you plan your success formula from your product that is “selling” that might not always be successful. Your distribution channels should be continuous with unbroken links and strong. The kind of self confidence that you exuberate makes you a reliable person and in the long run you become iconic. Technology Updates Businessmen have trained the customers to expect something new everyday, because such is the power of technology and the competitor force. So it is better to keep yourself updated with the latest technology available in the market. Take your product to your customers in a convincing manner by which it proves to be a win-win situation for both sides; profit making and customer satisfaction for the entrepreneur and buying products the money’s worth and the real benefits of the product for the...

Posted by Managementguru in Powerpoint Slides
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Basics of Accounting Purpose of Accounting Break Even Analysis Financial Accounting...









