Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Business Management, Financial Accounting
on Jul 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
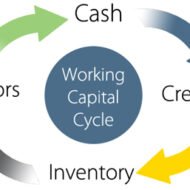
Understanding Working Capital: It is the life blood of business. Funds needed for the purchase of raw materials, payment of wages and other day-to-day expenses are known as working capital. It is part of the firm’s capital, which is being used for financing short-term operations. Hence, it may also be termed as Circulating Capital or Short-Term capital. “Working capital means current assets” –Mead, Malott and Field. “Any acquisition of funds which the current asset increases working capital, for, they are one and the same.” – J.S.mill Financial troubles and issues arise only when this entity called ‘working capital’ is not properly managed. Every successful company will hire a financial manager to deal with issues relating to finance while the CEO can look into matters relating to promotion of the product or service and the position of the company in the market. The ‘Sales Turnover or Sales Volume’ is the key issue you have to look into to gauge whether you have sufficient working capital to manage that big a volume for that particular period. You have to rotate your funds wisely keeping in mind the credit policies your company offers and the credits you may enjoy with your supplier, bank interest for the short-term loans etc. Concept of WC: Working capital implies excess of current assets over current liabilities. Funds invested in current assets is known as “Gross Working Capital.” The difference between current assets and current liabilities is known as “Net Working Capital.” What are the two types? Permanent or fixed: It is the minimum amount of current assets required for conducting the business operation. This capital will remain permanent in current assets and should be financed out of long-term funds. The amount varies from year to year, depending upon the growth of a company. Temporary or Variable: It is the amount of additional current assets required for a short period. It is needed to meet the seasonal demands at different times during a year. The capital can be temporary and should be financed out of short-term funds. The working capital starts decreasing when the peak season is over. Various Factors Influencing WC: Nature of business: Service oriented concerns like electricity; water supplies need limited working capital while a manufacturing concern requires sufficient working capital, since they have to maintain stock and debtors. Credit Policies: A company which allows credit to its customers shall need more amount while a company enjoying credit facilities from its suppliers will need lower amount of working capital. Manufacturing Process: Conversion of raw materials into finished goods is called manufacturing or production. Longer the process, higher the requirement of working capital. Rapidity of turnover: High rate of turnover requires low amount and lower and slow moving stocks need a larger amount of working capital. Say, jewelry shops have to maintain different types of designs calling for high working capital. Fast moving goods like grocery requires low working capital. Business cycle: Changes in economy has a say over the requirement of working capital. When a business is prosperous, it requires huge amount of capital; also during depression huge amount is needed for unsold stock and uncollected debts. Seasonal variation: Industries which are manufacturing and selling goods seasonally require large amount of working capital. Fluctuation of supply: Firms have to maintain large reserves of raw material in stores, to avoid uninterrupted production which needs large amount of working capital. Dividend policy: If a conservative dividend policy is followed by the management, the need for working capital can be met with the retained earnings, it consequently drains off large amounts from working capital pool. ...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Technology
on Jun 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
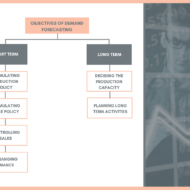
Objectives of Forecasting The objective of this post is to impart some light on the uses and importance of forecasting and to get you acquainted with various forecasting techniques. What is Forecasting? Forecasting is a technique that uses historical data as inputs to make informed estimates that are predictive in determining the direction of future trends. And also to know how these techniques are used in an organization’s decision making process. Nature of Forecast A forecast is an estimate of an event which will happen in future – be it, demand of a product, rainfall at a particular place, population of a country, or growth of a technology.It is estimated based on the past data related to a particular event and hence it is not a deterministic quantity.In any industrial enterprise, forecasting is the first level decision activity before consolidating other decision problems like, materials planning, scheduling, type of production system.Forecasting provides a basis for co-ordination of plans for activities in various units of a company.All the functional managers in any organization will base their decision on the forecast value. So, it provides vital information for that organization. Classification of Forecasts Technology forecastsEconomic forecastsDemand forecasts 1. Technology Forecast Technology is a combination of hardware and software. Hardware is any physical product while software is the know-how, technique or procedure. Technology forecast deals with certain characteristics like level of technical performance, rate of technological advances. It is a prediction of the future characteristics of useful machines, products, process, procedures or techniques. TIFAC – Technology Information Forecasting and Assessment Council is an autonomous organization set up in 1988 under the Department of Science & Technology. In 1993, TIFAC embarked upon the major task of formulating a Technology Vision for the country in various emerging technology areas. 2. Economic Forecast Government agencies and other organizations involve in collecting data and prediction of estimate on the general business environment. Economic forecast This involves the application of statistical models utilizing variables sometimes called indicators. Some of the most well-known economic indicators include inflation and interest rates, GDP growth/decline, retail sales and unemployment rates. This is used to predict future tax revenues, level of business growth, level of employment, level of inflation etc. Also, these will be useful to business circles to plan their future activities based on the level of business growth. 3. Demand Forecast This gives the expected level of demand for goods or services. This is the basic input for business planning and control. Hence, the decisions for all the functions of any corporate house are influenced by demand forecast. Factors Affecting Demand Forecast Business cycleRandom variationCustomer’s planProduct’s life cycleCompetitor’s efforts and pricesCustomer’s confidence and attitudeQualityCredit policyDesign of goods or servicesReputation for serviceSales...

Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Economics, International Business, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
Factors That Influence Global Economy The industrial and business environment of developing countries has been subjected to a sea of changes owing to the economic reforms and policies in the light of globalization, privatization and liberalization. A long term economic vision is necessary for these countries to establish themselves in the global market which facilitates the process of becoming self sufficient in due course of time. Let me present you with a synopsis of how this change can happen and how countries are adapting themselves in lieu of the global economic boom. Multi Brand Retail Markets: Many multinational companies have acquired and are trying to acquire a major part of equity in multibrand retail markets of the host country and sometimes they opt for Joint ventures to factorize the economy of scale which also proves to be a win-win situation for both the parties. Developing countries have altered their economic views on foreign direct investment and are very liberal in their attitude in providing with the necessary licenses. The entry of multinational companies and their potential investment has even altered core sectors like power, oil and telecommunications. Moreover, the benefit of cheap labor, economic subsidies for the start of operations in economically backward regions lures foreign investors. Rush of Entrepreneurship: There is a rush of entrepreneurship in the developing countries, in the form of setting up of small scale industries, cottage industries for which liberal subsidies are provided by the governments to encourage the act of entrepreneurialism. Also people want to go for diversification, mergers and acquisitions in the wake of global competition. Capital Markets’ Role: Capital markets have gained new buoyancy. The rapid growth of stock market and its influence over the international economic scenario have made foreign brokers to keenly follow the market changes for potential investment. The one striking feature of the economy of developing countries is that, it is a self made economy and withstands the pressures of the business cycle, such as recession and inflation, unlike foreign markets that have failed to stabilize their markets owing to what is called sub prime lending, a plan that has failed to achieve the desired economic growth. Instead of making the capital market alive with fresh infusions of funds, it has left many banks and financial institutions bankrupt. Banking Sector: Banking sector has scaled to greater heights and has come under a competitive environment. Deregulation of interest rates to attract potential investors, new technology, products and aggressive marketing usher in new competition; disinvestment of government equity in nationalized banks have made banks to operate as commercial institutions and their services get marketed as branded consumer products. Financial services have emerged as a new business and funding options are aplenty increasing the chances of raising capital. This has evolved as a separate and major source of business fetching revenue to the service providers. Private Sector: Private sector is gaining importance in countries like India, where they have entered all the core industries like oil, mining, telecommunications, road building, railways, ports, civil aviation etc. This serves as a revenue source for the government and this kind of economic restructuring has brought a wave of enthusiasm amongst the potential investors. Imports have become an entrepreneurial activity and are out of the government domain and this has been facilitated by relaxation of licensing hassles. These are some of the recent trends in the developing countries that have captured the interest of multinational...






