Posted by Managementguru in Management Accounting
on Mar 24th, 2015 | 0 comments
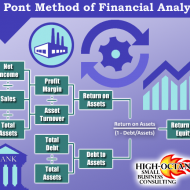
What are the advantages and limitations of ratio analysis? Advantages: It is an important and useful tool to determine the efficiency with which working capital is being managed in a business organization. It is a ‘health test‘ for a business firm in that it can gauge whether the firm is financially healthy or not. It aids the management of business concern in evaluating its financial position and performance efficiency. It clearly shows the trend of changes in the market position (upward, downward or static), as it covers a number of previous accounting (financial) periods. The progress or downfall of a firm is clearly indicated by this analysis. It assists in preparing financial estimates for the future (financial forecasting). It facilitates the task of managerial control to a great extent. It helps the credit suppliers and investors in deciding upon a business firm as a potential investment outlet or desirable debtor. Ideal or Standard ratios can be established which can be used as reference points of comparison for a firm’s progress over a period of time. It communicates important information with relation to financial strength, earning capacity, debt (borrowing) capacity, liquidity position, capacity to meet fixed commitments, solvency, capital gearing, working capital management, future prospects etc. of a business concern. This analysis is also useful for bench marking purpose- to compare the working result and efficiency of performance of a business enterprise with that of other firms engaged in the same industry (inter-firm comparison). It helps the management to discharge their basic functions of planning, coordinating, controlling etc. It serves as an instrument for testing management efficiency too. It acts as a useful tool for deciding on certain policy matters. Limitations: Accounting ratios calculated based on ratio analysis will be correct only if the accounting data on which they are based are correct. It is only an analysis of past financial data. In certain cases ratio analysis might prove to be misleading with regard to profits. Continuous fluctuation in price levels ( or, purchasing power of money) seriously affect the validity or comparison of accounting ratios calculated for different accounting periods and make such comparisons very difficult. Comparisons become difficult also on account of difference in the definition of several financial (accounting) terms like gross profit, operating profit, net profit etc. There is lot of diversity in practice as regards to the measurement of ratios. Different firms use different accounting methods and the validity of comparison is severely affected by window dressing in the basic financial statements. A single ratio will not be able to convey much information. This analysis only gives part of the total information required for proper decision-making. This should not be taken as a substitute for sound judgement. It should not be overlooked that business problems cannot be solved mechanically through ratio analysis or other types of financial analysis. Follow ManagementGuru Net’s board Accounting – Financial and Management Accounting on...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 7th, 2014 | 0 comments

Performance Optimization Through Effective Management An organization is a network of people striving to achieve their targets. So it is a wise thing to synchronize their activities in-order to enhance the harmony and build a strong team as well that protects the network from crumbling by means of mutual trust and behavior. It is imperative for the management to define the structure and hierarchy as well as the techniques that help the organization to efficiently function. Here are some means to make your organization to function efficiently and you’re your team stand apart from the crowd. Training of Subordinates: The better the training of subordinates, the fewer the number of necessary supervisors. Well trained subordinates require not only less of their manager’s time but also less contact with their managers. ‘On the job’ training programmes have found to be more effective in industries which are labor intensive. Coaching and mentoring improve the understanding and efficiency of the workforce and help them to maximize their effort and in turn productivity. Clarity of Delegation of Authority: The most serious symptom of poor organization affecting the span of management is inadequate or unclear authority delegation. If a manager clearly delegates authority to perform a well defined task, a well trained subordinate can get it done with the minimum of manager’s time and attention. But if the subordinate’s task is not clearly defined, either the task will not be performed or it will be a colossal waste of time for the manager to supervise and guide the subordinates’ effort. Clarity of Plans: The character of a subordinates‘ job is defined by the plans to be put into effect. If these plans are well defined, if they are workable, if the authority to undertake them has been delegated, and if the subordinate understands what is expected, little of a supervisor’s time will be required. Such is often the case with a production supervisor, who bears the responsibility of achieving targets within the stipulated time period. If the plans cannot be drawn accurately, subordinates must do much of their own planning where they may lack direction. On the other hand if the superior has setup clear policies to guide decisions and has made sure they are consistent with the operations and goals of the department, work becomes simple and easy for the subordinates to follow. Communication Techniques: If every plan, instruction, order or direction has to be communicated by personal contact and every organization change or staffing problem has to be handled orally, it slows down the managerial activity. The ability to communicate plans and instructions clearly and concisely also tends to increase a manager’s span. At the same time the subordinate’s job is greatly facilitated by superiors who can express themselves well. A manager’s casual easy style may please subordinates, but it reduces the effective span of management and lowers morale as well. Amount of Personal Contact Needed: Many situations cannot be completely handled with written reports, memorandums, policy statements, planning documents and other communication techniques that do not involve personal contact which an executive find it valuable. There are other situations in which the best way of communicating a problem, instructing a subordinate, or “getting a feel” of how people really think is to spend time in personal contact . The high percentage of time spent in meetings and committees might be reduced some what by better training, better policy making and planning, clearer delegation, more thorough staff work, better control system and objectives standard. Studies have revealed that, effective spans were narrower at lower and middle levels of organization but were increased at upper levels and size had little...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments
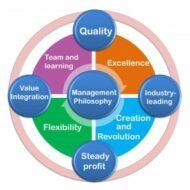
Corporate Philosophy of Management CORPORATE PHILOSOPHY OF MANAGEMENT calls for creating a framework of values, beliefs and ethical standards which are considered to be vital for an effective management. They must be embedded in formal and informal philosophical statements which are then communicated to the fraternity of that organization. From a broader perspective, the LEADER has to have a VISION as to where he is heading his company in the next three to four years. Corporate Objectives provide vision as well as direction and map for bold decisions to be taken regarding NEW MARKETS MARKET SHARE PRODUCTS SERVICES etc. , Now the organization is in a position to decide and prioritise the VALUES AND COMPETENCIES it expects from its managers. For example, if the situation favors the business expansion to new markets, say, European or Asian, then an organization has to develop competence in areas like LANGUAGE AND CULTURE, besides marketing and business skills. Different Philosophies of Management: Well, you might have been inspired with JAPANESE PHILOSOPHY OF MANAGEMENT, EASTERN OR WESTERN PHILOSOPHY OF MANAGEMENT t. But what is the fun? If you don’t have A SOUND MANAGEMENT PHILOSOPHY of your own, to simply put it, you don’t have a broad set of principles to back up your management development process which is a generic one. Ideally speaking, you should be able to develop a concrete SYSTEM that is made up of FOOL PROOF policies and procedures; try to develop a professional team of executives who can take up your vision to the next level; these measures will prove worthwhile in the long run. You are left without any choice but to develop “truly” INTERNATIONAL MANAGERS who could transcend nationally and the location of any specific job consideration. This is what Ideal management philosophy means to me, A holistic vision of the future A solid set of principles(values, beliefs) Sound policy definition Management development programmes Autonomy to my work force Always “yes “to new technology Development of women managers Flexible leadership Social responsibility Contribution to the growth of my Country’s economy Strategic Perspective: Major environmental shifts now demand a more strategic perspective from those who manage and lead in organizations; “GLOBALISING” in the quest for major market share brings in new opportunities for growth and prosperity. Organizations are now espousing values that regard people, not as costs to be minimized, but AS “ASSETS TO BE MAINTAINED AND DEVELOPED.” An open systems approach of management is likely to overcome many of the problems created by the piecemeal approach. Instead of looking at management development in isolation, see it as an integral part of a wider organizational system that takes care of the processes through which people working for the firm take care of themselves leading to self...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

Theory of Management History and Evolution To understand the concept of management, a recap of its history and its slow but steady evolution is absolutely necessary. After the advent of machines, thanks to the industrial revolution of the eighteenth century, management has become an entity by itself. Pic Courtesy: Management Theories Since business activity is increasing by leaps and bounds globally, a more organized set up is called for, which has led to the development of different management concepts. Whether you consider management an art or a science, one definite thing is that, science and art complement each other and not mutually exclusive. Management gurus like Peter Drucker, Henry Fayol, Taylor and others have classified the essential features of management, for the benefit of the industry. Theory comes first followed by practice. Management knowledge certainly improves your style of working. How long do you think, luck, intuition or experience can be relied on, without a scientific knowledge of management. It is a thought to be pondered. Hypotheses Practical experimentation and analysis of theoretical hypotheses, yield better results and in course of time you tend to gain more scientific knowledge. Management is a process of planning, organizing, staffing, leading and controlling. Picture Courtesy: Technofunc.com The management process is applicable to all kinds of organizations and firms, be it a private firm, a government institution, a hospital, a school, a college, an university and other financial, profit making or non profit making NGO’s. This clearly indicates that management is a process that involves individuals who work in groups to accomplish their objectives in an effective and efficient manner. Levels of Management Does management pertain only to the top level management? A big no! It applies to managers at all levels. It is a chain reaction and a successful management totally depends on the synergistic activities of the people belonging to that organization. So, care must be taken by the managers to create and design an internal environment that is conducive for the smooth operations of the firm thus increasing the productivity. This does not mean that the external environment can be overlooked. A manager has to respond to the periodic changes, be it social, technological, economic or political in the external environment also. Management styles Management is a must for every organization and the style of management may vary according to the nature and size of business. Large organizations now-a-days prefer a “flat structure“, as it brings their employees closer and reduces the span of management, thus making communication faster. The more the number of levels, the more the conflict and improper communication. Although management pervades the entire organization, it is the duty of the top management cadre to initiate and maintain consistency in the process of management. All managers (by the term “manager “which is a much generalized term, we denote persons who hold authority to get things done; he may be a financial, administrative, human resource or a production executive) have a common aim, that is to create surplus. To increase productivity, create a suitable environment for the effective performance of their group and to solve crisis situations, they must be capable of seeing the “big picture”. Recent Developments A sea of changes has swept the theory of management area in recent times, owing to the development of different approaches. Management theory is criticized to have all the characteristics of a jungle as numerous management practitioners have recorded their findings in the management history. This led to severe confusion as to what management is, and how things should be organized; however, in modern corporate business world, the managerial activity is directed towards growth, thanks to the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Objectives and Functions of HRM Human Resource Management is very challenging because of the dynamic nature of the people and it is not only managing men but involves administering a social system. According to Dale Yoder “Man power management is the function or activity in directing working men and women in maximizing their satisfaction in employment.” George R. Terry says, “Personnel management is concerned with the obtaining and maintaining of a satisfactory and satisfied work force.” OBJECTIVES OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. Social Objectives: a) Facing the challenge of unemployment and providing people with maximum employment opportunities is the first and foremost priority of countries like India where there is pressure of population growth. b) The employees must be able to derive maximum satisfaction from the work performed. c) The system should facilitate harmony and co-operative endeavor for one and all. 2. Personal Objectives: Job satisfaction and rewards in the form of pay, promotion and recognition is aimed at, on the part of employees. This can be achieved by providing adequate remuneration, opportunities for advancement, facilities for training and development, job security and proper work. 3. Enterprise Objectives: This can be achieved by selecting the right people for the right job, empowering them through training, development and participation. FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. Planning: Assessment of future man power requirement is done with the help of man power inventory chart followed by the recruitment and selection process. A clean job description is needed to lure people with the right skills for the right position. It is the responsibility of the manager of a firm to lay down specifications of the qualities and skills required by the workers and determining sources from where the workers are to be recruited. Selection is done by means of written test and personal interviews. 2. Organizing: This involves proper designing of organizational structure, the inter relationship between jobs, establishing smooth channels of communication, assignment of authority, responsibility and creating accountability, establishing line and staff relationship etc. 3. Directing: Issuing orders and instructions down the line and motivating the work force to carry out those instructions satisfactorily. Positive motivation in the form of financial and non-financial incentives, a good working environment is essential on the part of the management. 4. Controlling: The motive is to ensure that performance of each worker coincides with the plans or standards. Bench marking, Total quality management and Six sigma are some of the popular concepts of standardization. → Scope and Characteristics of...










