Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management, Productivity
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
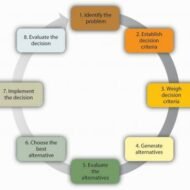
The Process of Decision Making There is a need to broaden our understanding about decision-making process. Decision making is not an independent entity and relies upon many other factors like precedence, social processes and random eventualities. It has three components; identification of the issue, the possible course of action and choosing the best amongst the choices of action available. The decision-making process is continuous since the business environment is dynamic and constantly poses challenges to the decision makers. Organizations are viewed as “Garbage can models” of decision making, in which actions, decisions and outcome are randomly mixed in the flow of events. With this introduction let us proceed to know more about the nature and types of decision making. NATURE OF DECISION-MAKING: 1. It is closely related to solving problems and issues 2. It is associated with all the important management functions like planning, organizing and controlling 3. Fayol and Urwick feels that decision-making is concerned only to the extent that it affects delegation and authority 4. Chester I Bernard in his “Functions of the Executive” says that the process is nothing but narrowing down of choice 5. Herbert A Simon considers decision-making as a process of intelligence, design and choice activities 6. According to Peter Drucker, it is a central part of the management process THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS: The following steps are involved in the process of decision-making Recognizing the problem: Think about this; if there is a decline in the sales volume of your company or say if the value of your stock decreases, you are forced to make decisions to manage the contingency. In such situations, the first step would be to recognize or identify the problem area. A problem identified is half done. In this instance, the reason might be competitor strength or lack of necessary investment in the key strategic business units. Deciding priorities among the problems: A manager need not and cannot look after all the problems prevailing in the organization. He should know how to delegate authority and the responsibility that goes along with it. Subordinates can be entrusted with the handling of small and trivial problems while the manager can handle very important ones that might affect the functioning of the firm. He should ask the following questions to diagnose the situation. 1. What is the real problem? 2. What are the causes and effects of the problem? 3. Is this problem very important? 4. Can sub-ordinates handle this problem? 5. Which is the most pressing problem to be solved? Diagnosing the problem: Now the manager must start diagnosing the problem. Each and every individual has a different perspective and perceive the problem from a different angle. This depends upon the background orientations and training. The right way of approach for any manager would be to systematically analyze the problem for identifying the alternative courses of action. Developing alternative courses of action: This step involves creativity and innovative capabilities as the manager has to think from all possible angles and directions. Managers holding senior corporate positions are exposed to more of this kind of atmosphere where they are forced to make quick decisions in accordance with what the situation demands. Outside expert consultants are also put into use by some companies for developing choice alternatives. The following are the five PSYCHOLOGICAL STEPS for developing alternatives: 1. Saturation– A manager must be thoroughly familiar with the problem 2. Deliberation– Analyzing the problem from several points of view 3. Incubation– Temporarily switching off the conscious search to relax for the purpose of clear thinking 4. Illumination– A flash of light may occur after sometime giving him the right insights and ideas. 5. Accommodation– The ideas are made into a concrete proposal Evaluating the alternatives: The pros and cons of each and every choice is thoroughly subjected to scrutiny in terms of cost, time, risk, results expected, deviations anticipated...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 15th, 2014 | 0 comments

Functions of Management MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS The objective of this topic is to make students understand the functions of management and the role of managers in an organization. The five basic management functions are listed below: · PLANNING · ORGANISING · STAFFING · LEADING · CONTROLLING PLANNING: The managerial activities aid in selecting the objectives, examine and forecast changes, develop policies, procedures and choose future course of action from among alternatives. Planning proceeds from “Where we are” to “Where we want to go.” Planning activities are 1. Analysing the current situation (also called the SWOT Analysis) 2. Anticipating or predicting the future based on the analysis 3. Determination of organizational objectives to be achieved 4. Deciding on the action plan 5. Evolving proper strategies 6. Pooling the resources (physical, financial and monetary) to accomplish enterprise objective ORGANISING: It is a process which integrates people and tasks; In order to achieve their tasks people are given sufficient authority, tools and information. Organising activities include 1. Specification of job responsibilities 2. Grouping of jobs into respective work units 3. Allocation of resources STAFFING: Human resource management is one of the key areas that decides the success of a firm’s activity. Staffing involves the selection of “Right person for the right job.” The activities are 1. Recruitment 2. Selection 3. Training and Development 4. Compensation 5. Promotion 6. Evaluation and 7. Rewarding people to achieve enterprise goals. LEADING: Leadership is the set of interpersonal behaviors that influence people to contribute to the organization and group goals. The activities under this category are 1. Providing proper direction 2. Guidance and Motivation 3. Clarity in communication to the work force CONTROLLING: This is a process that is necessary to keep track of the performace of individuals by setting some standards for direction. The activities include 1. Establishing performance standards enabling the work force to achieve the goals (both short term and long term) 2. Enhancing the employee performance through performance appraisal or rating of work 3. Comparison of performance against the standards to identify deviation or work problems and take corrective measures 4. Bench marking is one of the management techniques that facilitates an organization to uplift its performance levels to the best of industry standards and also catch hold of the strengths of the competitors and rectify the weaknesses prevailing in one’s own firm. CO-ORDINATION: It is regarded as a key function of a manager to bring in harmony among individuals and an effort towards accomplishment of goals. 1. Marginal decision making and 2. Sub Optimisation are some of the new approaches developed in the field of decision making. MANAGERIAL SKILLS: Skill is the resultant effect of knowledge, experience and expertise. It is the ability of an individual to perform a task which is obvious from the results he/ she shows. There are 3 kinds of skills that a manager should possess in order to excel. 1. The Conceptual Skill: Assessing a situation and acting accordingly depicts the manager’s perceiving ability of the abstract elements in force. A manager has to improve this kind of skill as he moves up the ladder in the management level or let us say that he can move up the ladder only if he possesses this kind of skill. · Management Consultants · Managing Director of a firm · President of a company · Economists · Startegists are conceptual analytic experts 2. The Technical Skill: This skill is purely based on one’s knowledge and on the job experience. This is needed at a lower level of management · Computer Operators · Engineers · Accountants · Machine Operators possess this kind of skill 3. The Human Relations Skill: This...

Posted by Admin in Accounting, Management Accounting
on Jan 29th, 2014 | 0 comments

Management accounting combines accounting, finance and management with the leading edge techniques needed to drive successful businesses. The process of preparing management reports and accounts that provide accurate and timely financial and statistical information required by managers to make day-to-day and short-term decisions






