Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Dec 29th, 2014 | 0 comments

Scope of Financial Management Facebook Buys WhatsApp: Boneheaded or Brilliant? This was the title of a Forbes Article when Mark Zuckerberg acquired Whatsapp for $19 billion dollars, the price that may exceed the GNP of some of those countries. Mark is said to be an unconventional thinker and the WhatsApp acquisition shows Facebook’s determination to follow the road not yet paved. It is a bold move, yet filled with risks along the way. This is one of the finest examples of the big investment decisions of recent times and the right course of action, if you measure the number of potential users of the mobile messaging service rather than the cost of acquiring each user and the potential for selling ads to each user today. Follow these mind blowing tips to become prosperous Picture Courtesy : YoungHstlrs Financial management is one of the important aspects of overall management, which is directly asscoiated with various functional departments like personnel, marketing and production. Financial management embraces wide area with multidimensional approaches. The following are the important scope of financial management. Some of the major scope of financial management are as follows: 1. Investment Decision 2. Financing Decision 3. Dividend Decision 4. Working Capital Decision. 1. Investment Decision: The investment decision involves Risk EvaluationMeasurement of cost of capital andEstimation of expected benefits from a project. Capital budgeting and liquidity are the other two major components of investment decision. Capital budgeting takes care of the distribution of capital and commitment of funds in permanent assets to harvest revenue in future. Capital budgeting is a very focal decision as it impacts the long-term success and growth of a firm. All the same it is a very tough decision because it encompasses the estimation of costs and benefits which are uncertain and unknown. Picture Courtesy: Crowdfundingheroes 2. Financing Decision: Financing decision is related to financing mix or financial structure of the firm. The raising of funds requires decisions regarding Methods and sources of financeRelative proportion and choice between alternative sourcesTime of floatation of securities, etc. In order to meet its investment needs, a firm can raise funds from various sources. Long Term Sources of Finance: Share Capital or Equity SharesPreference Capital or Preference SharesRetained Earnings or Internal AccrualsDebenture / BondsTerm Loans from Financial Institutes, Government, and Commercial BanksVenture FundingAsset SecuritizationInternational Financing by way of Euro Issue, Foreign Currency Loans, ADR, GDR etc. Picture Courtesy: Cash & Treasury Management file Medium Term Sources of Finance: Preference Capital or Preference SharesDebenture / BondsMedium Term Loans fromFinancial InstitutesGovernment, andCommercial BanksLease FinanceHire Purchase Finance Short Term Sources of Finance: Trade CreditShort Term Loans like Working Capital Loans from Commercial BanksFixed Deposits for a period of 1 year or lessAdvances received from customersCreditorsPayablesFactoring ServicesBill Discounting etc. 3. Dividend Decision: In order to accomplish the goal of wealth maximization, a proper dividend policy must be established. One feature of dividend policy is to decide whether to distribute all the profits in the form of dividends or to plough back the profit into business. While deciding the optimum dividend payout ratio (proportion of net profits to be paid out to shareholders), the finance manager should consider the following: Investment opportunities available to the firmPlans for expansion and growth,Dividend stabilityForm of dividends, i.e., cash dividends or stock dividends, etc. 4. Working Capital Decision: Working capital decision is related to the FINANCING in current assets and current liabilities. Current assets include cash, receivables, inventory, short-term securities, etc. Current liabilities consist of creditors, bills payable, outstanding expenses, bank overdraft, etc. Current assets are those assets which are convertible into cash within a year. Similarly, current liabilities are those liabilities, which are likely to mature for payment within...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments

Understanding Net Present Value One method of deciding or not a firm should accept an investment project is to determine the net present value of the project. The net present value (NPV) of a project is equal to the present value of the expected stream of net cash flows from the project, discounted at the firm’s cost of capital, minus the initial cost of the project. The value of the firm will increase if the NPV of the project is positive and decline if the NPV is negative. Thus, the firm should undertake the project if the net present value is positive and reject proposals whose values are negative. This method is considered the best, as it takes into account, the initial investment, and cost of capital and cash inflow over a period. Estimation of Future Cash Flow: One of the most important and difficult aspects of capital budgeting is the estimation of the net cash flow from the project. It is the difference between cash receipts and cash payments over the life of a project. Projected cash flow statement is an important criterion for banks to decide on sanctioning medium and long-term loans to prospective clients. Since cash receipts and expenditures occur in the future, a great deal of uncertainty is involved in their estimation. Some general guidelines are to be followed while estimating cash flows. First; cash flows should be measured on an incremental basis. That is, measurement of the firm’s cash flows with and without the project must be ascertained. Any increase in expenditure or reduction in the receipts of other divisions of the firm resulting from the adoption of a given project must be considered. Effect of Depreciation: Second thing is that, net cash inflow must be estimated on an after-tax basis, using the firm’s marginal tax rate.Third, as a non-cash expense, depreciation affects the firm’s cash flow only through its effect on taxes. The initial investment to add a new product line may include the cost of purchasing and installing new equipment, reorganizing the firm’s production process, providing additional working capital for inventory and accounts receivable and so on. The monetary flows generated by this kind of investment include, the incremental sales revenue form the project, salvage value of the equipment at the end of its economic life, if any and recovery of working capital at the end of the project. The outflow will be in the form of taxes, fixed costs and incremental variable costs. Internal Rate of Return or IRR: Another method of determining the acceptance rate of a project proposal is internal rate of return method (IRR).This is nothing but the discount rate that equates the present value of the net cash flow from the project to the initial cost of the project. The firm should undertake a project if the IRR on the project exceeds or is equal to the marginal cost of capital. Capital Rationing and Pay Back Period: More techniques are available for evaluating the feasibility of investment proposals, like, capital rationing, profitability index, pay back period and others. It is always a good thing to analyze the rate of return on investment before the start of the project. If it happens to be satisfactory, then the firm can take a step forward to finalize the proposal. The cost of capital climbs up when the investment return declines, and the firm is subjected to undue pressures of mounting interest rates and capital depletions....

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
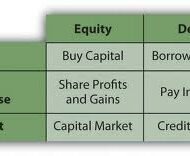
What is your Capital Structure Make up A company in course of charting out its financial schema has to take into account two things. 1) The amount of capital to be raised. 2) Make-up of the capital. Decisions regarding the composition or capitalization are reflected in capital structure. Capital structure of a firm is a combination of debt and equity, which supports long term financing of the firm. The pattern of capital structure has to be planned very carefully by the finance manager in such a way that it minimizes the cost of capital and maximizes value of stocks, thus protecting the interest of the share holders. What is the right capital mix? There needs to be a right mix of different securities in total cpaitalisation that facilitates control, flexibility and maneuverability. From a broad perspective, following are the three fundamental ways in which the schema of capital structure is finalized: Financing purely or exclusively by equity Financing by equity and preferred stock Financing by equity, preferred stocks and bonds. Which of the above most suits a firm depends on multifarious internal and external factors within which a firm operates. Equity: A firm can raise substantially large amount of fund by issuing different types of shares. The money thus raised is a permanent source of resource and without any obligation to refund to the respective owners. Small and growing companies go for equity fund raising as no banks or other financial institutions are prepared to fund these firms in lieu of poor credit worthiness. Even big corporate firms opt for issuing equities when there is a need to raise large sums. But smaller firms, whose major share of capital comprises of common stock, have to be careful, in that, some large concerns might become interested in controlling these stocks. Picture Courtesy : GrowthFunders The one big advantage of equity shareholders is that they are free to trade the shares in the market. They can sell the shares to anybody at any time and if the market warrants, at a higher price. One has really nothing to lose, if he is planning to invest in equities. On the other hand, if the company goes bankrupt, the share holders stand a chance to receive only the residual amount, after the creditors’ claims are cleared and satisfied. What’s in it for Investors? Debt: Debt has a maturity date upon which the stipulated sum of principal is repaid. It places the burden of obligation on the shoulders of the company in the form of periodical interest settlements and principal repayments. Creditors can go for legal action if the company defaults in payment of the assured sum on the specific date. That’s why companies think twice before they go for issuing debentures and other bonds. One good thing for the company is that, it can avail tax rebate on the securities of debt, but at the other end it has to satisfy the interest payments and factorise the cost of capital. Cost and Control Principles Cost principle supports induction of additional doses of debt, but it might prove risky, if the company is not able to service the additional debt. Control principle supports the issue of bonds in order to tighten the rein of ownership, but maneuverability principle discounts this and favors issue of common stock to reduce the interest burden. Four factors are important in the purview of the finance manager, cost, risk, control and timing. He should be able to evolve a pattern that satisfactorily brings a compromise among these conflicting factors, which are then assigned weights in the wake of economic and industrial...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Feb 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
Debtor Management or Receivables Management Profit is directly proportional to the volume of sales, provided all your business transactions are cash based. Is it possible for a manufacturer, wholesaler or retailer to carry on his business without offering credit in this competitive business environment? The answer is a definite “no”, because extension of credit improves your sales and thus your profit. Problems arise only when a firm is not able to recover the debt within the stipulated period of time from the customers. What is receivables management or debtors’ management? It covers two aspects- one, the kind of money that is being invested in debt rotation; second, the risk factor which includes loss of money or the opportunity cost foregone by the organisation. Had these funds not been tied in receivables, the firm would have invested the same elsewhere and earned income thereon. A transaction entirely through cash is definitely a possible option, but whether it is lucrative in the long run must be subject to consideration. When customers are not offered credit, they choose concerns that extend credit facilities and thus you may lose your earlier customers and also exposed to the risk of declining sales proportions. Credit Sales In credit sales, the supplier offers credit for a specific time period, which is an investment from the angle of supplier and largest single source of short term financing from the angle of the customer. The supplier should be able to recover the amount of interest on the credit investment he has made. How? Recovery of debt within the stipulated credit period Taking interest from the customer for the period of delay Volume sales Surplus capital to offset these negative impacts on rotation of funds Proper formulation and execution of credit policies by the finance manager Discipline in collection policy and its execution. Discounts Cash discounts, quantity discounts and trade discounts are offered by many firms to the customers to encourage credit sales, favoring bulk purchases. A firm cannot be expected to survive long by pursuing the policy of cash sales while similar firms can overtake it by adapting to liberal credit policies. The main aspects of receivables management decisions are as follows: Time period of credit Credibility of the customer Cash discounts Trade discounts Learn the basics of the Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement and understand how they fit together. Credit Policy Credit policy on one hand stimulates sales and so also its gross earnings, but on the other may be accompanied by added costs, such as: 1) Clerical expenses involved in investigating additional accounts and servicing added volume of receivables, 2) increased bad-debt losses due to credit extension to less credit worthy customers, 3) higher cost of capital. Incremental earnings from increased sales should be matched with incremental costs that arise due to credit terms, to avoid funds being tied up in receivables. In course of time it would deprive you of your profits. The pivotal consideration of your credit policy would be the selection of credit worthy customers or debtors. If your funds become sticky, recovery becomes next to impossible and you need to proceed legally to claim your rights. Properly maintained accounting records and vouchers will stand as a testimony in your favor, in the court of...








