Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments
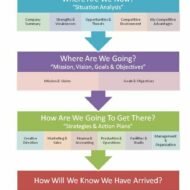
The Management Planning Process We have heard of “Master Plans” being structured and engineered to give astounding results that is purely systematic in approach and masterly in execution. Planning facilitates to make use of the opportunities that are available in the environment to make it to the top. Opportunity Analysis is nothing but, an awareness of the factors in the external environment; understanding of the strength and weaknesses of the organization. This is the first step of planning where we have to scrutinize the market, competition, customers’ preferences, tastes, our strengths and weaknesses. Establishing Objectives is another criterion that ensures “Where we want to be, and what we want to accomplish and when”. What are Objectives? Objectives are set for the organization and each subordinate is also entrusted with them. Objectives lay emphasis on goal setting which normally emanates from the top, but it may also originate from the bottom. Management by objectives is a great concept that involves all the employees working for the organization to be a part of goal setting and decision making. Planning Premises: Premises are “Assumptions” about the ‘environment.’ It involves identification of critical factors of the environment that affect the planning. Examples of critical factors are government policies, tax rates, business cycle development, economic indicators, economic forecasts etc. No body can precisely predict the environment factors precisely and make an accurate forecast. However one can fairly predict the critical factors required for the plan. Identifying Alternatives is very significant in a corporate business environment as every plan has got a set of alternative course of action. A reasonable number of alternatives can be developed for a plan. Evaluating Alternatives and Selecting the Best: A reasonable number of alternatives can be evaluated on the basis of the principle of limiting factor. The limiting factors may be costs, time, manpower and other resources. By applying techniques of operations research, every alternative can be evaluated. For e. g. alternative ‘A’ may benefit the organization in the short term but may be more expensive and alternative ‘B’ may benefit in the long run but may be less expensive. If one wants to earn immediate profits by spending more money he can choose alternative ‘A’. If the limiting factor is cost, he is forced to choose alternate plan ‘B’. Planning is not complete with selecting the best alternative; a set of derivative plans are developed to support the basic plan. For example an educational institution might like to own a fleet of buses, for which derivative plans for selection has to be made- training of drivers and maintenance staff are supportive plans for the main plan-procurement of buses. Developing budgets completes the planning course of action and budget is referred in financial terms and they are required to control the plans. Planning is the Prime Function: Planning is the prime function of all as it precedes all functions. 1. The objectives must be clear, verifiable and attainable. 2. Planning premises are vital to the success of planning as they supply information related to future like probable competitive behavior, general economic conditions, capital and material availability, government control etc. 3. All the critical factors are clearly and thoroughly analyzed and taken into consideration. One should be able to identify clearly the critical factors that limit the attainment of the goal. It could be costs, time, manpower or any other resources. 4. In a practical business situation, one should be clearer in identifying these factors, only then the selection of the best alternative is possible. 5. Any decision taken in a plan is valid for a particular period i.e., the plan may be short term or long-term, the commitment principle...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

A Process of Intelligence Effective Decision making is a process of Intelligence, Design and choice activities and “is a central part of the management process”. Decisions are hard to make but once decided there should be no second take. The following steps are involved in the process of Decision-making: 1. Recognizing the problem 2. Deciding priorities among problems 3. Diagnosing the problem 4. Developing alternative courses of action 5. Evaluating alternatives 6. Selecting the best alternative 7. Effective implementation and follow-up action. Recognizing the Problem– Herbert A Simon calls this step as an “intelligent activity“. It is important to find out whether there is any deviation from the past experience. For e.g. Sales might decrease, expense might decrease, sometimes there might be deviations from the plan, sales budget, and competitors may outperform by improved systems. Deciding priorities among the problems: A manager would face many problems at the same time. He should not be bogged down with small and unimportant problems. Some problems can be easily solved by the sub-ordinates. Some may not be important. A manager must see that – he selects carefully the most important problem. Peter Drucker says that “once the right problem is perceived then half of the problem is solved”. A manager must diagnose carefully by asking the following questions. a. What is the real problem? b. What are the causes and effects of the problem? c. Is this problem very important? d. Can they be solved by sub-ordinates? e. Which is the right and most important problem to be solved? Diagnosing the Problem: After choosing the right problem the manager must now start diagnosing the problem. There is no simple answer to the question of how to diagnose the problem, because every individual differs in his or her own way of diagnosing the problem depending on the different background orientations and training. A manager must systematically analyze the problem for identifying the alternative causes of action. Developing Alternative Courses of Action: This step is creative and innovative where a manager analyzes from all perspectives Sometimes a manager can also use a technique called “brainstorming” where a few individuals discuss at length the various possible available alternatives. First of all, a manager must be thoroughly familiar with the problem. This is called saturation. Later, he must think about the problem from several view-points which is called deliberation. Sometimes the manager may not get into the crux of the problem, i.e. there may not be any fruitful result of deliberation, and then the manager might temporarily switch off his conscious search and relax. This process of realization is called incubation. Then after sometime, a flash of light may occur, and the manager may get some insights and ideas. This stage is called illumination. In the last stage, which is called accommodation, the manager resynthesises his ideas into a usable proposal. Evaluating the Alternatives: The manager must now give proper weightage to the positive and negative aspects of the alternatives and evaluate by using some criteria like (a) time; (b) cost; (c) risk; (d) results expected; (e) deviations anticipated; (f) resources available for implementation. Selecting the Best Alternative: This is the most important step where the manager selects the best alternative that will yield maximum profits or results with minimum cost, input or resources. To put it in simple terms, the solution should be able to solve the problem in the best possible way. Effective Implementation and Follow-up Action: Any decision without proper implementation becomes futile and hence proper care must be taken by the manager to pool resources and start implementing the decision taken. In large organizations, follow-up procedures are available in the system...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
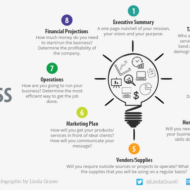
Your business structure will affect a lot of factors – You can start with an initial business structure and change it as your business thrives. But first and foremost you need a solid business plan that details your mission, vision and purpose. These 7 steps in planning will guide you through and give your project a headstart. The business plan cheatsheet is given in a pictorial form for your benefit. ☝️ A. Opportunity Analysis: SWOT analysis– the analysis of strength and weaknesses, opportunities and threats in the external environment is the first and foremost step in planning. The target market, competitor strength, internal weaknesses, customer’s preferences are some of the key areas to be focused. B. Setting objectives: Where we want to be, and what we want to accomplish and when are answered in this step. Each and every employee of the organization has to be apprised about the enterprise objectives in order to achieve the expected or desired result. Management by objectives is one of the proven methods where-in the objectives are set by the subordinates themselves under the guidance of their superior and periodical reviews are conducted to check whether the set objectives are accomplished within the stipulated time. C. Developing Premises: The critical factors that affect the planning process are analyzed thoroughly. Say, government policies, business cycle trends, economic indicators, inflation, tax rates etc are analyzed and the plans are developed based on these premises. D. Identifying Alternatives: It is better to have an alternate plan or plans which helps in deciding the alternate course of action. Alternatives identification is a technique used for identifying different methods or ways of accomplishing the work of the project. For example, brainstorming might be used to discover alternative ways of achieving one of the project objectives. E. Evaluating Alternatives and selecting the suitable plan: The limiting factors can be set as a criterion for evaluating the alternatives. The limiting factors may be cost, time, manpower and other resources. Operations research helps in the assessment of alternatives and selecting the best. Think about this, if plan A fetches you more profit but proves to be expensive and plan B fetches you consistent profit and less expensive, what will be your choice? Even banks look into the fund flows of different projects submitted by clients and select the ones that proves to fetch consistent returns on the long run. F. Formulating Supportive plans: Download this Business Planner Printable which comes in handy when you want to weigh your choices👇 Business-Journal-Planner-1Download Derived plans are those that stem from the main ones that support the basic plan. Recruiting and inducting may be the basic plan of a HR department but training and development is the supporting plan that gives shape to the basic plan. G. Developing Budgets: Budget is referred in financial terms and they are required to control plans. There is always a constraint for resources and hence it is the responsibility of a manager to decide on the investment in a particular plan that will tide away the risk of the...






