Posted by Managementguru in Accounting
on Aug 6th, 2016 | 0 comments
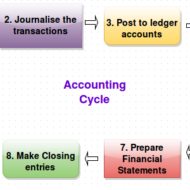
Financial statements have to be produced accurately at the end of the accounting period for tax purposes. An accounting period may be a month, a quarter of a year, or a whole year. The accounting cycle is the series of steps that take place in order to produce financial statements. A term that describes the steps when processing transactions (analyzing, journalizing, posting, preparing trial balances, adjusting, preparing financial statements) in a manual accounting system. Today many of the steps occur simultaneously when using accounting software. Following are the steps that complete an accounting cycle: Identify the transaction: This transaction could be the revenue from the sale of a product or a payment to another business for services. Analyze the transaction and how it is related to the accounting balance sheet. For example, determine which accounts are affected by the transaction and how they are affected. Record the transaction to a journal such as a sales journal. Journals are kept in chronological order and may be updated continuously, daily, or however often it is necessary. Record the transaction to the general ledger: Take all of your entries and categorize them by the account. Perform a trial balance: Debits and credits need to be equal at the end of an accounting cycle, so calculate the entries to ensure they match. Prepare adjustments: Just because entries are recognized, does not mean the work has been performed. Revenue can only be recognized when the work has been completed, so adjust the entries accordingly. Perform trial balance with adjustments: Take the adjustments from Step 6 and prepare a trial balance. If the debits and credits do not match, then you need to adjust them to make sure they do match. Prepare financial statements: From the adjusted trial balance, these corrected balances are used to prepare the financial statements. Close the accounts in preparation of the next accounting cycle. Revenues and expenses need to be closed out, which means they need to have zero balances. Balances are moved to the next cycle. Some Important Accounting Terms: Account A record in the general ledger that is used to collect and store similar information. For example, a company will have a Cash account in which every transaction involving cash is recorded. A company selling merchandise on credit will record these sales in a Sales account and in an Accounts Receivable account. Accounting Department Part of a company’s administration that is responsible for preparing the financial statements, maintaining the general ledger, paying bills, billing customers, payroll, cost accounting, financial analysis, and more. The head of the accounting department often has the title of controller. Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. For a corporation the equation is Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity. For a nonprofit organization the accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Net Assets. Because of double-entry accounting this equation should be in balance at all times. The accounting equation is expressed in the financial statement known as the balance sheet. Accounts Payable This current liability account will show the amount a company owes for items or services purchased on credit and for which there was not a promissory note. This account is often referred to as trade payables (as opposed to notes payable, interest payable, etc.) Accounts Receivable A current asset resulting from selling goods or services on credit (on account). Invoice terms such as (a) net 30 days or (b) 2/10, n/30 signify that a sale was made on account and was not a cash sale. Adjusting Entries Journal entries usually dated the last day of the accounting period to bring the balance sheet and income statement up to date on an accrual basis (as required by the matching principle and...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting
on Feb 24th, 2015 | 0 comments

What are known as Final Accounts? Trading, profit & loss account and balance sheet, all these three together, are called as final accounts. Final result of trading is known through Profit and Loss Account. Financial position is reflected by Balance Sheet. These are, usually, prepared at the close of the year hence known as final accounts. They serve the ultimate purpose of keeping accounts. Their purpose is to investigate the consequence of various incomes and expenses during the year and the resulting profit or loss. 1. Trading and Profit and Loss A/c is prepared to find out Profit or Loss. 2. Balance Sheet is prepared to find out financial position of a concern. Trading Account Trading refers buying and selling of goods. Trading A/c shows the result of buying and selling of goods. This account is prepared to find out the difference between the Selling prices and Cost price. Profit and Loss Account Trading account discloses Gross Profit or Gross Loss. Gross Profit is transferred to credit side of Profit and Loss A/c. Gross Loss is transferred to debit side of the Profit Loss Account. Thus Profit and Loss A/c is commenced. This Profit & Loss A/c reveals Net Profit or Net loss at a given time of accounting year. Trading Profit And Loss CMD from knoxbusiness Balance Sheet Trading A/c and Profit & Loss A/c reveals G.P. or G.L and N.P or N.L respectively; besides the Proprietor wants i. To know the total Assets invested in business ii. To know the Position of owner’s equity iii. To know the liabilities of business. Definition of Balance Sheet The Word ‘Balance Sheet’ is defined as “a Statement which sets out the Assets and Liabilities of a business firm and which serves to ascertain the financial position of the same on any particular date.” On the left hand side of this statement, the liabilities and capital are shown. On the right hand side, all the assets are shown. Therefore the two sides of the Balance sheet must always be equal. Capital arrives Assets exceeds the liabilities. BUY “ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS AND CONCEPTS” OBJECTIVES OF BALANCE SHEET: 1. It shows accurate financial position of a firm. 2. It is a gist of various transactions at a given period. 3. It clearly indicates, whether the firm has sufficient assents to repay its liabilities. 4. The accuracy of final accounts is verified by this statement 5. It shows the profit or Loss arrived through Profit & Loss A/c. PREPARATION OF FINAL ACCOUNTS Preparation of final account is the last stage of the accounting cycle. The basic objective of every firm maintaining the book of accounts is to find out the profit or loss in their business at the end of the year. Every businessman wishes to find out the financial position of his business firm as a whole during the particular period. In order to accomplish the objectives for the firm, it is essential to prepare final accounts which include Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. It is mandatory that final accounts have to be prepared, every year, in every business. Trading and profit & loss accounts are prepared, after all the accounts have been completely written and trial balance is extracted. Before preparing final accounts, it becomes obligatory to scritinize whether all the expenses and incomes for the year for which accounts are prepared have been duly provided for and included in the accounts. Form of Final Accounts: There is a standard format of final accounts only in the case of a limited company. There is no fixed prescribed format of financial accounts in the case of a proprietary concern and partnership...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Apr 8th, 2014 | 0 comments

Interest Free Sources and Unsecured Interest Bearing Sources A firm obtains its funds from a variety of sources. Some capital is provided by suppliers, creditors, and owners, while other funds arise from earnings retained in business. In this segment, let me explain to you the sources of short-term funds supplied by creditors. Characteristics of short-term financing: Cost of Funds: Some forms of short-term financing may prove to be expensive than that of intermediate and long-term financing while some short-term sources like Accruals and Payables provide funds at no cost to the firm. Rollover Effect: Short-term finance as the name indicates must be repaid within a period of one year – though some sources provide funds that are constantly rolled over. The funds provided by payables, may remain relatively constant because, as some accounts are paid, other accounts are created. Clean-up: This happens when commercial banks or other lenders demand the firm to pay-off its short term obligation at one point in a financial year. Goals of Short-Term Financing: Funds are needed to finance inventories during a production period. Short term funds facilitate flexibility wherein, it meets the fluctuating needs for funds over a given cycle, commonly 1 year. To achieve low-cost financing due to interest free loans. Cash flow from operations may not be sufficient to keep up with growth-related financing needs Interest Free Sources: Accounts Payable Accounts payable are created when the firm purchases raw material, supplies, or goods for resale on credit terms without signing a formal note for the liability. These purchases on “open account” are, for most firms, the single largest source of short-term financing. Payables represent an unsecured form of financing since no specific assets are pledged as collateral for the liability. Even though no formal note is signed, an accounts payable is a legally binding obligation of a firm. Postponing payment beyond the end of the net (credit) period is known as “stretching accounts payable” or “leaning on the trade.” Possible costs of “stretching accounts payable” are Cost of the cash discount (if any) forgone Late payment penalties or interest Deterioration in credit rating Accruals: These are short term liabilities that arise when services are received but payment has not yet been made. The two primary accruals are wages payable and taxes payable. Employees work for a week, 2 weeks or a month before receiving a paycheck. The salaries or wages, plus the taxes paid by the firm on those wages, offer a form of unsecured short-term financing for the firm. The Government provides strict rules and procedures for the payment of withholding and social security taxes, so that the accrual of taxes cannot be readily manipulated. It is however, possible to change the frequency of paydays to increase or decrease the amount of financing through wages accrual. Wages — Benefits accrue via no direct cash costs, but costs can develop by reduced employee morale and efficiency. Taxes — Benefits accrue until the due date, but costs of penalties and interest beyond the due date reduce the benefits. Unsecured Interest Bearing Sources: Self-Liquidating Bank Loans The bank provides funds for a seasonal or cyclic business peak and the money is used to finance an activity that will generate cash to pay off the loan. Borrowed Funds → Finance Inventory → Peak Sales Season → Receivables → Cash → Pay Off the Loan. Three types of unsecured short-term bank loans: Single payment note – A short-term, one-time loan made to a borrower who needs funds for a specific purpose for a short period of time. Line of Credit – An informal arrangement between a bank and its customer specifying the maximum amount of...

Posted by Managementguru in Powerpoint Slides
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Basics of Accounting Purpose of Accounting Break Even Analysis Financial Accounting...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Feb 20th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is fund ? Cash, total current assets, net current assets and net working capital are also interpreted as fund. So, it is necessary to clearly define the meaning of fund and demarcate its scope and function. To put it precisely, fund is nothing but, net working capital of a firm. The flow of fund occurs when a business transaction takes place that leads to an increase or decrease in the amount of fund. Firms prepare fund flow statement to explain the sources and applications of fund, which also serves as a technical tool to ascertain the financial condition of a business enterprise. Balance Sheet In a business firm, everyday numerous financial transactions take place. These are summarized into a balance sheet that gives an idea about the assets and liabilities at a specific point of time. When two balance sheets of consecutive periods are compared, we come to know about the inflow and outflow of funds and thereby the net working capital available is ascertained. This is step one. Profit and Loss Statement The next step would be to prepare an adjusted profit and loss account to determine fund inflow or fund lost from business operations. Accounts have to be prepared to ascertain hidden information (for all non-current items of assets and liabilities). Finally fund lost or gained from operations is arrived at and presented in a statement form. It is not that, only accountants could understand these operations and adjustments. Any person with logical reasoning and business acumen can understand the nuances of accounting, of course with some guidance. Few points that highlight the ways in which funds flow outside and inside a business enterprise will give you a better idea on the nature of fund flow: Sources of fund: Sale of fixed assets – sale of land, building, machinery, furniture etc. But you have to take into consideration a factor called “depreciation“. It is nothing but the wear and tear of the assets due to continuous usage, reduction in market value over a period of time, obsolescence, accidents etc. Remember, land is a non-depreciable asset in developing countries like India, whereas it may not be so in certain developed countries where the real estate values are nose diving. Issue of Equity shares – To raise capital free of interest, many big corporate firms go for equity capital from the general public. But the firms should make it a point to declare dividends if it happens to reap enormous profit to retain their market share. Their main aim should be to protect the interests of the equity share holders who are also the owners. Fund that comes into the firm through business operations – through sale of goods and services. Here the firm has to factorise its cost of production and economy of scale in order to make it cost-effective and fix a feasible profit margin. Borrowing of loans from banks and other financial institutions – Although it is a quick way of raising fund, care should be exercised in that, you should be in a comfortable position to “service the debt“. If not, there lurks the danger of bankruptcy where the firm might become insolvent, if it is unable to repay the interest and principal over a period of time. Issue of debentures – Debentures are also a form of equity but it comes with a price. The firm has to pay a percentage as interest on debentures and repayment period is also fixed in advance. The only solace for the firms would be the tax rebate that can be availed on loans and...









