Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Financial Management, Project Management, Startups
on Jul 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is a Startup Cost? Non-recurring costs associated with setting up a business, such as accountant’s fees, legal fees, registration charges, as well as advertising, promotional activities, and employee training. Also called startup expenses, preliminary expenses, or pre-opening expenses. Let me clarify that this discussion pertains to small and medium size enterprise startup costs and not about capital budgeting. Any project that an entrepreneur wishes to undertake has four factors to be considered. Men Material Machine Money Finance is the lifeblood of any business and to be successful, one must, inject sufficient capital into it. Many businesses fail because of under-capitalization. Seed Money Requirements To determine how much seed money you need to start, you must estimate the costs of doing business at least for the first year. Expenses may be categorized as ‘one-time costs’ such as the fee for incorporating your business or the price of a sign for your building. Some will be ‘ongoing costs’, such as the cost of utilities, inventory, insurance, etc. There is a pressing need for you to bring enough working capital to run the day-to-day business affairs. Without a projected fund flow statement and proposal, no bank or financial institution shall offer you long term loans to run the business. First of all, you need to write the business plan and ask yourself the following questions. Ask yourself these 20 questions to make sure you’re thinking about the right key business decisions: Why am I starting a business? What kind of business do I want? Who is my ideal customer? What products or services will my business provide? Am I prepared to spend the time and money needed to get my business started? What differentiates my business idea and the products or services I will provide from others in the market? Where will my business be located? How many employees will I need? What types of suppliers do I need? How much money do I need to get started? Will I need to get a loan? How soon will it take before my products or services are available? How long do I have until I start making a profit? Who is my competition? How will I price my product compared to my competition? How will I set up the legal structure of my business? What taxes do I need to pay? What kind of insurance do I need? How will I manage my business? How will I advertise my business? Courtesy – http://www.sba.gov/ See ‘Short Term Financing’ to know more about financing your business. The term finance sanctioned in the form of ‘Term Loan’ is required for Land and site development Building and civil works Plant and Machinery Installation expenses and Miscellaneous fixed assets which comprise vehicles, furniture and fixtures, office equipment, workshop and laboratory equipment, distribution of power and water supply etc. Expenditure on infrastructure facilities like water supply, power connection, roads, transportation etc., has to be particularly considered if the units are located in economically backward areas. Startup...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments
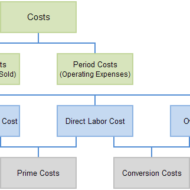
Costing is the technique and process of ascertaining cost whereas cost accounting is the application of costing and cost accounting principles, methods and techniques to the science, art and practice of cost control and ascertainment of profitability.

Posted by Managementguru in Operations Management
on Feb 24th, 2014 | 0 comments

Production systems can be classified as Job-shop, Batch, Mass and Continuous production systems. Here we will explain about Batch and Jobshop production systems, their benefits and limitations. Batch Production What is batch production? A manufacturing process in which components or goods are produced in groups (batches) and not in a continuous stream. Characteristics: 1. Shorter production runs. 2. Plant and machinery are flexible. 3. Plant and machinery set up is used for the production of item in a batch and change of set up is required for processing the next batch. 4. Manufacturing lead-time and cost are lower as compared to job order production. Benefits 1. Better utilisation of plant and machinery. 2. Promotes functional specialisation. 3. Cost per unit is lower as compared to job order production. 4. Lower investment in plant and machinery. 5. Flexibility to accommodate and process number of products. 6. Job satisfaction exists for operators. Limitations 1. Material handling is complex because of irregular and longer flows. 2. Production planning and control is complex. 3. Work in process inventory is higher compared to continuous production. 4. Higher set up costs due to frequent changes in set up. Job Shop Production What is job-shop production? A job shop is a type of manufacturing process in which small batches of a variety of custom products are made. In the job shop process flow, most of the products produced require a unique set-up and sequencing of process steps. Job shops are usually businesses that perform custom parts manufacturing for other businesses. However, examples of job shops include a wide range of businesses—a machine tool shop, a machining center, a paint shop, a commercial printing shop, and other manufacturers that make custom products in small lot sizes. These businesses deal in customization and relatively small production runs, not volume and standardization. This is a custom made furniture design! Characteristics: 1. High variety of products and low volume. 2. Use of general purpose machines and facilities. 3. Highly skilled operators who can take up each job as a challenge because of uniqueness. 4. Large inventory of materials, tools, parts. 5. Exhaustive planning is essential for sequencing the requirements of each product, capacities for each work centre and order priorities. Benefits 1. Because of general purpose machines and facilities variety of products can be produced. 2. Operators will become more skilled and competent, as each job gives them learning opportunities. 3. Full potential of operators can be utilised. 4. Opportunity exists for Creative methods and innovative ideas. Limitations 1. Higher cost due to frequent set up changes. 2. Higher level of inventory at all levels and hence higher inventory cost. 3. Production planning is complicated. 4. Larger space...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
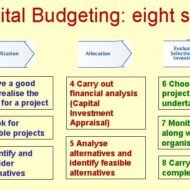
Capital Budgeting- Long Term Resource Planning What is Capital Budgeting? Capital Budgeting refers to the process of planning expenditures that give rise to revenues or returns over a number of years. The process of investment analysis is essential to have a sustainable advantage in the competitive market and to stabilize the profits through resourceful strategic business units. The firm’s management must be on the alert to explore the opportunities present in the market. Obsolete product lines and changes in consumer tastes may present additional problems to a business enterprise affecting the profitability and growth. When a firm decides to venture into projects that demand huge investments, the management has to scrutinize the economic feasibility of such projects. The process of capital investment is also crucial because the projects are for the most part irreversible. Say, for example, if a business firm purchases a special type of machinery, and after installation, if the firm reverses its decision to sell the merchandise due to some technical reasons, it will have only a very small second hand value. Business firms based on the cash flow of the project and the capital recovery period do long-term investment. Why do firms opt for capital budgeting. The reasons may be: To replace worn out equipments that will affect the production efficiency To replace obsolete equipments to install new and more efficient ones To expand production facilities in lieu of increasing demand for the firm’s products and to capture new markets To divest the surplus funds from other business units and to rotate the funds, as idle funds will not generate any revenue To develop new products Research and development Investments made to comply with government regulations, such as projects undertaken to meet government’s health and safety regulations, pollution control and to satisfy other legal requirements. People Involved The proposals for new projects come from the internal environment, such as department heads, executives, employees and of course the management. Experts in product development, marketing research, industrial engineering examine the investment proposals and they may regularly meet with the heads of other divisions in brainstorming sessions to zero in on the proposals. This free course from Udemy is Ideal for people interested in entrepreneurship, fintech, big data, startups, finance, private equity, VCs, & investing. https://www.udemy.com/crowdfund-investing-101-the-basics-of-equity-crowdfunding/ Departments Involved While the firm’s top management makes the final say or decision to undertake or not a major investment project, the process is likely to involve most of the firm’s divisions. Each department has to present its view on the feasibility and viability of the project. The marketing department- on the demand for the new or modified products that the firm plans to sell The production, engineering, personnel and purchasing departments- on the estimation and cost of the investment projects The financing department on- how the required investments funds have to be raised. Thus, the process of expenditure analysis can truly be said to integrate the operation of all the major divisions of the...








