Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments

How well employees know about your Organization? Now, this is a million dollar question and a prominent issue that has to be taken care of when it comes to motivating your employees. Transparency is a booster pack that works out wonders in the area of motivation. 25 Great Motivational Quotes to Kickstart Your Life How can a management be transparent in key areas like finance and business deals, my question is WHY NOT? The success of operations of a firm relies solely upon the performance of individuals who work towards the accomplishment of goals. They are the key persons who should be kept abreast about the activities of the firm. What makes some organizations stand out? When the Boss wants each and every employee to be truthful and loyal to him, the same expectancy would be there on the part of the workforce –Why don’t the bosses understand this? Integrated Organizational Development I would cite TVS Group as a classic example that commands respect from the employees and many a times I’ve heard people say that they are proud to work for TVS. What makes the employees so motivated to work for certain firms overlooking the pay scale and perks? One should deeply delve into the psychological theories that support motivation, perception and attitude. Etiquette of the company: This is one thing that a firm has to clearly communicate to its work force. The ideology and principle behind the running of the business should be genuine and authentic. The pathway to achieve those missions should be realistic and achievable-to put it clearly a firm should have its business roots stemming out from clear cut intent and purpose. When JRD Tata wanted to start a steel plant in India, not many believed it to be a possible venture. The business legend had clear cut intent of installing a steel plant to utilize the resources available in India and to pass on the proceeds for the economic benefit of the country. Nobody suspected his intent; such was his determination and resolve. This infographic beautifully portraits the scenario of how the future employees would be: Communication of Goals: The management will have clear plans of production target which has to be communicated properly to the lowest level with the same amount of clarity. This has to be done via channels or different levels of management and executives have to play their roles properly. Nobody needs to show their prowess or power; only thing needed is proper delegation of authority and responsibility. This gives clear direction to the work force and when their immediate boss sits with them for periodic discussions to decide on the short term as well as long term objectives, they feel part of the show which immensely motivates them. Ethical Standards of the company: This again adds image to the company and “As is the Leader so is the Employee.” The management should not involve itself in any kind of lobbying – When there is political corruption, malpractices become the order of the day. What Kind of a Leader Are You? A country like India needs more educated leaders who can bring awareness on the importance of economic independence and even distribution of wealth to the masses. If people clearly know what is right and what is wrong, the unwanted elements cannot take them for a ride. Given the population, India though marching towards becoming a developed nation, the growth is hindered by poor policy decisions and sky rocketing inflation. Clarity in Structure: Ego clashes start when the organizations have more number of levels and generate chaos in communication. Misunderstanding creeps in because there...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

A Process of Intelligence Effective Decision making is a process of Intelligence, Design and choice activities and “is a central part of the management process”. Decisions are hard to make but once decided there should be no second take. The following steps are involved in the process of Decision-making: 1. Recognizing the problem 2. Deciding priorities among problems 3. Diagnosing the problem 4. Developing alternative courses of action 5. Evaluating alternatives 6. Selecting the best alternative 7. Effective implementation and follow-up action. Recognizing the Problem– Herbert A Simon calls this step as an “intelligent activity“. It is important to find out whether there is any deviation from the past experience. For e.g. Sales might decrease, expense might decrease, sometimes there might be deviations from the plan, sales budget, and competitors may outperform by improved systems. Deciding priorities among the problems: A manager would face many problems at the same time. He should not be bogged down with small and unimportant problems. Some problems can be easily solved by the sub-ordinates. Some may not be important. A manager must see that – he selects carefully the most important problem. Peter Drucker says that “once the right problem is perceived then half of the problem is solved”. A manager must diagnose carefully by asking the following questions. a. What is the real problem? b. What are the causes and effects of the problem? c. Is this problem very important? d. Can they be solved by sub-ordinates? e. Which is the right and most important problem to be solved? Diagnosing the Problem: After choosing the right problem the manager must now start diagnosing the problem. There is no simple answer to the question of how to diagnose the problem, because every individual differs in his or her own way of diagnosing the problem depending on the different background orientations and training. A manager must systematically analyze the problem for identifying the alternative causes of action. Developing Alternative Courses of Action: This step is creative and innovative where a manager analyzes from all perspectives Sometimes a manager can also use a technique called “brainstorming” where a few individuals discuss at length the various possible available alternatives. First of all, a manager must be thoroughly familiar with the problem. This is called saturation. Later, he must think about the problem from several view-points which is called deliberation. Sometimes the manager may not get into the crux of the problem, i.e. there may not be any fruitful result of deliberation, and then the manager might temporarily switch off his conscious search and relax. This process of realization is called incubation. Then after sometime, a flash of light may occur, and the manager may get some insights and ideas. This stage is called illumination. In the last stage, which is called accommodation, the manager resynthesises his ideas into a usable proposal. Evaluating the Alternatives: The manager must now give proper weightage to the positive and negative aspects of the alternatives and evaluate by using some criteria like (a) time; (b) cost; (c) risk; (d) results expected; (e) deviations anticipated; (f) resources available for implementation. Selecting the Best Alternative: This is the most important step where the manager selects the best alternative that will yield maximum profits or results with minimum cost, input or resources. To put it in simple terms, the solution should be able to solve the problem in the best possible way. Effective Implementation and Follow-up Action: Any decision without proper implementation becomes futile and hence proper care must be taken by the manager to pool resources and start implementing the decision taken. In large organizations, follow-up procedures are available in the system...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments

Creating a Niche Market for Your Product Range Abstract to Concrete Ideas: The process of new product development starts with the search for new ideas. Abstract ideas are molded in such a way to suit the market needs. Business persons who want to capture a major share of the market have to think out of the box, to tide over the competition. Small things can make a big difference. Monotonous pattern of thinking will not help you in the long run to survive and sustain in the market. The Significance of R&D: The objective is to obtain ideas for new products, new attributes for the existing products and new usage for the existing product line. Why do you think so much of investment goes into research and development? The fruits of such R and D activities are reflected in the form of improved sales turn over. Market updates on a daily basis also gives you an excellent feedback about the new products that throng the market. Think about this, it is not possible for every organization to invest such huge sums in R and D which demands technically qualified personnel to carry out the research activities and it is next to impossible that each and every firm in the market can establish the necessary infrastructure for the purpose of research. SWOT Analysis: What might be the solution? Companies generally rely on internal sources, customers, competitors, distributors, suppliers and others for new product ideas. The sales force of a firm can provide excellent inputs as they meet customers on a regular basis. Through SWOT analysis, a company can make a conscious, deliberate and systematic effort to identify opportunities that can be profitably exploited. Top management should encourage the employees to think more imaginatively to create a niche market for its product range. The management has to prioritise its objectives first and channelise the efforts of employees accordingly. Picture Courtesy : The power of Product Thinking Steps to be followed in new product development: Generation of new product ideas Screening of ideas – It serves the purpose of reducing the large number of ideas generated, to spot the good ones and drop the bad ones. Concept development and testing – An inherent idea must be developed into a product concept, should include the customer, the major customer benefits and the features defining it. Development of marketing strategy – This is helpful in launching the product at the right time and right place to the right people. Business analysis – A review of cost versus profit analysis, estimated size and growth rate of the market segment, estimated sales and market share for the new product in the light of financial feasibility. Development of the product – If the business analysis gives a satisfactory report as to the rate of return on investment and pay back period, the R and D department goes ahead with manufacturing the prototype which is the preliminary version of the final product. Test marketing – It provides an opportunity to understand market response to the new product and its proposed marketing programme in a more realistic market environment than in simulated conditions. Commercialization – The product is released into the market, distribution channels are established, thus initiating its life cycle. The success of new products can be attributed to two aspects, one is creativity and the other being...

Posted by Managementguru in Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments
What Do You Mean by New Product Development? In business and engineering, new product development (NPD) is the complete process of bringing a new product to market. Innovate or Die: Product management should be viewed form a broader perspective by business firms, in that, it has to include new product development as part of the action plan, apart from appraising the existing product line, positioning them effectively and taking brand decisions wisely. “Innovate or die’, is the modern entrepreneurial slogan. Unless organizations innovate and introduce new products, they cannot survive in the competitive market. Strategies defining the organization’s future are built upon the portfolio of new products. Picture Cortesy: Coschedule Need for new product development: People always welcome change and new product development is an opportunity for the firms to meet the changes in consumer demands. They are a source of competitive advantage. Your new product may infuse a fresh lease of life to your sagging profits. New products may turn out to be the star performers of your firm and provide long term financial return on your investment. Some firms take the smart strategic choice of using the idle capacity of their plant for manufacture of a new product that may utilize the existing production and operation resources to an optimum level. They capitalize on research and development. Products that create a wave are a result of research on market trend and consumer preference. Firms can make it, if their research is customer-centric rather than product-centric. They provide opportunities for reinforcing or changing strategic direction. It is wiser to discontinue production of a product that does not find acceptance and divest the funds in a beneficial venture. They leverage marketing and brand equity. Big corporate firms while introducing new products make a big publicity, so that it can attract potential investors and consumers. They enhance the corporate image. You cannot expect a firm to make it big with a single product line or confined to one area of development. The growth of a company is evident only when it ventures into multifarious disciplines reflecting its capacity for expansion and diversification. Picture Courtesy: Staenz Also if a company grows, the growth of the stake holders is rest assured as the company would be in a position to offer decent dividends with bonus. Even if a growing company ploughs back its profits for expansion, it is again a good thing for the investors as further expansion obviously means growing profits. They affect human resources-a new product is perceived differently by different people. It is a need satisfying concept with benefit for buyers; a bundle of need satisfying features for marketers; a way to add value for intermediaries; an opportunity to design for R and D and a chance; to assemble and process for the production department. They meet environmental threats-Until recent times, products were not subjected to environmental evaluation, but the recent crises regarding global warming and pollution has been an eye opener for all nations which are enforcing much rules and regulations, demanding for production aimed at environmentally safe products. New product development is a multi-dimensional concept, inherent in most organizations. The process is initiated when the organizations are subject to market pressure and the firms are left with no choice other than to take up the challenge. A List of Productivity Terms Automation – The use of robots or other automatic equipment to do certain tasks Business Productivity – The amount of goods or services produced by a business from a set amount of resources Capital Goods – Manufactured or constructed items that are used...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
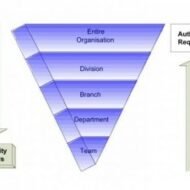
Centralization and De-Centralization Concepts CENTRALIZATION: The term “centralization” has several meanings: Centralization of Performance: Say, if the operations of a company is restricted to a single geographical location, it characterizes centralization of performance. Departmental Centralization: Specialized activities are carried out by a single department, say, maintenance of a whole plant, staff recruitment by HR department etc., Centralization as an aspect of management: This implies restricted delegation and exclusivity of decision-making by the top management. According to Allen, “Centralization is the systematic and consistent reservation of authority at central point in an organization.” According to Weihrich and Koontz, “Centralization (as an aspect of management) is the tendency to restrict delegation of decision-making. What are the special circumstances that force the managers to reserve authority and centralize decision making powers? 1. To facilitate personal leadership 2. To provide for integration 3. To handle emergencies 4. To utilize resources effectively and instantaneously. DECENTRALISATION: It is the tendency to disperse decision making authority in a structured and organized manner. It can be viewed as a philosophy rather than a principle where-in “discretion” plays a major role in deciding which decisions to push down into the organization structure and which to hold near the top. Capital expenditure, Investment analysis and major policy decisions have to be dealt with, by the top management. It is the systematic effort to delegate to the lowest levels of authority except that which can be exercised at central points. TYPES OF DECENTRALIZATION: Three approaches to the concept are: 1. PROFIT CENTRES 2. COST EXPENSE CENTRES 3. INVESTMENT CENTRES Profit Centre: Here the organization is split into divisions on a “product basis” and is given full authority to handle its own scheduled operations, right from placing orders to negotiating the sale of its finished products. Cost Expense Centre: Whenever it is easy to determine the cost of operations, cost centres are established. Cost centres run on “budgets” which acts as a control tool to run the units within the specified budgetary limits. Investment Centre: Useful in the case of big multi-product enterprises where product performance is measured by decentralizing the investment aspect. Each strategic business unit is responsible for the acquisition, use and disposition of fixed resources. Advantages of Decentralization: Managers and executives are relieved form excessive work pressure Even low level employees are involved in decision making thus bringing the decision making process closer to the scene of action. It facilitates product-diversification Creates an opportunity for learning Ensures effective control When a big organization is divided into relatively smaller units, it becomes flexible and also effects close control. Disadvantages of Decentralization: · Conflict arises between people belonging to different levels of the organization · Rising cost · Lack of co-ordination between production and marketing departments · No defined leadership Contingency Factors in Decentralizing: 1. Organizational goals 2. Organizational size 3. Geographical dispersion 4. Technical complexity of tasks 5. Time frame of discussions and decisions 6. Subordinates’ take on issues 7. Planning and control procedures 8. Environmental factors 9. Knowledge and experience of managers Effective Decentralization can be accomplished by · Establishing appropriate centralization · Developing efficient managers · Proper provision for communication and co-ordination · Establishing adequate controls Top management must be willing to delegate authority towards decision making; Middle management must be willing to accept responsibility that is being delegated. Only then effective decentralization is...










