Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
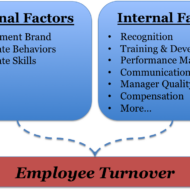
Smart Retention Strategies: Before going into the details of how to handle attrition, the first thing you must understand and realize is this. Each person working for you will have different expectations, perspectives and demands about his job, work environment and compensation respectively. Right at the time of recruiting and selecting the employee, his ideas must be taken into consideration and then it becomes the prerogative of the management whether to hire the person for that particular job. So the first step will be the right person for the right job, giving due importance to the anticipation of the employee who is going to become a member of your business family. Udemy Best Sellers:New Manager Training in Essential SkillsLeadership: Practical Leadership Skills Need for Open Conversation: In case of a small firm or company, it is easy for the manager to have a one on one conversation with each employee to settle his score of grievances then and there. Managers must have an open conversation without room for any ambiguity in the minds of his workers. The manager should try to protect the interest of the employees by representing their demands to the management at the right time. Many employees quit their positions because they have a nagging feeling at the back of their minds that their immediate boss is not the right kind of person to whom they can look up to and ask for support. In big corporates it is not easy to go for a one on one approach. A unique corporate culture that Trains the employees to have an uniform approach to all the systems of routineLed by an effective leader who controls and monitors the behavior and attitude of the workersPossesses sound management practices that make the employees come out with their suggestions freely and induce them to participateProvides satisfactory compensationIncorporates an open door policy catering to the different needs of people and also to the different levels of management, will help the managers to have a healthy relationship with the employees. Human Wants and Needs: Human wants are unlimited and when one want is satisfied, we want more of the same or yet another of a higher order. Approach your workforce to satisfy their craving either in terms of compensation or recognition which will also help to retain your workforce to a greater extent. There should be room for growth, especially for entrepreneurial minds and minds that have parallel thinking. Pic Courtesy: CuteHR Self-Motivation is the Key: Although motivation brings cheer amongst your workforce, self-motivated employees produce better results. Job satisfaction is a relative term; it differs with individuals, some like challenges and some are easily satisfied with an increase in salary quotient. A comprehensive appraisal on the personality of your workforce will give you a clear picture of the IQ (Intelligence Quotient) and EI (Emotional Intelligence) range of your employees which helps in designating employees in the appropriate slots. Such human rationing saves you a lot of time, energy and money as the employees are guaranteed satisfaction in their jobs. Contracts and Agreements: Contracts and agreements bind the employees to the firm only legally. How is that going to help you in terms of productivity? If one of your employees is going to work with discontent, he becomes a problem source spreading the same kind of feeling to others working with him. So it is also necessary for the management to spot out these problem persons either to bring them back into the groove or fire them without any further delay. Rising costs of living and unemployment ratios are really of economic concern, but still we find employees just like that quitting...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
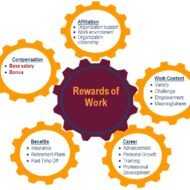
Operative Functions of HRM Staffing Staffing is one of the managerial functions. But this function is normally performed by the HR managers for all the departments of the firm. In most organizations, the HR department establishes personnel policies and coordinates the HR functions of all the departments. This function is also called the operative function or HRM function. It includes, amongst others, the processes of hiring, training, compensating, appraising and retaining employees, and attending to their labour relations, health and safety, and equality concerns. Procurement Procurement refers to a string of activities undertaken by the HR managers for filling the present and future vacancies of the organization. The activities include job analysis and designing, HR planning, recruitment and, finally, the selection of suitable employees. Here, job analysis refers to both the determination of specific tasks and responsibilities connected to a job and identifying the skills, knowledge and abilities required for the job holder. HR planning involves choosing and placing the right person at the right job and at the right time. Recruitment involves gathering a pool of applicants from which suitable employees may be selected. Lastly, selection involves screening, testing, interviewing and hiring the most suitable employees for the organization. SCOPE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF HRM Development Development here refers to both employees’ training and management development. HR managers are accountable for conducting and supervising training and development programmes for employees. The very purpose of a training and development programme is to increase the employees’ competencies in their job by improving their knowledge, skills and abilities. Training and development is widely accepted as a method for enhancing the employee skills, increasing the individual and organizational performance, improving the employee morale, and achieving the business growth and success. Compensation Compensation refers to the determination of the pay scale and other benefits for the employees. Establishing and maintaining the pay system of an organization is one of the principal jobs of the HR managers. They must devise ways to ensure fair and equitable pay rates. In addition, HR managers should regularly manage the performance evaluation system of the organization, and continuously design reward systems such as performance-linked incentive plans and bonus and flexible work schedules. Maintenance The maintenance function aims at retaining efficient and experienced employees in the organization. This calls for creativeHR practices. In this regard, HR managers are responsible for offering a wide range of HR programmes covering occupational safety, health promotion and physical fitness, canteen facilities, recreation activities, transportation programmes, employee suggestion schemes, career counselling and growth for creating a positive work environment. OBJECTIVES AND FUNCTIONS OF HRM Integration It consists mainly of industrial relations and aims at ensuring good relations between the management and the employees. HR managers have to implement industrial relations programmes that would ensure ethical and fair treatment in disciplinary action, grievance redressal, and career management processes. They should also counsel the employees and the management to prevent and, when necessary, resolve disputes over labour agreements or other labour relation issues. It is to be understood here that the functions of HRM can vary widely from one organization to another, depending upon its nature, size, and objectives. For instance, a smaller organization may follow a shorter HRM process with a greater emphasis on functions like procurement and compensation and little or no priority for activities like training and development and industrial relations maintenance. On the contrary, large organizations may pursue a longer and more comprehensive HRM process to meet the requirements of both the management and the workforce. WANNA TAKE A HR QUIZ N CHECK YOUR HR IQ? 1. The development and application of employees’ skills and energies to accomplish the goals and objectives of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
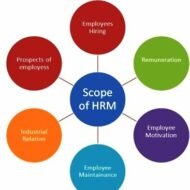
Scope and Characteristics of HRM 1. Personnel aspect: concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, lay off and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity, etc.; 2. Welfare aspect; dealing with working conditions and provision of amenities such as canteens, crèches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health, safety, recreation facilities, etc.; and 3. Industrial Relations aspect: the legal part which covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance redress and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc. Small Business Management and Marketing Essentials CHARACTERISTICS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. It is an art and a science: The art and science of HRM is indeed very complex. HRM is both the art of managing people by recourse to creative and innovative approaches; it is a science as well because of the precision and demanding application of theory that is required. 2. It is pervasive: Development of HRM covers all levels and all categories of people, and management and operational staff. No discrimination is made between any levels or categories. All those who are managers have to perform HRM. It is pervasive also because it is required in every department of the organisation. All kinds of organisations, profit or non-profit making, have to follow HRM. 3. It is a continuous process: First, it is a process as there are number of functions to be performed in a series, beginning with human resource planning to recruitment to selection, to training to performance appraisal. To be specific, the HRM process includes acquisition (HR planning, recruitment, selection, placement, socialisation), development (training and development, and career development), utilisation (job design, motivation, performance appraisal and reward management), and maintenance (labour relations, employee discipline, grievance handling, welfare, and termination). Second, it is continuous, because HRM is a never-ending process. 4. HRM is a service function: HRM is not a profit centre. It serves all other functional departments. But the basic responsibility always lies with the line managers. HRM is a staff function – a facilitator. The HR Manager has line authority only within his own department, but has staff authority as far as other departments are concerned. 5. HRM must be regulation-friendly: The HRM function has to be discharged in a manner that legal dictates are not violated. Equal opportunity and equal pay for all, inclusion of communities in employment, inclusion of tribal’s and farmers in the benefits and non-violation of human rights must be taken care of by the HRM. 6. Interdisciplinary and fast changing: It is encompassing welfare, manpower, personnel management, and keeps close association with employee and industrial relations. It is multi- disciplinary activity utilising knowledge and inputs from psychology, sociology, economics, etc. It is changing itself in accordance with the changing environment. It has travelled from exploitation of workers to treating them as equal partners in the task. 7. Focus on results: HRM is performance oriented. It has its focus on results, rather than on rules. It encourages people to give their 100%. It tries to secure the best from people by winning the whole hearted cooperation. It is a process of bringing people and organization together so that the goals of each are met. It is commitment oriented. 8. People-centred: HRM is about people at work both as individuals and a group. It tries to help employees to develop their potential fully. It comprises people-related functions like hiring, training and development, performance appraisal, working environment, etc. HRM has the responsibility of building human capital. People are vital for achieving organizational goals. Organizational performance depends on the quality of people and employees. 9. Human relations philosophy: HRM is a philosophy and the basic assumption is that employees are human beings and not a factor of production like...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Labor Management, Training & Development
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
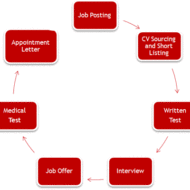
HR Selection Process and Techniques Following the process of recruitment is selection, where the management has to select the right employees at the right time. The intention is to choose appropriate candidates for the unfilled spots and to avoid commitments to those whom the management thinks will not work well. The best qualified individuals from the pool find their place whose qualifications match the job specifications. What is the Selection Process in Human Resource Management? Selection process depends upon the · Size of the company · Nature of the business · Kind and Number of persons to be employed · Government regulations to be followed etc. The process includes 1. Collection of data about the candidate’s qualification 2. Experience 3. Physical and mental ability 4. Nature and Behavior 5. Aptitude and the like Steps in Scientific Selection Process: A. Job Analysis: This is the basic step for finding the right candidate and each organization should lay down job analysis, job description and job specification with clarity in order to lure the right candidates for selection. B. Recruitment: Process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization. C. Application Form: This is also known as the application blank. This facilitates collecting detailed information from the prospective employees regarding their age, gender, family details, qualification, skills, experience, achievements etc. This is widely used to screen employees at the preliminary level. D. Written Examinations: are conducted to gauge the · Mathematical ability · Aptitude · Reasoning · Knowledge in various disciplines · General Knowledge and · English language abilities of the candidates. E. Preliminary Interview: This is suitable to eliminate the undesirable and unsuitable candidates and also to gather personal information from the candidates on a one to one basis. F. Group Discussion: Group discussions help the management to pick out bright candidates from among the group members and also the ability of each individual to adjust to the group. Each group is expected to analyze, interpret and find alternate solutions and select the best solution for a particular case study or subject matter. G. Tests: To further assess the skills of the employees the management conducts different kinds of tests. H. Final Interview: This is the most essential step in the process of selection. The interviewer matches the information obtained about the candidate through the application with that of his own observation and questioning. · Informal · Formal · Planned · Patterned · Non-Directive · Depth · Stress · Group and · Panel interviews are some of the types of interviews conducted in accordance with the job requirement. Also See: Interview Preparation Tips I. Medical Examination: Certain jobs require certain physical qualities like clear vision, perfect hearing, unusual stamina, tolerance of hard working conditions, clear tone etc. J. Reference Checks: The personnel department will engage in checking reference if the candidate passes all the tests and found suitable for the job. What kind of Companies the Employees are Attracted to – Here is an interesting infographic on “How to Attract the Perfect Employee”...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Training & Development
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
Definitions of Human Resource Management: 1. “A series of integrated decisions that govern employer-employee relations. Their quality contributes to the ability of organisations and employees to achieve their objectives.” (Milkovich & Boudreau, 1997). 2. “Concerned with the people dimension to management. Since every organisation comprises people, acquiring their services, developing their skills, motivating them to higher levels of performance and ensuring that they continue at the same level of commitment to the organisation are essential to achieving organisational goal. This is true, regardless of the type of organisation: viz. government, business, education, health, recreation, or social action.” (Decenzo & Robbins, 1989). 3.”The planning, organising directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, integration, and maintenance of human resource to the end those individual, organisational, and social objectives are accomplished.” (Flippo, 1984). 4. “The organisation function that focuses on the effective management, direction, and utilisation of people; both the people who manage produce and market and sell the products and services of an organisation and those who support organisational activities. It deals with the human element in the organisation, people as individuals and groups, their recruitment, selection, assignment, motivation, empowerment, compensation, utilisation, services, training, development, promotion, termination and retirement.”(Tracey,1994 ) Knowledge Workers Human resource management is therefore understood as the all significant art and science of managing people in an organisation. Increasing research output in behavioral sciences, new trends in managing ‘knowledge workers’ and advances in training methodology and practices have led to substantial expansion of the scope of human resource management function in recent years. HRM is not just an arena of personnel administration anymore but rather a central and pervasive general management function involving specialised staff as assistants to main line managers. Managing employee relationships is the role of the Human Resource department Human Resource Management is a process of valuing and developing people at work, this includes: Recruitment and selection Employee communication and engagement (participation) to increase employee retention Training and development Leadership WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST WEAKNESS Labour turnover & staff retention Labour turnover refers to the proportion of a workforce that leave during a period of time (usually one year) Labour turnover = number of staff leaving during the period x 100 average number of staff Staff retention refers to the ability of a firm to keep its workers. The disadvantages of having a large proportion of staff leaving each year include: The cost of recruiting replacement workers The cost of training the new workers Loss of productivity whilst replacements are found Loss of experienced workers Negative impact on reputation WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST STRENGTH Methods to control turnover: 1. Financial methods of motivation Bonuses Profit share Fringe benefits 2. Non financial methods of motivation Employee engagement and empowerment Training and development Promotion opportunities 3. Improved Human Resource Management procedures Four Fundamental Principles of HRM: Human Resource is the organisation’s most important asset; Personnel policies should be directed towards achievement of ENTERPRISE goals and strategic plans; Corporate culture exerts a major influence on achievement of excellence and must therefore be strengthened with consideration of employee welfare. Whilst integration of corporate resources is an important aim of HRM, it must also be recognised that all organisations are ‘pluralist societies’ in which people have differing interests and concerns, which they defend and at the same time function collectively as a cohesive group. →Evolution of...










