Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

A Process of Intelligence Effective Decision making is a process of Intelligence, Design and choice activities and “is a central part of the management process”. Decisions are hard to make but once decided there should be no second take. The following steps are involved in the process of Decision-making: 1. Recognizing the problem 2. Deciding priorities among problems 3. Diagnosing the problem 4. Developing alternative courses of action 5. Evaluating alternatives 6. Selecting the best alternative 7. Effective implementation and follow-up action. Recognizing the Problem– Herbert A Simon calls this step as an “intelligent activity“. It is important to find out whether there is any deviation from the past experience. For e.g. Sales might decrease, expense might decrease, sometimes there might be deviations from the plan, sales budget, and competitors may outperform by improved systems. Deciding priorities among the problems: A manager would face many problems at the same time. He should not be bogged down with small and unimportant problems. Some problems can be easily solved by the sub-ordinates. Some may not be important. A manager must see that – he selects carefully the most important problem. Peter Drucker says that “once the right problem is perceived then half of the problem is solved”. A manager must diagnose carefully by asking the following questions. a. What is the real problem? b. What are the causes and effects of the problem? c. Is this problem very important? d. Can they be solved by sub-ordinates? e. Which is the right and most important problem to be solved? Diagnosing the Problem: After choosing the right problem the manager must now start diagnosing the problem. There is no simple answer to the question of how to diagnose the problem, because every individual differs in his or her own way of diagnosing the problem depending on the different background orientations and training. A manager must systematically analyze the problem for identifying the alternative causes of action. Developing Alternative Courses of Action: This step is creative and innovative where a manager analyzes from all perspectives Sometimes a manager can also use a technique called “brainstorming” where a few individuals discuss at length the various possible available alternatives. First of all, a manager must be thoroughly familiar with the problem. This is called saturation. Later, he must think about the problem from several view-points which is called deliberation. Sometimes the manager may not get into the crux of the problem, i.e. there may not be any fruitful result of deliberation, and then the manager might temporarily switch off his conscious search and relax. This process of realization is called incubation. Then after sometime, a flash of light may occur, and the manager may get some insights and ideas. This stage is called illumination. In the last stage, which is called accommodation, the manager resynthesises his ideas into a usable proposal. Evaluating the Alternatives: The manager must now give proper weightage to the positive and negative aspects of the alternatives and evaluate by using some criteria like (a) time; (b) cost; (c) risk; (d) results expected; (e) deviations anticipated; (f) resources available for implementation. Selecting the Best Alternative: This is the most important step where the manager selects the best alternative that will yield maximum profits or results with minimum cost, input or resources. To put it in simple terms, the solution should be able to solve the problem in the best possible way. Effective Implementation and Follow-up Action: Any decision without proper implementation becomes futile and hence proper care must be taken by the manager to pool resources and start implementing the decision taken. In large organizations, follow-up procedures are available in the system...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
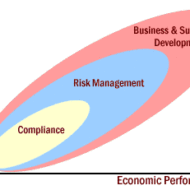
There is no Business Success Without Risk What is the Risk of Taking a Chance in a Business Activity? Business is often viewed as a game or a gamble in which success is always at risk. Think about it, risk is present in every sphere and aspect of our lives and even when you are not running a business. So why the fuss? A thorough knowledge and research of the business activity you are about to perform will give you the needed confidence to go about it. A true business man is an entrepreneur who treats risk as an opportunity rather than a challenge. Business organizations are started with a single purpose, to make profit and then more profit. Only when the organizations grow, there comes the awareness and necessity to think about stakeholders’ interest and working towards a social cause. Initial stages definitely pose threats for the very survival of the organization. Risk is an inherent part of a business as you are not sure about the outcome of your business activity. What are the Chances or Probability? We talk more about probability and chance outcomes when you deal with a particular product. Retail segment is one area where the risk of duplication is high and people have to be cautious and careful in order to protect their copyrights and symbols from being replicated. Mild inflations can benefit the market but recessions put you in doldrums especially if you are dependent on a wholesaler or a manufacturer. Risk can aspect itself in the following ways: Economically- Attrition and effects of global economy Legally- Labor laws and enactments Socially- Expectations from the public in general Government rules and regulations- Government policies and export duties Stakeholder expectations- Wealth maximization and assured profits Environmental – Need to comply with changing standards like waste affluent treatment plants Political scenario- Effects due to changing governments Risk and Uncertainty Risk and uncertainty go hand in hand and you need a risk management template or a model for your reference to solve or manage risks. The first and foremost step would be to identify the risks in your sphere of business activity. Risk documentation or creating a risk profile is an inevitable move for a new organization. This prepares the organization mentally to face challenges in a structured manner and reduces disorientation. It is very important to keep in mind the organisation’s objectives while documenting the risk profile to keep your focus unaltered. Risks evolve continuously and it is the responsibility of the top management to be in line with the market economy to manage the adverse conditions that come in the way. How to Manage Risks? Risk management is an ongoing and continuous process and it cannot be looked upon as a distinct area to be managed by a set of individuals. In a small and upcoming organization the responsibility lies on the shoulders of each and every individual to self assess, evaluate and manage risks and find the right kind of solution that will not be detrimental to the core objectives of the organization. Bigger organizations can afford to have expert opinion by commissioning PROFESSIONALS to identify, assess and manage risks. An overall and broad perspective of risk is what has been analysed here. There are numerous possibilities of risks, whether big or small in magnitude, affecting an organization. A thorough study of the field you are about to venture into, the pros and cons of the business activity, time of launch are few things that will help you to analyse what the market niche warrants for and act accordingly. In further segments, let us look into the factors of risk, identifying and...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments

What forms the Basis for your Investment Decisions? Profit seeking is the ultimate aim of corporate management and the finance manager acts as the anchor point of the management structure. He has to provide specific inputs into the decision-making process, with respect to profitability. Corporate Investment Decisions Cost control What are the Cost Centres? It is the finance manager’s responsibility to have an eagle’s eye on rising costs by continuously monitoring the cost centers of his organization. Production department where there is always a need for additional resources or inflow of funds, should be his first target of contol. Costs are incurred by each and every department of an organization, namely, the production, marketing, personnel and of course finance and accounting. It is a difficult task to control the rising costs. That is the reason why, big corporate companies go for annual budget formulation at the start of the year and reformulates the finance plan by comparing actual with the projected figures. This kind of evaluation helps the firm to fix responsibilities for various centers of operation. Resource Allocation A finance manager is the first person to recognize rising costs for supplies or production, and he can make immediate recommendations to the management to bring back costs under control. While cost control talks about allocating resources to different responsibility centers in the desired proportion, cost reduction focuses on conserving the resources. Cost reduction can be achieved through modifying product and process designs, cutting down throughput time, doubling labor productivity, mass customization, standardistion etc., Pricing Price Fixation It is always a joint venture between marketing and finance departments when it comes to price fixation of products, product lines and services. Pricing decisions are important in that, they affect market demand and the company’s competitive stand in the market. Pricing strategies have to be evolved in the wake of existing competitor strategies and market preference. The demand forecast is the prerequisite factor of the production process and in-depth market analysis and understanding is inevitable on the part of the executives. Future Levels of Profit The finance manager is also responsible for charting out the future levels of profit, based on the relevant data available. He has to consider the current costs, likely increase in costs and likely changes in the ability of the firm to sell its products at the established selling prices. So, it becomes clear that, such market evaluation cannot be periodical, as the market is highly dynamic and has to be done in a day-to-day basis. Before a firm commences a project, its discounted future fund flow and expected profits must be ascertained which will serve as a basis for comparison. Risk versus Return: Investment decisions always are risky as the gestation period of invested funds is very long and not to return immediately. Further, the firm has to calculate the time period in which its initial investment can be recovered and the feasibility of the rate of return on its investment. Fund Management The finance manager is engaged in activities like, mobilization of funds, deployment of funds, and control over the use of funds and also he is to evaluate the risk return trade-off. Profit maximization is the fundamental objective of any organization and the finance manager plays a key role in restructuring the financial philosophy of a firm to take it to greater...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
Every business organisation’s aim is to make profit and more profit. Does it end there? What should be the real motive behind running an organization? Profit maximization alone does not help the organization to firmly plant its feet in the business environment, as the success of an organization in the long run is decided by many critical factors like, market share, value of the company shares, market stand, image etc. So, shall we say, let wealth maximization be the goal of any organization, which focuses on increasing the “earnings per share” of the share holders. What is Profit Maximization? Profit maximization does not take into consideration, the interest of share holders or stake holders, who ought to be the ultimate beneficiaries. Concentrating on short term profits confines a firm and limits its scope and growth whereas; value creation is something that the management should aim for, as it helps to increase the “net worth” of a company. Mere price versus output calculations make firms to operate in a profitable manner, but it should never be the only objective of a firm, as it has the moral and social responsibility to patronize its shareholders by increasing the net worth of the company. Underlying Logic While maximizing profit, a firm either produces maximum output for a given amount of input, or uses minimum input for producing a given output. Thus the underlying logic for profit maximization is efficiency. Under perfect competitive market conditions, profit serves as a perfect measure for the performance of a firm. If profit is the motive of a firm, it fails to consider the time value of money which is an important criterion that decides the success of a firm, and also it values benefits received today and after a period as the same. Moreover the uncertainty factor is there to be considered too. Firms always prefer to have smaller but surer profits rather than larger benefits but less certain. Impact of Taxes When we talk about profits, the next indispensable factor will be the taxes that demand a portion of your profit. Maximizing profits after the payment of taxes facilitates the firm to increase the net profit ratio to serve the best interests of the owners. But, this also fails to maximize the economic welfare of the owners, as it does not take into account, the timing and uncertainty of the benefits. Wealth maximization is the ideal alternative that is consistent with the survival goal and also with the personal objectives of managers such as recognition, power, status and personal wealth. The Right Balance between Risk and Return Mangers while deciding on investment options, seek to achieve a right balance between risk and return. If the firm borrows heavily to finance its operations, care should be taken to ensure that, the rate of return on investment should be sufficient enough to support the payment of interests on borrowings and also to repay the principal. If the firm is not able to “service the debt” there is a danger of the firm becoming bankrupt or insolvent. The firm’s investment and financing decisions are unavoidable and continuous. In order to make rational decisions, the firm must have a goal, which is nothing but the “shareholder’s wealth maximization” which is theoretically logical and operationally...








