Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Dec 29th, 2014 | 0 comments

Scope of Financial Management Facebook Buys WhatsApp: Boneheaded or Brilliant? This was the title of a Forbes Article when Mark Zuckerberg acquired Whatsapp for $19 billion dollars, the price that may exceed the GNP of some of those countries. Mark is said to be an unconventional thinker and the WhatsApp acquisition shows Facebook’s determination to follow the road not yet paved. It is a bold move, yet filled with risks along the way. This is one of the finest examples of the big investment decisions of recent times and the right course of action, if you measure the number of potential users of the mobile messaging service rather than the cost of acquiring each user and the potential for selling ads to each user today. Follow these mind blowing tips to become prosperous Picture Courtesy : YoungHstlrs Financial management is one of the important aspects of overall management, which is directly asscoiated with various functional departments like personnel, marketing and production. Financial management embraces wide area with multidimensional approaches. The following are the important scope of financial management. Some of the major scope of financial management are as follows: 1. Investment Decision 2. Financing Decision 3. Dividend Decision 4. Working Capital Decision. 1. Investment Decision: The investment decision involves Risk EvaluationMeasurement of cost of capital andEstimation of expected benefits from a project. Capital budgeting and liquidity are the other two major components of investment decision. Capital budgeting takes care of the distribution of capital and commitment of funds in permanent assets to harvest revenue in future. Capital budgeting is a very focal decision as it impacts the long-term success and growth of a firm. All the same it is a very tough decision because it encompasses the estimation of costs and benefits which are uncertain and unknown. Picture Courtesy: Crowdfundingheroes 2. Financing Decision: Financing decision is related to financing mix or financial structure of the firm. The raising of funds requires decisions regarding Methods and sources of financeRelative proportion and choice between alternative sourcesTime of floatation of securities, etc. In order to meet its investment needs, a firm can raise funds from various sources. Long Term Sources of Finance: Share Capital or Equity SharesPreference Capital or Preference SharesRetained Earnings or Internal AccrualsDebenture / BondsTerm Loans from Financial Institutes, Government, and Commercial BanksVenture FundingAsset SecuritizationInternational Financing by way of Euro Issue, Foreign Currency Loans, ADR, GDR etc. Picture Courtesy: Cash & Treasury Management file Medium Term Sources of Finance: Preference Capital or Preference SharesDebenture / BondsMedium Term Loans fromFinancial InstitutesGovernment, andCommercial BanksLease FinanceHire Purchase Finance Short Term Sources of Finance: Trade CreditShort Term Loans like Working Capital Loans from Commercial BanksFixed Deposits for a period of 1 year or lessAdvances received from customersCreditorsPayablesFactoring ServicesBill Discounting etc. 3. Dividend Decision: In order to accomplish the goal of wealth maximization, a proper dividend policy must be established. One feature of dividend policy is to decide whether to distribute all the profits in the form of dividends or to plough back the profit into business. While deciding the optimum dividend payout ratio (proportion of net profits to be paid out to shareholders), the finance manager should consider the following: Investment opportunities available to the firmPlans for expansion and growth,Dividend stabilityForm of dividends, i.e., cash dividends or stock dividends, etc. 4. Working Capital Decision: Working capital decision is related to the FINANCING in current assets and current liabilities. Current assets include cash, receivables, inventory, short-term securities, etc. Current liabilities consist of creditors, bills payable, outstanding expenses, bank overdraft, etc. Current assets are those assets which are convertible into cash within a year. Similarly, current liabilities are those liabilities, which are likely to mature for payment within...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Business Management, Financial Accounting
on Jul 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
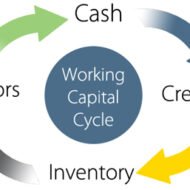
Understanding Working Capital: It is the life blood of business. Funds needed for the purchase of raw materials, payment of wages and other day-to-day expenses are known as working capital. It is part of the firm’s capital, which is being used for financing short-term operations. Hence, it may also be termed as Circulating Capital or Short-Term capital. “Working capital means current assets” –Mead, Malott and Field. “Any acquisition of funds which the current asset increases working capital, for, they are one and the same.” – J.S.mill Financial troubles and issues arise only when this entity called ‘working capital’ is not properly managed. Every successful company will hire a financial manager to deal with issues relating to finance while the CEO can look into matters relating to promotion of the product or service and the position of the company in the market. The ‘Sales Turnover or Sales Volume’ is the key issue you have to look into to gauge whether you have sufficient working capital to manage that big a volume for that particular period. You have to rotate your funds wisely keeping in mind the credit policies your company offers and the credits you may enjoy with your supplier, bank interest for the short-term loans etc. Concept of WC: Working capital implies excess of current assets over current liabilities. Funds invested in current assets is known as “Gross Working Capital.” The difference between current assets and current liabilities is known as “Net Working Capital.” What are the two types? Permanent or fixed: It is the minimum amount of current assets required for conducting the business operation. This capital will remain permanent in current assets and should be financed out of long-term funds. The amount varies from year to year, depending upon the growth of a company. Temporary or Variable: It is the amount of additional current assets required for a short period. It is needed to meet the seasonal demands at different times during a year. The capital can be temporary and should be financed out of short-term funds. The working capital starts decreasing when the peak season is over. Various Factors Influencing WC: Nature of business: Service oriented concerns like electricity; water supplies need limited working capital while a manufacturing concern requires sufficient working capital, since they have to maintain stock and debtors. Credit Policies: A company which allows credit to its customers shall need more amount while a company enjoying credit facilities from its suppliers will need lower amount of working capital. Manufacturing Process: Conversion of raw materials into finished goods is called manufacturing or production. Longer the process, higher the requirement of working capital. Rapidity of turnover: High rate of turnover requires low amount and lower and slow moving stocks need a larger amount of working capital. Say, jewelry shops have to maintain different types of designs calling for high working capital. Fast moving goods like grocery requires low working capital. Business cycle: Changes in economy has a say over the requirement of working capital. When a business is prosperous, it requires huge amount of capital; also during depression huge amount is needed for unsold stock and uncollected debts. Seasonal variation: Industries which are manufacturing and selling goods seasonally require large amount of working capital. Fluctuation of supply: Firms have to maintain large reserves of raw material in stores, to avoid uninterrupted production which needs large amount of working capital. Dividend policy: If a conservative dividend policy is followed by the management, the need for working capital can be met with the retained earnings, it consequently drains off large amounts from working capital pool. ...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Feb 20th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is fund ? Cash, total current assets, net current assets and net working capital are also interpreted as fund. So, it is necessary to clearly define the meaning of fund and demarcate its scope and function. To put it precisely, fund is nothing but, net working capital of a firm. The flow of fund occurs when a business transaction takes place that leads to an increase or decrease in the amount of fund. Firms prepare fund flow statement to explain the sources and applications of fund, which also serves as a technical tool to ascertain the financial condition of a business enterprise. Balance Sheet In a business firm, everyday numerous financial transactions take place. These are summarized into a balance sheet that gives an idea about the assets and liabilities at a specific point of time. When two balance sheets of consecutive periods are compared, we come to know about the inflow and outflow of funds and thereby the net working capital available is ascertained. This is step one. Profit and Loss Statement The next step would be to prepare an adjusted profit and loss account to determine fund inflow or fund lost from business operations. Accounts have to be prepared to ascertain hidden information (for all non-current items of assets and liabilities). Finally fund lost or gained from operations is arrived at and presented in a statement form. It is not that, only accountants could understand these operations and adjustments. Any person with logical reasoning and business acumen can understand the nuances of accounting, of course with some guidance. Few points that highlight the ways in which funds flow outside and inside a business enterprise will give you a better idea on the nature of fund flow: Sources of fund: Sale of fixed assets – sale of land, building, machinery, furniture etc. But you have to take into consideration a factor called “depreciation“. It is nothing but the wear and tear of the assets due to continuous usage, reduction in market value over a period of time, obsolescence, accidents etc. Remember, land is a non-depreciable asset in developing countries like India, whereas it may not be so in certain developed countries where the real estate values are nose diving. Issue of Equity shares – To raise capital free of interest, many big corporate firms go for equity capital from the general public. But the firms should make it a point to declare dividends if it happens to reap enormous profit to retain their market share. Their main aim should be to protect the interests of the equity share holders who are also the owners. Fund that comes into the firm through business operations – through sale of goods and services. Here the firm has to factorise its cost of production and economy of scale in order to make it cost-effective and fix a feasible profit margin. Borrowing of loans from banks and other financial institutions – Although it is a quick way of raising fund, care should be exercised in that, you should be in a comfortable position to “service the debt“. If not, there lurks the danger of bankruptcy where the firm might become insolvent, if it is unable to repay the interest and principal over a period of time. Issue of debentures – Debentures are also a form of equity but it comes with a price. The firm has to pay a percentage as interest on debentures and repayment period is also fixed in advance. The only solace for the firms would be the tax rebate that can be availed on loans and...






