Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on May 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
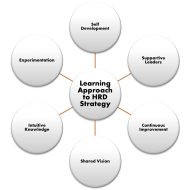
What are Learning Organizations? Need for Learning Organizations: The ever evolving, dynamic business environment and the complex relationship among various countries in the political and business arena necessitate the need for a learning organization. This becomes essential for organizations to be flexible and be able to respond to change which is the only enduring source of competitive strength. What is a learning organization? A learning organization is the term given to a company that facilitates the learning of its members and continuously transforms itself. Learning organizations develop as a result of the pressures facing modern organizations and enables them to remain competitive in the business environment. Learning is used to reach their goals and avoid repeating mistakes. Employees learn to link their personal goals to organizational goals and link rewards to key measures of performance. The managers learn to design systems and procedures to motivate learning process and to encourage employees to feel free to share information and take risks. Characteristics of a learning organization: It nurtures a climate of trust in the organization and people are encouraged to learn and develop their #knowledge and skill sets. It inspires human resources in the immediate external environment such as customers, suppliers, creditors etc., to learn as and when possible. The whole business policy revolves around #HRD strategy. The organization subjects itself to continuous transformation in which learning and working run hand-in-hand. Learning Based Techniques: Organizational learning concept is the latest OD (#Organizational Development) technique. #Ernst & Young, the largest #accounting firm has set the following procedures for learning purpose. Managers play a vital role in this transformational process of learning. They are responsible for choosing employees who are willing to and capable of learning, and must ensure that the participants in the program are trainable. They must get the support of #trainees and others. Trainees must be appraised about the benefits that will result from training and the managers also should enjoy the support of supervisors, #co-workers and their sub-ordinates. This is very essential to facilitate learning process, to ensure availing of honor and respect of peers and sub-ordinates. The opinion of trainees, supervisors, co-workers and sub-ordinates must be obtained on the content of training, the location and the time and duration of the training. Managers also play a key role in assisting others in goal-setting and meeting those goals. Goal setting is necessary to improve their performance and direct their attention to specific #behavior that needs to be changed. Managers may assist the sub-ordinates and peers to identify tools and resources for acquiring knowledge. Managers must also focus on providing performance feedback as it serves two objectives; it provides information on performance and serves as a motivating tool. Managers should urge their employees to analyze their performance, identify weaknesses and take action to overcome weaknesses. Managers may assist the employee to transfer the learned skills/knowledge to work. It will be a wiser move to design #training methods in such a way as to enable the trainees to practice skills on their jobs between training sessions. DOWNLOAD THE PDF VERSION...

Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour
on May 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
Organizational Climate – An Analogy Organizational climate is a measure of the feel of the internal environment of an organization which is perceived by an outsider and/or an employee according to their business with the organization. Organizational climate has a great effect on employees’ behavior. If the climate of an organization is open and friendly, employees feel relaxed and if it is very formal, then such a comfort level may not be felt. Climate for an organization is somewhat like personality for a person. “Just as every individual has a personality that makes him/her unique, an organization has a climate that clearly distinguishes its personality from other organizations. Human religionists introduced the concept of organizational climate in the late 1940’s. Now this has become a very useful metaphor for thinking about and describing the social aspects of a firm. Some definitions: “A set of characteristics that describe an organization and that i. Distinguish one organization from another ii. Are relatively enduring over a period of time and iii. Influence the behavior of people in the organization.” – Forehand and Gilmber “A mutually agreed internal (or molar) environmental description of an organization’s practices and procedures.” – Benjamin Schneider (1975) “A relatively ending quality of the internal environment that is experienced by the members, which influences their behavior and can describe in terms of values of a particular set of characteristics of the organization.” – Renato Tagiuri (1968) Features: It is an abstract and intangible concept. But it exercises a significant impact on the behavior and performance of organization members. It is the perceived aspect of organization’s internal environment. It refers to the relatively enduring characteristics which remain stable over a period of time. It gives a distinct identity to organization and differentiates it from others. It is a total expression of what the organization is. It is the summary perception which people have about organizations. It is a multi-dimensional concept. It consists of all organizational factors – authority pattern, leadership pattern, communication pattern, control etc. Elements of Organizational Climate: Individual Autonomy: The extent to which employees are entrusted with to make decisions, the degree to which they are free to manage themselves and have the freedom to exercise their responsibility come under the purview of individual autonomy. Position Structure: It means the extent of direct supervision, formalization and centralization in an organization. Reward Orientation: The degree to which an organization rewards individuals for hard work or achievement. It will be high when an organization orients people to perform better and rewards them for doing so. Task Orientation: If the outlook of the top management is task oriented, the employees will have to speed up the pace of work to please their bosses. Relations Orientation or Consideration: Here the climate is conducive and supportive where the managers are relations-oriented while dealing with their sub-ordinates. The needs and aspirations of the workers will be given due importance resulting in enhanced team spirit. Job Satisfaction: The workers feel happy if the jobs are designed to allow the worker to use their innovative skills. Morale: Morale represents a composite of feelings, attitude and sentiments of organizational members towards the organization, superiors and fellow workers. If it is high, there will be an atmosphere of co-operation and if it is low, there will be conflicts and poor co-operation among the workers. They will also feel dis-oriented in their work. Control: The control systems may be either rigid or flexible. An impersonal or bureaucratic atmosphere is seen in the former situation where the scope of self-regulation will be minimum. DOWNLOAD THE PDF...

Posted by Managementguru in Video Lecturers
on Apr 20th, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategic Management Video Lecture by David Kryscynski This is the introduction lecture for Strategic Management. Very Innovative and Informative video. A List of Strategic Management Terms Business – A strategy that pertains to single departments or units within a company.Combination – A type of grand strategy that employs several different grand strategies at once.Concentration – A growth strategy that extends the sale of current products or services to a company’s current market.Differentiation – A business strategy that strives to make the company’s product or service unique.Diversification – A growth strategy that moves a company into a similar kind of business with new or different products or services.Divestiture – A type of defensive strategy in which a company sells some part of its business, often an unprofitable part.Evaluating – The process of continuously monitoring the company’s progress toward its long-range goals and mission.Focus – A business strategy that directs marketing and sales towards a small segment of the market.Formal – The type of planning that involves systematic studying of an issue and the preparation of a written document to deal with the problem.Formulating strategy – Developing the grand- and business-level strategies to be used by the company.Functional – A strategy which involves short-range operational plans which support business strategies by emphasizing practical implementation.Goal – A concise statement that provides direction for employees and set standards for achieving the company’s strategic planGrand – A type of strategy that provides overall direction for the company.Growth – A type of grand strategy developed when a company tries to expand sales, products, or number of employees.Implementing – Putting a strategy to work after it has been formulated.Intermediate – Covers the time span between short-range and long-range, usually 1-3 years or 1-5 yearsLiquidation – A type of defensive strategy in which the entire company is sold or dissolved.Long Term– A three-to-five year period of time, but possibly as far as 20 years into the future.Mission Statement – A brief summary explaining why a company exists.Operational – Short-range planning that focuses on forming ideas for dealing with specific functions in the company.Overall Cost Leadership – A business strategy that is designed to produce and deliver a product or service for a lower cost than the competition.Planning – The process that businesses use to decide the company’s goals for the future and the ways to achieve those goals.Policy – A broad general guide to action that establishes boundaries within which employees must operate.Procedure – A detailed series of related steps of tasks written to implement a policy.Retrenchment – A type of strategy that aims to reverse negative trends in a company, such as losses in sales.Rule – A specific and definite corporate action that employees must follow.Short Term– A one-year period of time.Stability – A type of strategy that aims to keep the company operating at the same level that it has for several years.Strategic – Long-range planning done by the highest management levels in the company.Strategic Management – The application of the basic planning process at the highest levels of the company.Strategy – An outline of the basic steps management is going to take to achieve a goal.SWOT Analysis – The most utilized process for determining a company’s overall health; it involves analyzing internal strengths, internal weaknesses, external opportunities, and external threats.Turnaround – A type of defensive strategy that is used to regain success.Vertical Integration – A growth strategy that moves a company into a market it previously served either as a supplier or as a customer. Take The Test to Check Your Strategic...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Apr 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

Business Policies – Framing and Execution Business policies are the keystone in the arch of management and the life-blood for the successful functioning of business, because without well-laid down policies, there cannot be lasting improvements in the economic condition of the firm and labor-management relations. A policy is a positive declaration and a command to its followers. It translates the goals of an organization into selected routes and provides the general guidelines that prescribe and proscribe programmes, which in turn, dictate practices and procedure. Attainment of Objectives: Buisness policies are general statement of principles for the attainment of objectives which serve as a guide to action for the executives at different levels of management. They pave a broad way in which the sub-ordinates tread along towards accomplishing their objectives. Hierarchy: For each set of objectives at each level, there is a corresponding set of policies. The Board of Directors determine the basic overall corporate policiesThe top management decides on the executive corporate policiesManagers decide on the departments / divisional policiesMiddle managers handle the sectional policies Consistent Decisions contributing to the Objectives: The policies delimit the area within which a decision has to be made; however, they do allow some discretion on the part of the man on the firing line, otherwise, they would be mere rules. At the same time too much of discretion in policy matters may prove harmful to the accomplishment of organizational objectives and hence it is generally within limits. Mutual Application: Policies in general are meant for mutual application by sub ordinates. They are fabricated to suit a specific situation in which they are applied, for they cannot apply themselves. Unified Structure: Policies tend to predefine issues, avoid repeated analysis and give a unified structure to other types of plans, thus permitting managers to delegate authority while maintaining control. Policies for all Functional Areas: In a well-structured and managed organization, policies are framed for all functional levels of management. Corporate planningMarketingResearch and DevelopmentEngineeringManufacturingInventoryPurchasePhysical DistributionAccountingFinanceCostingAdvertisingPersonal SellingSpecial Promotion, are some areas that require clear-cut policies. Clear-Cut Guidelines: Policies serve an extremely useful purpose in that they avoid confusion and provide clear-cut guidelines. This enables the business to be carried on smoothly and often without break. They lead to better and maximum utilization of resources, human, financial and physical, by adhering to actions for...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource
on Apr 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Entrepreneurs are the mechanism by which our economy turns demand into supply. They create new ventures that provide new, improved products and services. Here we list some of the principal qualities of entrepreneurs and how those qualities help in shaping up our economy. Productivity Accelerators: Entrepreneurship raises productivity through technical and other forms of innovation. Entrepreneurs as risk bearers find resources and fill market gaps that would be missed by larger, more bureaucratic organizations. They allow a country to extract every last bit of marginal capacity out of whatever resources exist within the society. Brilliant Tips on Productivity by some Popular Entrepreneurs: Focus on one thing at a time: It may seem like a no-brainer, but multitasking can actually cut back on your productivity. Instead of juggling multiple projects at once, schedule out blocks of time — or even entire days — during which you only focus on one task or one project. Steph Auteri, @stephauteri, Word Nerd Pro Outsource, outsource, outsource: Everything may be a priority, but you are not equally brilliant at everything. Eliminate the unnecessary tasks and outsource your weaknesses so your time and focus is directed to where you’ll make the biggest impact for the business. Kelly Azevedo, @krazevedo, She’s Got Systems Define roles and divide work: Make sure everyone on the team has distinct roles defined, and divide work accordingly. Everyone on a proactive team will want to do everything, and clearly defined roles make it clear who should do what. David Gardner, @david_gardner, ColorJar Job Creators: It is a powerful tool of job creation –Entrepreneurship as a whole contributes to social wealth by creating new markets, new industries, new technology, new institutional forms, new jobs and net increases in real productivity. The jobs constructed through their activities in turn lead to equitable distribution of income which leads to higher standards of living for the population. Entrepreneurship facilitates the transfer of technology. Entrepreneurs play a strategic role in commercializing new inventions and products. They play a critical role in the restructuring and transformation of economy. Their behavior breathes vitality into the life of large corporations and governmental enterprises. Market Competitiveness: They make the markets more competitive and thereby reduce both static and dynamic market inefficiencies. Micro-preneurs working in the informal sector circumvent established government authority when governments and their programmes inhibit economic development. They stimulate redistribution of wealth, income and political power within societies in ways that are economically positive and without being politically disruptive. Social Welfare: They improve social welfare of a country harnessing dormant, previously overlooked talent. They create new markets and help in expansion into international markets. The unique feature of entrepreneurship – that it is a low cost strategy of economic development, job creation and technical innovations. Technology Innovation: Technology entrepreneurship is also important for sustainable development as Nobel Prize Laureate prof. Dan Schechtman puts it: “Technological entrepreneurship is a key to the well-being of the world”. India has been the first among the few developing countries to have assigned a significant and categorical state role to small scale industries from the first Five Year Plan itself, and the small scale sector has emerged as a dynamic and vibrant sector of the economy during the eighties. If the country develops pucca infrastructure and removes the hurdles in the operative environment politically and legally, no doubt the Indian economy will be scaling to greater heights. Surplus manpower (educated and un-educated), which has been a great liability can become an asset once those with potential are selectively groomed for self-employment and enterprise formation, leading to further job...










