Posted by Managementguru in Accounting
on Aug 6th, 2016 | 0 comments
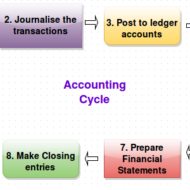
Financial statements have to be produced accurately at the end of the accounting period for tax purposes. An accounting period may be a month, a quarter of a year, or a whole year. The accounting cycle is the series of steps that take place in order to produce financial statements. A term that describes the steps when processing transactions (analyzing, journalizing, posting, preparing trial balances, adjusting, preparing financial statements) in a manual accounting system. Today many of the steps occur simultaneously when using accounting software. Following are the steps that complete an accounting cycle: Identify the transaction: This transaction could be the revenue from the sale of a product or a payment to another business for services. Analyze the transaction and how it is related to the accounting balance sheet. For example, determine which accounts are affected by the transaction and how they are affected. Record the transaction to a journal such as a sales journal. Journals are kept in chronological order and may be updated continuously, daily, or however often it is necessary. Record the transaction to the general ledger: Take all of your entries and categorize them by the account. Perform a trial balance: Debits and credits need to be equal at the end of an accounting cycle, so calculate the entries to ensure they match. Prepare adjustments: Just because entries are recognized, does not mean the work has been performed. Revenue can only be recognized when the work has been completed, so adjust the entries accordingly. Perform trial balance with adjustments: Take the adjustments from Step 6 and prepare a trial balance. If the debits and credits do not match, then you need to adjust them to make sure they do match. Prepare financial statements: From the adjusted trial balance, these corrected balances are used to prepare the financial statements. Close the accounts in preparation of the next accounting cycle. Revenues and expenses need to be closed out, which means they need to have zero balances. Balances are moved to the next cycle. Some Important Accounting Terms: Account A record in the general ledger that is used to collect and store similar information. For example, a company will have a Cash account in which every transaction involving cash is recorded. A company selling merchandise on credit will record these sales in a Sales account and in an Accounts Receivable account. Accounting Department Part of a company’s administration that is responsible for preparing the financial statements, maintaining the general ledger, paying bills, billing customers, payroll, cost accounting, financial analysis, and more. The head of the accounting department often has the title of controller. Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. For a corporation the equation is Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity. For a nonprofit organization the accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Net Assets. Because of double-entry accounting this equation should be in balance at all times. The accounting equation is expressed in the financial statement known as the balance sheet. Accounts Payable This current liability account will show the amount a company owes for items or services purchased on credit and for which there was not a promissory note. This account is often referred to as trade payables (as opposed to notes payable, interest payable, etc.) Accounts Receivable A current asset resulting from selling goods or services on credit (on account). Invoice terms such as (a) net 30 days or (b) 2/10, n/30 signify that a sale was made on account and was not a cash sale. Adjusting Entries Journal entries usually dated the last day of the accounting period to bring the balance sheet and income statement up to date on an accrual basis (as required by the matching principle and...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting
on Feb 24th, 2015 | 0 comments

What are known as Final Accounts? Trading, profit & loss account and balance sheet, all these three together, are called as final accounts. Final result of trading is known through Profit and Loss Account. Financial position is reflected by Balance Sheet. These are, usually, prepared at the close of the year hence known as final accounts. They serve the ultimate purpose of keeping accounts. Their purpose is to investigate the consequence of various incomes and expenses during the year and the resulting profit or loss. 1. Trading and Profit and Loss A/c is prepared to find out Profit or Loss. 2. Balance Sheet is prepared to find out financial position of a concern. Trading Account Trading refers buying and selling of goods. Trading A/c shows the result of buying and selling of goods. This account is prepared to find out the difference between the Selling prices and Cost price. Profit and Loss Account Trading account discloses Gross Profit or Gross Loss. Gross Profit is transferred to credit side of Profit and Loss A/c. Gross Loss is transferred to debit side of the Profit Loss Account. Thus Profit and Loss A/c is commenced. This Profit & Loss A/c reveals Net Profit or Net loss at a given time of accounting year. Trading Profit And Loss CMD from knoxbusiness Balance Sheet Trading A/c and Profit & Loss A/c reveals G.P. or G.L and N.P or N.L respectively; besides the Proprietor wants i. To know the total Assets invested in business ii. To know the Position of owner’s equity iii. To know the liabilities of business. Definition of Balance Sheet The Word ‘Balance Sheet’ is defined as “a Statement which sets out the Assets and Liabilities of a business firm and which serves to ascertain the financial position of the same on any particular date.” On the left hand side of this statement, the liabilities and capital are shown. On the right hand side, all the assets are shown. Therefore the two sides of the Balance sheet must always be equal. Capital arrives Assets exceeds the liabilities. BUY “ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS AND CONCEPTS” OBJECTIVES OF BALANCE SHEET: 1. It shows accurate financial position of a firm. 2. It is a gist of various transactions at a given period. 3. It clearly indicates, whether the firm has sufficient assents to repay its liabilities. 4. The accuracy of final accounts is verified by this statement 5. It shows the profit or Loss arrived through Profit & Loss A/c. PREPARATION OF FINAL ACCOUNTS Preparation of final account is the last stage of the accounting cycle. The basic objective of every firm maintaining the book of accounts is to find out the profit or loss in their business at the end of the year. Every businessman wishes to find out the financial position of his business firm as a whole during the particular period. In order to accomplish the objectives for the firm, it is essential to prepare final accounts which include Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. It is mandatory that final accounts have to be prepared, every year, in every business. Trading and profit & loss accounts are prepared, after all the accounts have been completely written and trial balance is extracted. Before preparing final accounts, it becomes obligatory to scritinize whether all the expenses and incomes for the year for which accounts are prepared have been duly provided for and included in the accounts. Form of Final Accounts: There is a standard format of final accounts only in the case of a limited company. There is no fixed prescribed format of financial accounts in the case of a proprietary concern and partnership...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Financial Management, Marketing, Strategy
on Sep 29th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is meant by Mergers and Acquisitions? This is a general term used to refer to the #amalgamation of companies. A merger is a combination of two companies to form a new company, while an acquisition is the purchase of one company by another in which no new company is formed. Mergers and acquisitions refers to the buying, selling and combining of different companies to aid a company in a specific industry to grow quickly without having to create another business entity. Growth due to Internal and #External Expansion: A business might grow either by #internal expansion or by external expansion. In the case of internal expansion, a firm grows progressively through procurement of new #assets, substitution of the technologically out-dated equipments and the setting up of new product line. But in external expansion, a firm secures a running business and grows overnight through corporate combinations. These combinations are in the form of mergers, acquisitions, amalgamations and takeovers and have now become important features of #corporate restructuring. Why Mergers & Acquisitions: Mergers and acquisitions are strategic decisions taken for boosting up company’s growth by augmenting its production and marketing operations. One of the main reasons that companies opt for a merger or acquisition is that, by conjoining business undertakings, performance will increase and costs will decrease. Essentially, a business will attempt to merge with another business that has complementary #strengths and weaknesses. Many M&A deals allow the #bidder to thrash future competition and gain a larger market share in its product’s market. Mergers or amalgamations may take two forms:- #Merger through Absorption:- An absorption is a combination of two or more companies into an ‘existing company’. All companies except one lose their identity in such a merger. Example: 1999 merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham, both firms ceased to exist and a new firm GlaxoSmithKline was created. #Merger through Consolidation:– A consolidation is a combination of two or more companies into a ‘new company’. In this form of merger, all companies are legally dissolved and a new entity is created. Here, the acquired company transfers its assets, #liabilities and shares to the acquiring company for cash or exchange of shares. A fundamental characteristic of merger is that the acquiring company (existing or new) assumes the #ownership of other companies and combines their operations with its own operations. Reverse Merger Is a deal facilitating a private company to become a public company. The deal enables private company by listing in a short time period. Occurs when a private company has strong prospects and is eager to raise financing, buys a publicly listed shell company. Usually the public one is one with, no business and limited assets Acquisitions and Takeovers #Reverse Takeover Acquisition usually refers to purchase of smaller firm by larger firm Sometimes, smaller firm acquire #management control of a larger / longer established company Keep its name for combined entity Friendly Acquisition Companies accomodate in negotiations Identical to merger of equals Cognizant to Acquire TriZetto, creating a fully-integrated healthcare technology and operations leadership. With more than $3 billion in combined healthcare revenue, Cognizant and TriZetto will serve nearly 245,000 healthcare providers. Hostile Acquisition Takeover target reluctant to be purchased If the #acquiree company has no prior knowledge of offer Hostile takeovers do turn friendly most of the times. Offer is usually upgraded for smooth acquisitions Benefits of Mergers and Acquisitions Greater Value Generation Generate Cost Efficiency #Economies of Scale Increase in Market Share Gain higher...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Quotes and Quotes Only, Training & Development
on Jul 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

Popular HR Quotes by Industry Experts and Management Scholars We have compiled 50 top notch hr quotes from doyens in the field of business and management that will sure fire inspire you with creative ideas. 1. “Great Vision Without Great People Is Irrelevant.” -Jim Collins, Good To Great 2. “Human Resources Isn’t A Thing We Do. It’s The Thing That Runs Our Business.” -Steve Wynn, Wynn Las Vegas 3. “You Need To Have A Collaborative Hiring Process.” -Steve Jobs, Apple 4. “You Can’t Teach Employees To Smile. They Have To Smile Before You Hire Them.” -Arte Nathan, Wynn Las Vegas 5. “Never Hire Someone Who Knows Less Than You Do About What He’s Hired To Do.” -Malcolm Forbes, Forbes Top 50 HR Quotes 6. “When Hiring Key Employees, There Are Only Two Qualities To Look For: Judgement And Taste. Almost Everything Else Can Be Bought By The Yard.” John W. Gardner 7. “Recently, I Was Asked If I Was Going To Fire An Employee Who Made A Mistake That Cost The Company $600,000. No, I Replied, I Just Spent $600,000 Training Him. Why Would I Want Somebody To Hire His Experience?” -Thomas John Watson Sr., Ibm 8. “It’s More Than Just Selling Pizzas. It’s Being A Good Fit For The Community. We Hire Based On The Betterment Of The Community As Much As Anything.” -Mark Starr, David’s Pizza. 9. “You Can Have The Best Strategy And The Best Building In The World, But If You Don’t Have The Hearts And Minds Of The People Who Work With You, None Of It Comes To Life.” -Renee West, Luxor And Excalibur Hotel 10. “I am convinced that nothing we do is more important than hiring and developing people. At the end of the day you bet on people, not on strategies.” -Lawrence Bossidy, Ge CURRENT TRENDS IN HRD 11. “Do Not Hire A Man Who Does Your Work For Money, But Him Who Does It For The Love Of It.” -Henry David Thoreau, Life Without Principle 12. “If You Think Hiring Professionals Is Expensive, Try Hiring Amateurs” -Anonymous 13. “The Key For Us, Number One, Has Always Been Hiring Very Smart People.” -Bill Gates, Microsoft 14. “Time Spent On Hiring Is Time Well Spent.” -Robert Half 15. “I Hire People Brighter Than Me And Then I Get Out Of Their Way” -Lee Iacocca, Ford 16. “You Cannot Push Anyone Up The Ladder Unless He Is Willing To Climb.” -Andrew Carnegie 17. “Management Is Nothing More Than Motivating Other People.” -Lee Iacocca, Ford 18. “There Are Few, If Any, Jobs In Which Ability Alone Is Sufficient. Needed, Also, Are Loyalty, Sincerity, Enthusiasm And Team Play.” -William B. Given, Jr. 19. “When People Go To Work, They Shouldn’t Have To Leave Their Hearts At Home.” -Betty Bender 20. “One Machine Can Do The Work Of Fifty Ordinary Men. No Machine Can Do The Work Of One Extraordinary Man.” -Elbert Hubbard 21. “To Find Joy In Work Is To Discover The Fountain Of Youth.” -Pearl S. Buck 22. “One Of The Symptoms Of An Approaching Nervous Breakdown Is The Belief That One’s Work Is Terribly Important.” -Bertrand Russell 23. “Opportunity Is Missed By Most People Because It Is Dressed In Overalls And Looks Like Work.” -Thomas A. Edison 24. “Far And Away The Best Prize That Life Offers Is The Chance To Work Hard At Work Worth Doing.” -Theodore Roosevelt 25. ”Being Busy Does Not Always Mean Real Work. The Object Of All Work Is Production Or Accomplishment And To Either Of These Ends There Must Be Forethought, System, Planning, Intelligence, And Honest Purpose, As Well As Perspiration. Seeming To Do Is Not Doing.” -Thomas A. Edison 26. “Going To Work For A Large Company Is Like...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Jun 25th, 2014 | 0 comments
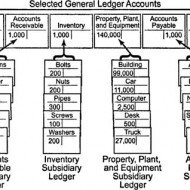
Ledger is a register with pages numbered consecutively. Each account is allotted one or more pages in the Ledger. If one page is completed, the account will be continued in the next page. An index of various accounts opened in the Ledger is given at the beginning of the Ledger for the purpose of easy reference. A general ledger is a complete record of financial transactions that holds account information needed to prepare financial statements, and includes accounts for assets, liabilities, owners’ equity, revenues and expenses. What is meant by Posting? Transactions recorded in the Journal and Subsidiary journal are transferred to the concerned accounts in the Ledger in a summarized and classified form. This process is called posting. “Interesting Statistics on Accounting The first book on double-entry accounting was written in 1494 by Italian mathematician and Franciscan friar Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli. Although double-entry bookkeeping had been around for centuries, Pacioli’s 27-page treatise on the subject has earned him the title “The Father of Modern Accounting. Accounting plays a major role in law enforcement. The FBI counts more than 1,400 accountants among its special agents. The state of New York gave its first certified public accountant (CPA) exam in 1896. Rules for posting: Separate account should be opened in the Ledger for posting transactions relating to separate persons, assets, expenses or losses as shown in the journal. The account concerned which has been debited in the journal should also be debited in the Ledger. However, a reference must be made of the other account which is to be credited in the journal. In other words, in the account to be debited, the name of the other account to be credited is entered in the debit side for giving a meaning to this posting. The debit posting is prefixed by the word ‘To’. Similarly, the account concerned which has been credited in the journal has to be credited in the Ledger, but a reference should be made to the other account which has been debited in the journal. This posting is prefixed by the word ‘By’. Advantages of keeping a Ledger: Ledger provides information regarding all transactions of a particular account whether it is personal a/c, Real a/c or nominal a/c. The final effect, of a series of transactions of a certain customer or a certain property or a certain expense is known at a glance. Ledger provides immediately the totality of certain dealings. E.g., total purchases, Total sales, total expenditure, on a specified head. What is a Ledger account? Give a Proforma of a Ledger account. A Ledger account is nothing but a summary statement of all transactions relating to a person, asset, expense or income, which have taken place during a given period of time showing their net effect. Proforma of a Ledger account: What are the methods of balancing the Ledger account? At the end of the each month or year or any specific day it is essential to determine the balance in an account. To do that, add the totals of both sides (Debit and credit sides) and find out the difference in both the sides. The difference in both the sides is ‘Balance’. If the Debit is greater than the credit side, it is a Debit balance or vice-versa. There are two methods: The bigger total is taken first and is written on both sides of the account. On the smaller side, the balance is Witten above the total next to the last entry on that side. This method is more commonly used. In another method, the totals are written on both sides, one side showing smaller amount and the other showing bigger amount. The difference is...










