Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Motivation, Video Lecturers
on Mar 17th, 2015 | 0 comments

THE BEST FINANCE DECISIONS EVERY ENTREPRENEUR MUST MAKE Tony Robbins is an American life coach and self-help author. He became well known through his infomercials and self-help books, Unlimited Power, Unleash the Power Within and Awaken the Giant Within. Tony Robbins is a catalyst for change and a strategist for success. He creates change in minutes, when normally it couldn’t be accomplished in years. An Inspiring Quote: “To effectively communicate, we must realize that we are all different in the way we perceive the world and use this understanding as a guide to our communication with others.” Tony Robbins is an entrepreneur, best-selling author, philanthropist and the nation’s #1 Life and Business Strategist. A recognized authority on the psychology of leadership, negotiations and organizational turnaround, he has served as an advisor to leaders around the world for more than 38 years. https://www.tonyrobbins.com/ https://www.youtube.com/tonyrobbinslive https://gumroad.com/l/wqbu...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Financial Management, Project Management, Startups
on Jul 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is a Startup Cost? Non-recurring costs associated with setting up a business, such as accountant’s fees, legal fees, registration charges, as well as advertising, promotional activities, and employee training. Also called startup expenses, preliminary expenses, or pre-opening expenses. Let me clarify that this discussion pertains to small and medium size enterprise startup costs and not about capital budgeting. Any project that an entrepreneur wishes to undertake has four factors to be considered. Men Material Machine Money Finance is the lifeblood of any business and to be successful, one must, inject sufficient capital into it. Many businesses fail because of under-capitalization. Seed Money Requirements To determine how much seed money you need to start, you must estimate the costs of doing business at least for the first year. Expenses may be categorized as ‘one-time costs’ such as the fee for incorporating your business or the price of a sign for your building. Some will be ‘ongoing costs’, such as the cost of utilities, inventory, insurance, etc. There is a pressing need for you to bring enough working capital to run the day-to-day business affairs. Without a projected fund flow statement and proposal, no bank or financial institution shall offer you long term loans to run the business. First of all, you need to write the business plan and ask yourself the following questions. Ask yourself these 20 questions to make sure you’re thinking about the right key business decisions: Why am I starting a business? What kind of business do I want? Who is my ideal customer? What products or services will my business provide? Am I prepared to spend the time and money needed to get my business started? What differentiates my business idea and the products or services I will provide from others in the market? Where will my business be located? How many employees will I need? What types of suppliers do I need? How much money do I need to get started? Will I need to get a loan? How soon will it take before my products or services are available? How long do I have until I start making a profit? Who is my competition? How will I price my product compared to my competition? How will I set up the legal structure of my business? What taxes do I need to pay? What kind of insurance do I need? How will I manage my business? How will I advertise my business? Courtesy – http://www.sba.gov/ See ‘Short Term Financing’ to know more about financing your business. The term finance sanctioned in the form of ‘Term Loan’ is required for Land and site development Building and civil works Plant and Machinery Installation expenses and Miscellaneous fixed assets which comprise vehicles, furniture and fixtures, office equipment, workshop and laboratory equipment, distribution of power and water supply etc. Expenditure on infrastructure facilities like water supply, power connection, roads, transportation etc., has to be particularly considered if the units are located in economically backward areas. Startup...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Business Management, Financial Accounting
on Jul 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
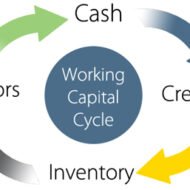
Understanding Working Capital: It is the life blood of business. Funds needed for the purchase of raw materials, payment of wages and other day-to-day expenses are known as working capital. It is part of the firm’s capital, which is being used for financing short-term operations. Hence, it may also be termed as Circulating Capital or Short-Term capital. “Working capital means current assets” –Mead, Malott and Field. “Any acquisition of funds which the current asset increases working capital, for, they are one and the same.” – J.S.mill Financial troubles and issues arise only when this entity called ‘working capital’ is not properly managed. Every successful company will hire a financial manager to deal with issues relating to finance while the CEO can look into matters relating to promotion of the product or service and the position of the company in the market. The ‘Sales Turnover or Sales Volume’ is the key issue you have to look into to gauge whether you have sufficient working capital to manage that big a volume for that particular period. You have to rotate your funds wisely keeping in mind the credit policies your company offers and the credits you may enjoy with your supplier, bank interest for the short-term loans etc. Concept of WC: Working capital implies excess of current assets over current liabilities. Funds invested in current assets is known as “Gross Working Capital.” The difference between current assets and current liabilities is known as “Net Working Capital.” What are the two types? Permanent or fixed: It is the minimum amount of current assets required for conducting the business operation. This capital will remain permanent in current assets and should be financed out of long-term funds. The amount varies from year to year, depending upon the growth of a company. Temporary or Variable: It is the amount of additional current assets required for a short period. It is needed to meet the seasonal demands at different times during a year. The capital can be temporary and should be financed out of short-term funds. The working capital starts decreasing when the peak season is over. Various Factors Influencing WC: Nature of business: Service oriented concerns like electricity; water supplies need limited working capital while a manufacturing concern requires sufficient working capital, since they have to maintain stock and debtors. Credit Policies: A company which allows credit to its customers shall need more amount while a company enjoying credit facilities from its suppliers will need lower amount of working capital. Manufacturing Process: Conversion of raw materials into finished goods is called manufacturing or production. Longer the process, higher the requirement of working capital. Rapidity of turnover: High rate of turnover requires low amount and lower and slow moving stocks need a larger amount of working capital. Say, jewelry shops have to maintain different types of designs calling for high working capital. Fast moving goods like grocery requires low working capital. Business cycle: Changes in economy has a say over the requirement of working capital. When a business is prosperous, it requires huge amount of capital; also during depression huge amount is needed for unsold stock and uncollected debts. Seasonal variation: Industries which are manufacturing and selling goods seasonally require large amount of working capital. Fluctuation of supply: Firms have to maintain large reserves of raw material in stores, to avoid uninterrupted production which needs large amount of working capital. Dividend policy: If a conservative dividend policy is followed by the management, the need for working capital can be met with the retained earnings, it consequently drains off large amounts from working capital pool. ...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Apr 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

Business Policies – Framing and Execution Business policies are the keystone in the arch of management and the life-blood for the successful functioning of business, because without well-laid down policies, there cannot be lasting improvements in the economic condition of the firm and labor-management relations. A policy is a positive declaration and a command to its followers. It translates the goals of an organization into selected routes and provides the general guidelines that prescribe and proscribe programmes, which in turn, dictate practices and procedure. Attainment of Objectives: Buisness policies are general statement of principles for the attainment of objectives which serve as a guide to action for the executives at different levels of management. They pave a broad way in which the sub-ordinates tread along towards accomplishing their objectives. Hierarchy: For each set of objectives at each level, there is a corresponding set of policies. The Board of Directors determine the basic overall corporate policiesThe top management decides on the executive corporate policiesManagers decide on the departments / divisional policiesMiddle managers handle the sectional policies Consistent Decisions contributing to the Objectives: The policies delimit the area within which a decision has to be made; however, they do allow some discretion on the part of the man on the firing line, otherwise, they would be mere rules. At the same time too much of discretion in policy matters may prove harmful to the accomplishment of organizational objectives and hence it is generally within limits. Mutual Application: Policies in general are meant for mutual application by sub ordinates. They are fabricated to suit a specific situation in which they are applied, for they cannot apply themselves. Unified Structure: Policies tend to predefine issues, avoid repeated analysis and give a unified structure to other types of plans, thus permitting managers to delegate authority while maintaining control. Policies for all Functional Areas: In a well-structured and managed organization, policies are framed for all functional levels of management. Corporate planningMarketingResearch and DevelopmentEngineeringManufacturingInventoryPurchasePhysical DistributionAccountingFinanceCostingAdvertisingPersonal SellingSpecial Promotion, are some areas that require clear-cut policies. Clear-Cut Guidelines: Policies serve an extremely useful purpose in that they avoid confusion and provide clear-cut guidelines. This enables the business to be carried on smoothly and often without break. They lead to better and maximum utilization of resources, human, financial and physical, by adhering to actions for...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Financial Management, Human Resource, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 30th, 2014 | 0 comments
What is Turnaround Strategy Distress signals start flying around when a particular company, whether multinational, corporate or medium sized, is subjected to financial pressure and is at the brink of bankruptcy. What was happening all along? No body knows and nobody wants to be held responsible. The CEO has to bear the brunt and alas, extermination! Aim of Turn-around Strategy: The overall aim of a turn around strategy is to bring back a firm to normalcy which has been under distress in terms of acceptable levels of profitability, solvency, liquidity and cash flow. Turn around strategies should be very carefully formulated so as to stabilize the firm in distress, i.e., to bring the company out of the hole and then go for long term planning. Turn around can be in the form of operational efficiency management, financial restructuring, marketing management or savings in the form of cost reduction or liquidity in the form of asset reduction. Facebook Marketing: A Step-by-Step to Your First 1000 Fans! Turn around to see what is around: We have seen so many such occurrences at the global level and micro level. Some companies rejuvenate like a phoenix bird from the ashes, some go haywire, and some dissolve into thin air. It all depends how well you handle the situation with either the help of an external expert consultant or you might want to go for joint venture or collaboration in order to save you skin from mounting interest payments or you right royally sell the company if somebody is ready to takeover. Either way you have to do something! “Turn around to see what is around”. Don’t see what you want to see See what has to be seen Change the CEO (He is the Ideal Victim!) Resurrect your employees’ confidence Cut down costs Look for Alternatives Lie low for Sometime(till the situation favors) Slowly capture the market by innovative Campaigns and ads Paint a new picture about your company Review your Mission and Vision statements Work on targets Bang on the right target customers and clients Strengthen your Channel of Distributors Go smooth with the bankers (You need them always!) Have confidence in yourself Crisis management is necessary Stress busters like yoga and meditation mandatory Evolve Strategies One step at a time (Slow and steady) Fear and Panic grips the organization in situations of crisis. So the first step would be to stay cool to assess the situation by calmly reviewing the damage with all the concerned people. The next step would be to stop the bleeding by cutting all unwanted costs, unnecessary overheads, and the final stage would be renaissance, recovery, renewal or by whatever name you want to call it, even if it means negative investment or profit. Proper Planning, Inventory Control, Strategic prepositions, Renewal of old strategies in accordance with the situation, Tightening finance controls, Defining the credit management limits, all these are precautionary measures which will hold you from falling into the danger of handling a crisis situation, as” recovery of damaged integrity is going to cost you more than ploughing back your profits....










