Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Dec 14th, 2016 | 0 comments

Income Tax and PAN Card Info What is meant by Income Tax? A percentage of income earned by an individual or a company (complying to Indian laws) is paid in the form of tax to the government. This is called Income Tax. This comes under Income Tax Act constituted by Parliament of India. Department of income tax operates under Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, Government of India. This is responsible for checking and collecting tax. Where should I pay Income Tax? Income tax should be paid to the I.T deparment. This is called income tax filing which is done at the end of July every year. What is the period for which a person’s income is taken into account for purpose of Income Tax? The income earned from April 1st to March 31st is considered for calculating income tax. This period is called a financial year. For example April 1, 2015 to March 31, 2016 is a financial year. This is also called previous year. What is an assessment year? The 12 month period that comes after the previous year is called an assessment year. This is the period to file income tax return for the previous year. For example, for the financial year 2015-16, the assessment year is 2016-17. During this period, a person files his return for the income earned in the previous year. How to file income-tax returns online What is PAN Number or Permanent Acount Number? PAN is a ten digit number issued by the Income Tax deparment. It also serves as a valid identity proof for an Indian citizen. PAN number is demanded at many places now-a-days. When you file income tax returns When you open a bank account or Demat account It is useful in applying telephone connection and credit card When you want to register for service tax and sales tax When you buy or sell a vehicle When you deposit or withdraw money to the tune of Rs.50,000 in the bank or post office, PAN is a must If you want to invest in mutual funds If you are buying a property worth more than 5 Lakhs When you exchange large volume of foreign currency (over and above Rs.25,000), you need to submit your PAN CARD. Even when you buy GOLD , giving your PAN number has become mandatory after the DEMONETIZATION EFFORTS taken by the government recently on November 8, 2016. PAN card Dont’s… Same person having more than one PAN card is an offence. You have to submit any one card to the income tax department and update your info. You can be charged a fine of upto Rs.10,000 if you are found to have more than one PAN card. If somebody puts the PAN card to mis-use he might be fined and subject to imprisonment too. You can view your PAN card details in their website. If you apply for PAN card through private agents, kindly check whether your details are updated in the government website. Issue of PAN card PAN card issuing has been made very simple. You will be asked to fill up FORM 49-A and attach your address proof (Aadhar card or Ration card). The form can be downloaded from the following addresses online: www.tin-nsdl.com http://www.incometaxindia.gov.in/Pages/form-pan.aspx Also you get these forms issued by the IT PAN and TIN service centres. Having a PAN card doesn’t mean that you have to pay Income Tax. It is to facilitate people to pay Income Tax when their income levels warrants for paying tax. A Complete Tutorial on Financial Markets and...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, How To, Human Resource, Operations Management, Training & Development
on Mar 15th, 2015 | 0 comments

Productivity Analysis: Productivity is defined in terms of utilization of resources, like material and labor or it is the ratio of output to input. For example, productivity of labor can be measured as units produced per labor hour worked. It is closely associated with quality, technology and profitability. Now you will be able to understand why there is a strong emphasis on productivity improvement in a competitive business environment. It can be calculated at firm level, at industry level, at national level and at international level. That is what we call as GDP, NDP, and PPP. Gross Domestic Product – ‘GDP’: The monetary value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period, though GDP is usually calculated on an annual basis. Net Domestic Product – ‘NDP’: An annual measure of the economic output of a nation that is adjusted to account for depreciation, calculated by subtracting depreciation from the gross domestic product (GDP). Purchasing Power Parity – ‘PPP’: An economic theory that estimates the amount of adjustment needed on the exchange rate between countries in order for the exchange to be equivalent to each currency’s purchasing power. Efficiency can be improved by (a) Controlling inputs, (b) Improving process so that the same input yields higher output, and (c) By improvement of technology. Factor Productivity: When it is measured individually for each input resource to the production process it is called factor or partial productivity. Total Productivity: When it is measured for all the factors of production together, it is called total factor productivity. What are the types of Productivity Analysis? 1. Trend analysis: Studying productivity changes for the firm over a period of time. 2. Horizontal analysis: Studying efficiency in comparison with other firms of same size and involved in similar business. 3. Vertical analysis: Studying output in comparison with other industries and other firms of different sizes in the same industry. 4. Budgetary analysis: Setting up a norm for productivity for a future period as budget and planning strategies to achieve it. FACTORS AFFECTING PRODUCTIVITY 1. Capital/labor ratio: It is a measure of whether enough investment is being made in plant, machinery, and tools to make effective use of labor hours. 2. Scarcity of some resources: Resources such as energy, water and number of metals will create problems. 3. Work-force changes: Change in work-force affect productivity to a larger extent, because of the labor turnover. 4. Innovations and technology: This is the major cause of increasing productivity problems. 5. Regulatory effects: These impose substantial limitations on some firms. 6. Bargaining power: Bargaining power of organized labor to command wage has a detrimental effect. 7. Managerial factors: The planning and strategic skills of a manager play a big role in boosting the productivity of an organization. 8. Quality of work life: It is a term that describes the organizational culture, and the extent to which it motivates and satisfies employees. Here are the top 10 productivity killers in the workplace you’ll want to watch out for: 1. Cell phone/texting 2. Gossip 3. The internet 4. Social media 5. Snack breaks or smoke breaks 6. Noisy coworkers 7. Meetings 8. Email 9. Coworkers dropping by 10. Coworkers putting calls on...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Accounting, How To, Project Management
on Nov 21st, 2014 | 0 comments

These article-embeds focus on the real estate scenario both in the US and India and how relaxation in Foreign Direct Investment Policies has brought about a sea change in the minds of foreign investors on viewing India as one of the major sources of potential investment. And most importantly real estate in India is in a boom thanks to the constant urbanization and interest of NRI people who want to invest in properties in big Indian cities like Mumbai, Cochin, Pune, Bangalore and Chennai. Some light is also thrown on how to handle the capital gains when a property is sold. One has to be aware of the tax implications that arise while selling a property and the proceeds have to be properly accounted for. Real Estate looks enterprising in India and always has been so since people of our country treat land and gold as dependable assets. Owning a house or a property is a status symbol too and people save money to buy land and build their dream houses. This saving tendency has supported the growth of our economy very well and has rather saved it from tumbling down unlike what happened in the recent recession in the US. Some Interesting Real Estate Quotes to keep you in Good Humor: “It is a comfortable feeling to know that you stand on your own ground. Land is about the only thing that can’t fly away.” ~Anthony Trollope “The best investment on earth is earth.” ~Louis Glickman “He is not a full man who does not own a piece of land.” ~Hebrew Proverb “A man complained that on his way home to dinner he had every day to pass through that long field of his neighbor’s. I advised him to buy it, and it would never seem long again.” ~Ralph Waldo Emerson “As long as you have more cash flowing in than flowing out, your investment is a good investment.” Robert Kiyosaki Read and enjoy the following articles: What To Expect From The Real Estate Market In 2014 Focus of Overseas Investors on Indian Real Estate Market How to save capital gain taxes in real estate? UDEMY, the educational platform is offering real estate courses at a big discount and I reckon the following courses would help real estate brokers and agents to hone their skills in terms of online presence and marketing. Gain Leads and Colleagues with a Real Estate Website/Blog Creative Real Estate Investing & Flipping...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Economics, Principles of Management, Strategy, Technology
on Mar 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
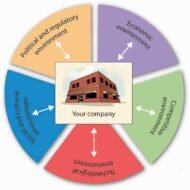
Technological Impact on Business Environment and Society The tremendous technological growth that is being witnessed is made possible through extensive programmes of technological research being conducted by many types of researchers working within universities, business, and non-profit research organizations. Technological developments are strong and all pervasive forces of the business environment. Technology is the scientific knowledge to practical problems. Technology feeds on itself and it affects business in two major ways: Through its impact on society in generalThrough its direct influence on business operations and activities. Technology and Economic Growth: Technology affects society. In fact, we feel its effect in our everyday lives. It affects economic growth, our standard of living and our culture. However, some of the effects of technology are highly beneficial and some detrimental. These effects on members of the society may in turn affect business practices. We are surrounded by so much of technology, that we take it for granted and usually do not realize how much it affects us until we have to do without electricity, water, transport or telephone. Technological developments have raised the standard of living. In spite of inflationary pressure and considerably a high degree of unemployment, generally families eat better, wear a wider variety of clothing, and live in more comfortable homes. Technology and Lifestyle: Technology also influences basic aspects of our culture, including religion, education, mobility, health care, art, language, laws and their enforcement. For example, technological advances in health care allow physicians to treat their patients in a virtual environment through video conferencing, which again is helpful in legal environment too for the judges to proceed with investigations on hard core criminals, who need not be produced before the court for security reasons. Creative Destruction: Every new technology is a force involved in creative destruction. Say, television hurts movies, synthetic fibers are considered rival for cotton fiber. The discovery of new technology even sometimes affects economic growth-TV with its high entertainment value takes away productive hours of mankind. Each new technology creates major long term consequences, which are not always foreseeable. How do you justify nations spending more money to develop missiles, nuclear weapons and bombs for the sake of security? Developing nations have to buy technology from foreign countries, as they are not resourceful in terms of capital needed for Research and Development, expertise, patents, licenses, and equipments and so on. This transfer of technology involves huge costs as a result of which a vicious circle is formed, in which weak technology creates dependence and dependence creates weakness. Conserve, Reduce, Recycle: The recent trend can be enumerated through this slogan, “Conserve, reduce and recycle”. The stress today is on clean production measures, advanced robotics, zero-emition vehicles, material recycling and alternative fuels and materials. This change towards love for environment by the technologists is a sure sign of positive...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Economics, International Business, Principles of Management, Technology
on Mar 26th, 2014 | 0 comments

Transfer of Technology- Commercialisation Vs.Benefit The total influx of technology in underdeveloped countries is from the advanced capitalist countries for obvious reasons, which will be the highlight of this discussion. Multinational corporations play a vital part in technology transfer, the motive being profit maximization for the parent company through their subsidiaries. These corporations act as the principal instrument of technology transfer, either through their subsidiaries or through contractual agreements made with developing countries. The idea is to bring mechanized processes and equipments that are not locally available. Dominance of Technology Supplier: The technology supplier usually takes the upper hand owing to his monopolistic strength that arises from the patent protection for differentiated products and processes. Very often, the terms and conditions of transfer are arbitrarily settled under highly imperfect market conditions by the technology supplying multinationals. Advanced nations have the advantages of reduced population density, even distribution of national wealth, high standard of living, more infusion of capital into research and development, availability of skilled personnel inclined towards research etc. Dependency of Developing Nations: Developing nations on the other hand are subject to the pressures of high population density, uneven distribution of economic wealth (poor people become more poor and the rich even richer), moderate or low living standards etc. Capital drain occurs due to heavy borrowings from the World Bank which leads to increase in the social overheads. In such a situation, it is next to impossible for a developing nation to pump capital into activities concerning research. Bargaining Power of Developing Nations: The bargaining power of developing nations is weak, as they have no access to information about alternate technologies and their sources nor the necessary infrastructure to evaluate the appropriateness of equipments, intermediates and processes. Moreover, the large part of the influx of technology in developing countries is in response to the policy of industrialization through import substitution. Transfer of technology from the developed to the underdeveloped countries is made in a number of ways. They are classified into two broad categories, viz., direct mechanism and indirect mechanism. The direct mechanism includes transfer of technology through banks, journals, industrial fairs, technical co-operation, movement of skilled people etc. Here there is a choice for the developing nation to select the appropriate technology that best suits their requirement. However, this is not the principal form of technology transfer that advanced nations would prefer. Price of Technology: The indirect mechanism implies technology transfer in a “package” or a “bundle” containing technology-embodying equipments, industrial properties like patents and trademark, skill, equity capital, etc. In this system, a local enterprise negotiates with multinational corporations for transport of the required elements of technology, and the terms and conditions are settled through a process of commercial transaction. Since the trading partners are unequal, the terms of contract are invariably restrictive and the price extended for the technology unreasonably high. All the underdeveloped countries, which have opted for growth along the classical path of capitalist development, are in a position to invite multinational corporations, if for no other reason than at least for the diffusion of...










