Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments
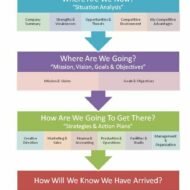
The Management Planning Process We have heard of “Master Plans” being structured and engineered to give astounding results that is purely systematic in approach and masterly in execution. Planning facilitates to make use of the opportunities that are available in the environment to make it to the top. Opportunity Analysis is nothing but, an awareness of the factors in the external environment; understanding of the strength and weaknesses of the organization. This is the first step of planning where we have to scrutinize the market, competition, customers’ preferences, tastes, our strengths and weaknesses. Establishing Objectives is another criterion that ensures “Where we want to be, and what we want to accomplish and when”. What are Objectives? Objectives are set for the organization and each subordinate is also entrusted with them. Objectives lay emphasis on goal setting which normally emanates from the top, but it may also originate from the bottom. Management by objectives is a great concept that involves all the employees working for the organization to be a part of goal setting and decision making. Planning Premises: Premises are “Assumptions” about the ‘environment.’ It involves identification of critical factors of the environment that affect the planning. Examples of critical factors are government policies, tax rates, business cycle development, economic indicators, economic forecasts etc. No body can precisely predict the environment factors precisely and make an accurate forecast. However one can fairly predict the critical factors required for the plan. Identifying Alternatives is very significant in a corporate business environment as every plan has got a set of alternative course of action. A reasonable number of alternatives can be developed for a plan. Evaluating Alternatives and Selecting the Best: A reasonable number of alternatives can be evaluated on the basis of the principle of limiting factor. The limiting factors may be costs, time, manpower and other resources. By applying techniques of operations research, every alternative can be evaluated. For e. g. alternative ‘A’ may benefit the organization in the short term but may be more expensive and alternative ‘B’ may benefit in the long run but may be less expensive. If one wants to earn immediate profits by spending more money he can choose alternative ‘A’. If the limiting factor is cost, he is forced to choose alternate plan ‘B’. Planning is not complete with selecting the best alternative; a set of derivative plans are developed to support the basic plan. For example an educational institution might like to own a fleet of buses, for which derivative plans for selection has to be made- training of drivers and maintenance staff are supportive plans for the main plan-procurement of buses. Developing budgets completes the planning course of action and budget is referred in financial terms and they are required to control the plans. Planning is the Prime Function: Planning is the prime function of all as it precedes all functions. 1. The objectives must be clear, verifiable and attainable. 2. Planning premises are vital to the success of planning as they supply information related to future like probable competitive behavior, general economic conditions, capital and material availability, government control etc. 3. All the critical factors are clearly and thoroughly analyzed and taken into consideration. One should be able to identify clearly the critical factors that limit the attainment of the goal. It could be costs, time, manpower or any other resources. 4. In a practical business situation, one should be clearer in identifying these factors, only then the selection of the best alternative is possible. 5. Any decision taken in a plan is valid for a particular period i.e., the plan may be short term or long-term, the commitment principle...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Nature of Organizational Planning What is Planning? “Planning is an intellectual process, the conscious determination of courses of action, and is a continuous process of decision making with built in flexibility.”- Herold Koonz and Weirich Planning is the most basic and primary of all management functions on the premise of which other functions evolve. It would be appropriate to compare planning to the basement or foundation of a building upon which the entire system rests. Planning bridges the gap from where we are to where we want to go. Planning involves selecting the best objectives and deciding on the suitable course of action. When we talk about planning, control is another entity that tags along like inseparable two-sides of a coin. Without planning there is no control and without control planning becomes meaningless. NATURE OF PLANNING: Prime function of management: Planning is the key to all other functions of management like organizing, leading, staffing and controlling. Is a continuous process: Plans need periodic review in the wake of external environment and internal resource potential and thus is a continuous process. Is an intellectual process: What is to be done, when, who and how are the very important questions that loom before a manager before making every decision. He has to use his intellect in order to make the right plans before acting. Is all pervasive: It penetrates right from the top to the bottom level of management, but it is the responsibility of the managers or executives at the top level to make the right moves at the right time. Is flexible: One has to understand that flexibility is restricted when it comes to irretrievable costs already incurred in fixed assets, training, advertising etc. Is goal oriented: Planning starts with setting up of objectives and completely goal oriented. TYPES OF PLANS: Purpose or Missions: Basic task of an organization. For example, teaching and research can be attributed as the basic function of an educational institution; the purpose of business is to produce, distribute goods and make a surplus. Objectives: These are the goals that have to be accomplished by the organization. Corporate companies chart out their production plan well in advance to meet the requirements on time. For this they break the objectives into short term goals i.e., for a quarter based on the sales forecast. This kind of planning gives clarity and direction for the production team to achieve the goals. Strategies: These are the set of action plans designed in order to achieve the future objectives backed up by long term perspective in the wake of environmental analysis and give direction in which the resources have to be channelized. Policies: These are basically the guideline books that direct the course of the organization’s function as what to do and what not to-do. They see to that the decisions made fall well within certain boundaries in order to ensure fair and equitable treatment to all the employees. HR policies govern all the functions related to pay, promotion and other disciplinary mechanisms related to the work force. Procedures: They are programmes designed to carry out the activities of the organization in a specified manner. The procedures for placing a purchase order, payment collection etc., Programmes: A programme is the sum total of goals, policies, procedures, rules, task etc., For example, new product development may be cited as a major programme while promotional campaign may be cited as a supporting programme. Budget: No plan is feasible without a budget allocated to it. A budget is a numberised programme and more of a control device. Revenue budgets, expense budgets, production budgets to name a few. Zero base budget: This kind of budget does not take into account the previous year’s performance record or budget but treats every progarmme afresh and starts working from ground up. Each programme is treated as a separate...




