Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
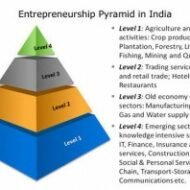
Entrepreneurship in Developing Economies Entrepreneurial development is a complex process of change. It has been recognized as an important ingredient of economic development. The development of entrepreneurial activity depends upon the closely interlinked economic, social, cultural, religious and psychological variables. Developing countries of late have adopted a deliberate policy of promoting and encouraging small enterprises as a strategy, for the overall development of their countries. Practical Problems Faced by Developing Countries The numerous problems confronted by developing countries such as, a high rate of population growth, a relatively low rate of economic growth, a low level of capital income with nearly fifty percent of the population subsisting below the poverty line and mounting increase in the figures of educated unemployed-all these check the growth of entrepreneurial activities. Countries have to plan realistically, mobilize and harness resources, have control over factors of growth and development and give direction to the development process. Naturally then, the national and economic goals will be focused towards: Production and productivity to be increased in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors Maximum harnessing and utilization of material and human resources Solving problems of unemployment Having a check on population growth Equitable distribution of wealth and income To increase the purchasing power parity To increase the gross national product To increase the real per capita income Improving the quality of life Industrial Development The larger scope and potential to achieve these goals lie in the development of the industrial sector of the national economy, and the only alternative to raise the level of living is development of industries. Here, we are not merely concerned with certain quantum of growth and development in the industrial field. Theoretically, the desired quantum of industrial development could be supported by a few large investments and capital intensive units run by a small number of big entrepreneurs. But what is envisaged is to have the same quantum of industrial development with a wider spread consisting of large number of small entrepreneurs all over the country. This would result in development of small scale and tiny sector industries all over the country and would generate employment opportunities to the educated unemployed, skilled people and other potential entrepreneurs from various segments of the society. Scenario of Asian Countries Most of the Asian countries like India and China are encouraging and promoting entrepreneurial development leading to industrial and economic development. India is now a hot spot for automobiles and its accessories. Being a cost-effective core market for auto components sourcing for global auto makers, the automotive sector is a potential sector for entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are risk bearers, find resources and fill market gaps that would be missed by larger, more bureaucratic organizations. Entrepreneurs improve the social welfare of a country by harnessing dormant, previously overlooked talent. Surplus manpower which is considered a great liability can be converted into assets once those with potential are selectively groomed for self-employment and enterprise formation, leading to further job...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Management, Principles of Management, Project Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
What is Business Risk? It is a term that explains the difference between the expectation of return on investment and actual realization. In CAPITAL BUDGETING, several alternatives of investments are examined before taking an investment decision and only then the Managing Director of the firm along with financial executives gear up for investing in a project that is sound and feasible. Even then the project may not become viable owing to the fluctuations in the economic environment. Money Manipulation So, the million dollar question arises, whether to invest and if invested, will it fetch me profit? See, you cannot have the cake and eat it too. Risk factor prevails in all kinds of environment and we try to over react in a business arena since it involves huge investments. But remember, MONEY WILL MULTIPLY IF YOU MANIPULATE IT WITH CARE. Business firms commit large sums of money each year for capital expenditure. It is therefore essential that a careful FINANCIAL APPRAISAL of each and every project which involves large investments is carried out before acceptance or execution of the project. These capital budgeting decisions generally fall under the consideration of highest level of management. Factors of risk to be considered before investing: Time value of money Pay back period Rate of return on investment(ROI) Uncertainties in the market Cost of debt Cost of equity Cost of retained earnings Factors to be monitored after investing: Maximising profit after taxes Maximizing earnings per share Maintaining the share prices Issue of dividends Ensuring management control Financial structuring Cost of capital refers to the opportunity cost of the funds to the firm I. e., the return on investment to the firm had it invested these funds elsewhere. Servicing the debt and Danger of Insolvency While making the decisions regarding investment and financing, the Finance Manager seeks to achieve the right balance between risk and return. If the firm borrows heavily to finance its operations, then the surplus generated out of operations should be sufficient to “SERVICE THE DEBT” in the form of interest and principal payments. The surplus would be greatly reduced to the owners as there would be heavy Debt Servicing. If things do not work out as planned, the situation becomes worse, as the firm will not be in a position to meet its obligations and is even exposed to the “DANGER OF INSOLVENCY“. Working Capital Management Considering all these factors, we have to come to the conclusion that FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT is like the BACKBONE of a business firm and WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT will be the blood flow infused into the body. Risks are inherent in a business environment whose management is quite possible with the right kind of farsightedness and planning. Luck does not favor anybody who is poor in planning and lack hard...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments

What forms the Basis for your Investment Decisions? Profit seeking is the ultimate aim of corporate management and the finance manager acts as the anchor point of the management structure. He has to provide specific inputs into the decision-making process, with respect to profitability. Corporate Investment Decisions Cost control What are the Cost Centres? It is the finance manager’s responsibility to have an eagle’s eye on rising costs by continuously monitoring the cost centers of his organization. Production department where there is always a need for additional resources or inflow of funds, should be his first target of contol. Costs are incurred by each and every department of an organization, namely, the production, marketing, personnel and of course finance and accounting. It is a difficult task to control the rising costs. That is the reason why, big corporate companies go for annual budget formulation at the start of the year and reformulates the finance plan by comparing actual with the projected figures. This kind of evaluation helps the firm to fix responsibilities for various centers of operation. Resource Allocation A finance manager is the first person to recognize rising costs for supplies or production, and he can make immediate recommendations to the management to bring back costs under control. While cost control talks about allocating resources to different responsibility centers in the desired proportion, cost reduction focuses on conserving the resources. Cost reduction can be achieved through modifying product and process designs, cutting down throughput time, doubling labor productivity, mass customization, standardistion etc., Pricing Price Fixation It is always a joint venture between marketing and finance departments when it comes to price fixation of products, product lines and services. Pricing decisions are important in that, they affect market demand and the company’s competitive stand in the market. Pricing strategies have to be evolved in the wake of existing competitor strategies and market preference. The demand forecast is the prerequisite factor of the production process and in-depth market analysis and understanding is inevitable on the part of the executives. Future Levels of Profit The finance manager is also responsible for charting out the future levels of profit, based on the relevant data available. He has to consider the current costs, likely increase in costs and likely changes in the ability of the firm to sell its products at the established selling prices. So, it becomes clear that, such market evaluation cannot be periodical, as the market is highly dynamic and has to be done in a day-to-day basis. Before a firm commences a project, its discounted future fund flow and expected profits must be ascertained which will serve as a basis for comparison. Risk versus Return: Investment decisions always are risky as the gestation period of invested funds is very long and not to return immediately. Further, the firm has to calculate the time period in which its initial investment can be recovered and the feasibility of the rate of return on its investment. Fund Management The finance manager is engaged in activities like, mobilization of funds, deployment of funds, and control over the use of funds and also he is to evaluate the risk return trade-off. Profit maximization is the fundamental objective of any organization and the finance manager plays a key role in restructuring the financial philosophy of a firm to take it to greater...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Operations Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
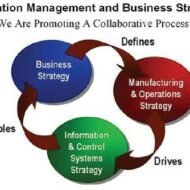
The management of conversion or transformation process which accepts inputs and delivers usable goods and services is what is called “operations management.” The inputs may be in the form of, capital, material, labor, technology, information, machines etc. The process takes place in an effective and efficient manner through operations planning, design, management and control. Don’t forget to download the 3 page Project Planner Printable at the end of this post 👇🏻 Absolutely Free Earlier it was called, production or manufacturing management. Since operation is a general term in a productive environment whose output may be goods or services, the term operations management has become more appropriate. The Aim of a Good Operational Management Would be High level of productivityCompetitive cost and qualityTimely deliveryProducing goods as per the requirements of the consumer, that is customer oriented.Flexibility and responsiveness in the production of goods and services Production or operation in the three important sectors of an economy, namely, agriculture, industry and service, creates national wealth and serves as an index for the growth of that economy. One has to understand the link between operations management and other functional areas to appreciate its scope. The goals of the operations strategy has to necessarily be in tandem with the overall corporate strategy to accomplish the goals of a firm. Scope of Operations Management From marketing department, cues regarding customer preference and market segmentation in terms of product, price and volume are supplied to the production department, based on which the production planning is concluded. From Research and development comes the product design and process technology. Human resource is an integral part of production process and also a crucial input. Man power planning by the human resource department plays a major role in recruiting, selecting, training, evaluating and empowering labor force. Operations Strategy The great diversity in products and services available in the market should be taken into consideration before deciding on your operations strategy. At one end we have custom made products that are designed and manufactured to suit the specific needs of the consumers. For instance, custom made shoes, shirts, suits, furniture etc. Here the emphasis is on quality and delivery where the customer is not very much bothered about the price. At the other end manufacturers go for highly standardized products that are available “off the shelf.” Say, home appliances, detergents, soaps etc., here the product differentiation is very minimal and the focus is on competitive pricing as the material is available in plenty. Economy of Scale A customized product would require a manufacturing set up that can handle a wide variety of general products. The sequence of operations for each product would vary in the manufacturing system making a customized product. So, a process oriented manufacturing system is designed, where similar facilities doing similar operations are grouped together and departmentalized. Standardized products go for a product focused manufacturing system, to reduce the “through put” time as large volumes are required. To be cost effective, each product should have a dedicated line of production to take advantage of the “economy of scale.” Intermediate types of products also find their place in the market and they are produced in a production layout that has a mix of product and process orientation. Here a whole range of products and services are created for the benefit of the customers. In a long term basis, manufacturers should aim to develop new technology, environmentally viable products, increase R and D activity, update skills of work force and managers and focus on development of new products, process and innovations....

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Feb 13th, 2014 | 0 comments

The purpose of accounting is to provide the information that is needed for sound economic decision making. The main purpose of financial accounting is to prepare financial reports that provide information about a firm’s performance to external parties such as investors, creditors, and tax authorities.










