Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments
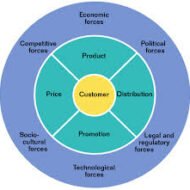
Key Components of Marketing System The core marketing system of a company comprises the suppliers, company, marketing intermediaries and target customers. The success of the company is also affected by competitor’s presence and other segments of public. The management has to watch and plan for all these factors to serve and satisfy the specified set of needs of a chosen target market. Supplier Selection: A company has to choose suppliers who offer the best mix of quality, delivery schedule, guarantee and low cost. Say, a firm involved in manufacturing confectioneries has to procure sugar, cocoa, caramel, milk powder; Labor, equipment, fuel, electricity and other factors of production are also to be obtained. If the company’s product has a good market, it can opt for continuous production. If it is a growing firm, it cannot go for voluminous production, but only supply goods against confirmed orders. In either case, the choice of suppliers is determined by one major factor called ‘cost’. Of course, one can never compromise on quality and so the company has to decide whether to purchase the inputs or make its own. Pic Courtesy : 5 Steps to Successful Supplier Selection The relationship of a company with the suppliers should be of a long-term nature, since any sudden change in the supplier’s environment will have a substantial impact on the company’s marketing operations. Sudden supply shortages, labor strikes and other events can interfere with the fulfillment of delivery promises to customers. This will result in sales decline in the short run and loss of goodwill in the long run. Back orders lead to loss of customers and in course of time their trust. The business firms must plan for alternate source of supply to avoid the risk of over-dependence on any one source of supplier. Company The marketing department has to work in tandem with the other departments of the company namely, finance, production, personnel and research and development, while designing and implementing its marketing plans. Finance department – has to be consulted regarding the availability and deployment of funds to carry out the marketing plans. Production department – to gauge market demand and to decide on the supply of products based on demand. R and D – new product development. Equally important is Digital Marketing which is considered to be an integral part of your promotional activities – What you are seeing above is a depiction of tools that help you in marketing your products online. Marketing intermediaries: Channel members are the link between the company and the customers. Agents and middlemen find customers who are wholesalers or retailers to take on the title and sell the merchandise. Also there are physical distribution firms who assist in stocking and moving goods from the warehouse to the destinations. The marketing executives have to deal with these intermediaries prudently in order to enhance the operational efficiency of the marketing function. Logistic firms, shippers and airliners help to move the goods from one location to another. Competitors: All the business firms in a particular market segment vie for the same resources and customers. A car manufacturing company in an automobile industry has to compete with other car manufacturers as well as with two wheelers. This implies that competition may come in different forms and each company has to identify potential threat from competitors, study their activities and capture their moves to win over the competition. Public: A company has to keep a close watch on people’s preferences to satisfy their requirements and also it is expected to give back something to the society in the form of social welfare measures. Employees belonging to different culture groups with differing attitudes,...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments

What forms the Basis for your Investment Decisions? Profit seeking is the ultimate aim of corporate management and the finance manager acts as the anchor point of the management structure. He has to provide specific inputs into the decision-making process, with respect to profitability. Corporate Investment Decisions Cost control What are the Cost Centres? It is the finance manager’s responsibility to have an eagle’s eye on rising costs by continuously monitoring the cost centers of his organization. Production department where there is always a need for additional resources or inflow of funds, should be his first target of contol. Costs are incurred by each and every department of an organization, namely, the production, marketing, personnel and of course finance and accounting. It is a difficult task to control the rising costs. That is the reason why, big corporate companies go for annual budget formulation at the start of the year and reformulates the finance plan by comparing actual with the projected figures. This kind of evaluation helps the firm to fix responsibilities for various centers of operation. Resource Allocation A finance manager is the first person to recognize rising costs for supplies or production, and he can make immediate recommendations to the management to bring back costs under control. While cost control talks about allocating resources to different responsibility centers in the desired proportion, cost reduction focuses on conserving the resources. Cost reduction can be achieved through modifying product and process designs, cutting down throughput time, doubling labor productivity, mass customization, standardistion etc., Pricing Price Fixation It is always a joint venture between marketing and finance departments when it comes to price fixation of products, product lines and services. Pricing decisions are important in that, they affect market demand and the company’s competitive stand in the market. Pricing strategies have to be evolved in the wake of existing competitor strategies and market preference. The demand forecast is the prerequisite factor of the production process and in-depth market analysis and understanding is inevitable on the part of the executives. Future Levels of Profit The finance manager is also responsible for charting out the future levels of profit, based on the relevant data available. He has to consider the current costs, likely increase in costs and likely changes in the ability of the firm to sell its products at the established selling prices. So, it becomes clear that, such market evaluation cannot be periodical, as the market is highly dynamic and has to be done in a day-to-day basis. Before a firm commences a project, its discounted future fund flow and expected profits must be ascertained which will serve as a basis for comparison. Risk versus Return: Investment decisions always are risky as the gestation period of invested funds is very long and not to return immediately. Further, the firm has to calculate the time period in which its initial investment can be recovered and the feasibility of the rate of return on its investment. Fund Management The finance manager is engaged in activities like, mobilization of funds, deployment of funds, and control over the use of funds and also he is to evaluate the risk return trade-off. Profit maximization is the fundamental objective of any organization and the finance manager plays a key role in restructuring the financial philosophy of a firm to take it to greater...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Strategy
on Feb 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
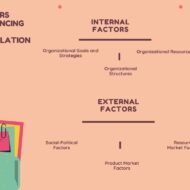
The basic factors that influence policy formulation are 1. The objectives of a business firm 2. Its management structure 3. Economic and financial resources available to it at a particular point of time 4. Attitudes, social values and norms of the top management 5. Fiscal and monetary policies of the government 6. Policies of sister concerns and business associations 7. Government regulations and control measures 8. Public opinion and expectations from business etc. You can never evade your responsibility towards the society and your policies must incorporate statements that reflect your interest in the welfare of the society. In corporate business environment, where voluminous business activity is carried on, corporations have very well understood the fact that, acquisition and utilization of resources from the society has to be repaid in the form of contributions to societal welfare. Otherwise their image might get tarnished. Moral and ethical values of a society also influence the mind set of business persons. In countries like India, where people ardently follow traditions and customs, a business person hailing from such a family will definitely try to maintain minimum ethical standards both in personal as well as business environments. Policy Aspects: Business policies cover all the functional areas such as production, marketing, personnel and finance aspects. Major policies pertaining to overall objectives, procedures and control affect the organization as a whole. Minor policies on the other hand, cover relationship in a segment of an organization, with considerable emphasis on details and procedures. Such policies are an outgrowth of major policies and preserve their unity of purpose. They meet the day-to-day requirements of the departments and are generally decided at the sectional and departmental levels. Various Corporate Policies: Strategic business policies cover aspects such as product-mix, promotion-mix, market-mix, administrative policies etc.; HR policies cover a wide range of aspects such as pay, promotions, recruitment, selection, induction, training and development, pension, disciplinary action, quality of work life and so on. So, to attain clear-cut objectives, firms need related business policies, in the absence of which, the firm may lose grip and direction in the overall management of the...






