Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Human Resource
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
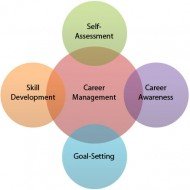
Career Management How to go about Career Management? Career Management is very essential which facilitates smooth transitions from one level to the next higher level in a profession. You cannot decide what to do unless you know what you are going to do or where you want to be tomorrow. Long term personal goals and professional goals are elemental in setting overall targets. According to Stephen P.Robbins, career is “a sequence of life positions occupied by a person during the course of a lifetime. Setting Goals for an Effective Career Your goals may be Long term Short term Personal or Professional Consider if you are goals are Realistic Whether you possess the skill set Achievable within the set time limit (duration) Based on these goals it is important to make long term and short term career plans. Also write down your Experience Skills and Qualification All these basic but vital things will give you a clear picture as to where you stand and what has to be done to improve your skills. Pic Courtesy: Cupcakes and Cashmere EYE Openers While Setting Personal Career Targets A. What do you want to accomplish from two or three years from now? B. What developments and knowledge can make this possible? C. How do you want to prepare yourself to achieve these targets or in what way you want to improve your skills? D. Is there a necessity for check points in the middle of the progress to make the necessary revisions? Tips to Manage Diversifying Careers Adaptability and flexibility are vital to reduce the stress of redundancy. Anticipate the changes and be prepared for anything at any time Look at the ‘Job Loss’ as an opportunity to pursue a new career that interests you. Career Planning A career will be satisfactory only when it interests the person and provides challenge and not by mere compensation or reward. Each organization should plan and help the individual, but every individual should take interest in his career. Career planning entails evaluating abilities and interests and considering alternative career development activities. The process results in Decisions to enter a certain occupation Join a particular organization Accept or decline new job opportunities{relocations, promotions or transfers} Leave an organization for another job or recruitment. Effects of Career Planning In corporate companies, a typical career planning program might include 1. Career counseling by members of the HR department 2. Workshops to help employees evaluate their skills, abilities, and interests to decide on their career development plans 3. Self directed programs to help the workforce guide their own careers through self-assessment and 4. Communication of job opportunities through job postings, videotapes and publications. One has to remember that career counseling may increase the pressure for managers and in turn the organization, as employees either become anxious about their present level of performance and chances for career advancement or they might use the opportunity to demand more from the firm in terms of pay, promotions etc., Key Career Issues of Employees Dual-career couples: When both husband and wife work, their earnings and stress are in surplus Stressors: Children under the age of six need parental care , but the amount of quality time of parents with that of the children is not at all balanced and this causes a heavy stress for both sides emotionally. Work schedule stressors: This increases as a person rises in an organization, job demands increase, with long hours of work and travel, but little time for family and vacation. Relocation: The increase in the number of dual career couple poses problems for many companies when they try to relocate...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 15th, 2014 | 0 comments

Functions of Management MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS The objective of this topic is to make students understand the functions of management and the role of managers in an organization. The five basic management functions are listed below: · PLANNING · ORGANISING · STAFFING · LEADING · CONTROLLING PLANNING: The managerial activities aid in selecting the objectives, examine and forecast changes, develop policies, procedures and choose future course of action from among alternatives. Planning proceeds from “Where we are” to “Where we want to go.” Planning activities are 1. Analysing the current situation (also called the SWOT Analysis) 2. Anticipating or predicting the future based on the analysis 3. Determination of organizational objectives to be achieved 4. Deciding on the action plan 5. Evolving proper strategies 6. Pooling the resources (physical, financial and monetary) to accomplish enterprise objective ORGANISING: It is a process which integrates people and tasks; In order to achieve their tasks people are given sufficient authority, tools and information. Organising activities include 1. Specification of job responsibilities 2. Grouping of jobs into respective work units 3. Allocation of resources STAFFING: Human resource management is one of the key areas that decides the success of a firm’s activity. Staffing involves the selection of “Right person for the right job.” The activities are 1. Recruitment 2. Selection 3. Training and Development 4. Compensation 5. Promotion 6. Evaluation and 7. Rewarding people to achieve enterprise goals. LEADING: Leadership is the set of interpersonal behaviors that influence people to contribute to the organization and group goals. The activities under this category are 1. Providing proper direction 2. Guidance and Motivation 3. Clarity in communication to the work force CONTROLLING: This is a process that is necessary to keep track of the performace of individuals by setting some standards for direction. The activities include 1. Establishing performance standards enabling the work force to achieve the goals (both short term and long term) 2. Enhancing the employee performance through performance appraisal or rating of work 3. Comparison of performance against the standards to identify deviation or work problems and take corrective measures 4. Bench marking is one of the management techniques that facilitates an organization to uplift its performance levels to the best of industry standards and also catch hold of the strengths of the competitors and rectify the weaknesses prevailing in one’s own firm. CO-ORDINATION: It is regarded as a key function of a manager to bring in harmony among individuals and an effort towards accomplishment of goals. 1. Marginal decision making and 2. Sub Optimisation are some of the new approaches developed in the field of decision making. MANAGERIAL SKILLS: Skill is the resultant effect of knowledge, experience and expertise. It is the ability of an individual to perform a task which is obvious from the results he/ she shows. There are 3 kinds of skills that a manager should possess in order to excel. 1. The Conceptual Skill: Assessing a situation and acting accordingly depicts the manager’s perceiving ability of the abstract elements in force. A manager has to improve this kind of skill as he moves up the ladder in the management level or let us say that he can move up the ladder only if he possesses this kind of skill. · Management Consultants · Managing Director of a firm · President of a company · Economists · Startegists are conceptual analytic experts 2. The Technical Skill: This skill is purely based on one’s knowledge and on the job experience. This is needed at a lower level of management · Computer Operators · Engineers · Accountants · Machine Operators possess this kind of skill 3. The Human Relations Skill: This...




