Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Business Management, Financial Accounting, How To, Marketing, Project Management, Sales
on Jun 15th, 2019 | 0 comments

Do you remember the first sale that you ever booked or made on your own? It was probably pretty exciting — that feeling of elation and top-of-the-mountain. You suddenly realize that you might understand how this whole business thing works and you might be able to do this. But of course there are practicalities to consider when you make a sale. It can be tempting to recognize revenue right away, but there’s always a risk. What if the sale cancels, for example? What if it costs more to create the product or service than you’ve booked? It just can be a difficult process to learn the ins and outs of recognizing revenue. Standards to Recognize Revenue Fortunately there are standards to use that others have figured out. These standards are a great way for companies to make sure that people understand what they are doing is on the up and up. Non-accountants must be aware of the concept of recognizing revenue from contracts with customers. Because payments are often not a straightforward affair, accountants have to allocate revenue using specific standards set by national and international accounting boards. While this information doesn’t seem important for non-accountants to understand, it is. Knowing when revenue can be recognized in your company’s financials affects everyone, from the salesperson’s commission to the marketing budget next quarter. What are those standards and what are the takeaways from them? This graphic explains it. To understand and accomplish the new revenue recognition standards, businesses should complete the following five steps: 1. Identify the contract with your customers Clearly identify the goods or services provided and describe each party’s right to them 2. Identify your performance obligations Specify exactly what you owe your customers and explain what defines “good performance.” 3. Determine the price of your products or services When doing so, don’t forget to consider promotions and other discounts. 4. Allocate a transaction price to the obligations specified in the contract Align the price of your services with your compnay’s performance obligations 5. Recognize revenue as performance obligations are satisfied Sales people also must understand the difference between booking and revenue. A booking is when the customer makes a commitment via a contract to buy your services or product. Revenue is when the revenue “counts” on the books – When accounting can account for the revenue as being...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management, How To
on Dec 19th, 2018 | 0 comments
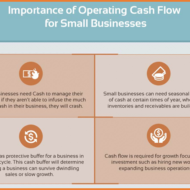
If you own a small business, then you’re probably no stranger to cash flow issues. In fact, 21% of businesses claim that cash flow problems were significant issues, potentially leading to closing down. One of the best ways business owners can ensure success is by carefully managing cash flow. Because no matter how great your business plan is, your business won’t survive if you run out of money. What Causes Cash Flow Problems? Before you can get a handle of your cash flow issues, you have to understand why they occur. Here are three common reasons why cash flow problems may arise: Unnecessary Spending Many business owners have head the old adage that you have to spend money to make money. Unfortunately, this belief has caused many ambitious business owners to overspend. Not all business expenses equally as important to your operations. Consider the cost-benefit of each expense. Overestimating Future Earnings Optimism is a great trait but it needs to be paired with a healthy dose of objectivity. It’s important to forecast your sales based on previous earnings and data. By not counting on future earnings that may never show up, you can prevent overspending. Inconsistent Sales Some businesses have occasional spikes in sales followed by months where they sell next to nothing. Trends like these cause problems with budgeting and makes it difficult for business owners to make operational decisions, often choosing to survive off of their “good” months. Get started with Flexible Funding today! Flexible Funding provides payroll-funding solutions in addition to back and front office support services as well. Flexible Funding works with staffing companies to implement the right staffing-industry software solutions for each client’s unique needs to create the best solutions and to save you time and money -from off-the-shelf accounting packages like QuickBooks and Sage 50 Accounting to in-house custom-built financial accounting software tools. Whether you are a start-up or an established staffing agency looking for best business practices, Flexible Funding will find the right solution for you– from payroll and invoice processing to W-2 preparation and filing, background checks, custom reporting, and so much more. Tips for Avoiding Cash Flow Problems Cash flow problems are a reality for nearly all business owners but there are ways to manage them. Here are five ways to mitigate your cash flow issues: 1) Take Out a Short-Term or P2P Business Loan A short-term business loan can provide the capital you need to run your business and pay for any expense, from inventory to office furniture. Short-term business loans have a high rate of approval even for businesses with limited credit history. You’ll receive the money faster than you would if you took out a traditional bank loan, which can be extremely helpful if you have immediate needs. Sometimes the application process can take as little as 24 hours. One of the first places to check for business loans as a business owner would be Small Business Administration. Or, if you prefer to bypass the government, you can try a peer-to-peer business loan. These loans are funded by individual investors through a lending platform. However, these loans usually require more frequent payments, and you will likely end up with a higher interest rate. 2) Use a Working Capital Loan Working capital loans can give you the cash flow to cover crucial operational costs like rent and payroll. This gives you the flexibility to invest in your company’s growth and still cover day-to-day expenses. Unlike other business loans, working capital loans don’t require that you state your reasons for taking out the loan. However, you will have to repay this loan quickly and your loan may have a...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Dec 14th, 2016 | 0 comments

Income Tax and PAN Card Info What is meant by Income Tax? A percentage of income earned by an individual or a company (complying to Indian laws) is paid in the form of tax to the government. This is called Income Tax. This comes under Income Tax Act constituted by Parliament of India. Department of income tax operates under Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, Government of India. This is responsible for checking and collecting tax. Where should I pay Income Tax? Income tax should be paid to the I.T deparment. This is called income tax filing which is done at the end of July every year. What is the period for which a person’s income is taken into account for purpose of Income Tax? The income earned from April 1st to March 31st is considered for calculating income tax. This period is called a financial year. For example April 1, 2015 to March 31, 2016 is a financial year. This is also called previous year. What is an assessment year? The 12 month period that comes after the previous year is called an assessment year. This is the period to file income tax return for the previous year. For example, for the financial year 2015-16, the assessment year is 2016-17. During this period, a person files his return for the income earned in the previous year. How to file income-tax returns online What is PAN Number or Permanent Acount Number? PAN is a ten digit number issued by the Income Tax deparment. It also serves as a valid identity proof for an Indian citizen. PAN number is demanded at many places now-a-days. When you file income tax returns When you open a bank account or Demat account It is useful in applying telephone connection and credit card When you want to register for service tax and sales tax When you buy or sell a vehicle When you deposit or withdraw money to the tune of Rs.50,000 in the bank or post office, PAN is a must If you want to invest in mutual funds If you are buying a property worth more than 5 Lakhs When you exchange large volume of foreign currency (over and above Rs.25,000), you need to submit your PAN CARD. Even when you buy GOLD , giving your PAN number has become mandatory after the DEMONETIZATION EFFORTS taken by the government recently on November 8, 2016. PAN card Dont’s… Same person having more than one PAN card is an offence. You have to submit any one card to the income tax department and update your info. You can be charged a fine of upto Rs.10,000 if you are found to have more than one PAN card. If somebody puts the PAN card to mis-use he might be fined and subject to imprisonment too. You can view your PAN card details in their website. If you apply for PAN card through private agents, kindly check whether your details are updated in the government website. Issue of PAN card PAN card issuing has been made very simple. You will be asked to fill up FORM 49-A and attach your address proof (Aadhar card or Ration card). The form can be downloaded from the following addresses online: www.tin-nsdl.com http://www.incometaxindia.gov.in/Pages/form-pan.aspx Also you get these forms issued by the IT PAN and TIN service centres. Having a PAN card doesn’t mean that you have to pay Income Tax. It is to facilitate people to pay Income Tax when their income levels warrants for paying tax. A Complete Tutorial on Financial Markets and...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Oct 24th, 2016 | 0 comments

Types of accounting information may be classified into four categories: Operating informationFinancial accounting informationManagement accounting information andCost accounting information 1. Operating Information: This is the kind of information which is required to conduct the day-to-day activities. Examples of operating information are: Amount of wages paid and payable to employeesInformation about the stock of finished goods available for sale andEach one’s cost and selling priceInformation about amounts owed to and owing by the business enterpriseInformation about stock of raw materials, spare parts and accessories and so on. By far, the largest quantity of accounting information provides the raw data (input) for financial accounting, management accounting and cost accounting. Spend Wisely 2. Financial Accounting: Financial accounting information is meant both for owners and managers and also for the use of individuals and agencies external to the business. This accounting is concerned with the recording of transactions for a business enterprise and the periodic preparation of various reports from such records. The records may be for general purpose or for a special purpose. Focus on the Long Term 3. Management Accounting: Management accounting makes use of both historical and estimated data in assisting management in daily operations and in planning for future operations. It deals with specific problems that is faced by enterprise managers at various organizational levels. The management accountant is often concerned with finding alternative courses of action and then helping to select the best one. For e.g. The accountant may help the finance manager in preparing plans for future financing or may help the sales manager in deciding the selling price to be fixed on a new product by providing suitable data. Generally management accounting information is used in three important management functions: ControlCo-ordination andPlanning 4. Marginal costing This is an important technique of management accounting which provides multi dimensional information that helps in decision making. Specialised Accounting Fields A number of specialized fields in accounting also have evolved besides financial accounting. Management accounting and cost accounting are the result of rapid technological advances and enhanced economic growth. The most important among them are explained below: 1. Tax Accounting: Tax accounting is all about the filing of tax returns and the consideration of the tax implications of proposed business transactions or alternative courses of action. Accountants specializing in this branch of accounting are familiar with the tax laws affecting their employer or clients and are up to date on administrative regulations and court decisions on tax cases. 2. International Accounting: This accounting is concerned with the special issues associated with the international trade of multinational business organizations or MNC’s. Accountants specializing in this area must be familiar with the influences that custom, law and taxation of various countries bring to bear on international operations and accounting principles. 3. Social Responsibility Accounting: This branch is the newest field of accounting and is the most difficult to describe. Social responsibility accounting is so called because it not only measures the economic effects of business decisions but also their social effects, which have previously been considered to be immeasurable. Social accounting is also known as social accounting and auditing, social and environmental accounting, corporate social reporting, corporate social responsibility reporting, non-financial reporting or accounting. Benefits of Social Accounting 4. Inflation Accounting: Inflation accounting is a term describing a range of accounting models designed to correct problems arising from historical cost accounting in the presence of highinflation and hyperinflation. Inflation accounting is used in countries experiencing high inflation or hyperinflation. 5. Human Resources Accounting: Human resource accounting is the process of identifying and reporting investments made in the human resources of an organization that are presently unaccounted for in the conventional accounting practices. It is an extension of standard accounting principles. This system of accounting...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting
on Aug 6th, 2016 | 0 comments
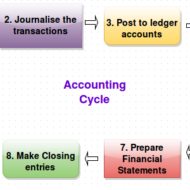
Financial statements have to be produced accurately at the end of the accounting period for tax purposes. An accounting period may be a month, a quarter of a year, or a whole year. The accounting cycle is the series of steps that take place in order to produce financial statements. A term that describes the steps when processing transactions (analyzing, journalizing, posting, preparing trial balances, adjusting, preparing financial statements) in a manual accounting system. Today many of the steps occur simultaneously when using accounting software. Following are the steps that complete an accounting cycle: Identify the transaction: This transaction could be the revenue from the sale of a product or a payment to another business for services. Analyze the transaction and how it is related to the accounting balance sheet. For example, determine which accounts are affected by the transaction and how they are affected. Record the transaction to a journal such as a sales journal. Journals are kept in chronological order and may be updated continuously, daily, or however often it is necessary. Record the transaction to the general ledger: Take all of your entries and categorize them by the account. Perform a trial balance: Debits and credits need to be equal at the end of an accounting cycle, so calculate the entries to ensure they match. Prepare adjustments: Just because entries are recognized, does not mean the work has been performed. Revenue can only be recognized when the work has been completed, so adjust the entries accordingly. Perform trial balance with adjustments: Take the adjustments from Step 6 and prepare a trial balance. If the debits and credits do not match, then you need to adjust them to make sure they do match. Prepare financial statements: From the adjusted trial balance, these corrected balances are used to prepare the financial statements. Close the accounts in preparation of the next accounting cycle. Revenues and expenses need to be closed out, which means they need to have zero balances. Balances are moved to the next cycle. Some Important Accounting Terms: Account A record in the general ledger that is used to collect and store similar information. For example, a company will have a Cash account in which every transaction involving cash is recorded. A company selling merchandise on credit will record these sales in a Sales account and in an Accounts Receivable account. Accounting Department Part of a company’s administration that is responsible for preparing the financial statements, maintaining the general ledger, paying bills, billing customers, payroll, cost accounting, financial analysis, and more. The head of the accounting department often has the title of controller. Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. For a corporation the equation is Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity. For a nonprofit organization the accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Net Assets. Because of double-entry accounting this equation should be in balance at all times. The accounting equation is expressed in the financial statement known as the balance sheet. Accounts Payable This current liability account will show the amount a company owes for items or services purchased on credit and for which there was not a promissory note. This account is often referred to as trade payables (as opposed to notes payable, interest payable, etc.) Accounts Receivable A current asset resulting from selling goods or services on credit (on account). Invoice terms such as (a) net 30 days or (b) 2/10, n/30 signify that a sale was made on account and was not a cash sale. Adjusting Entries Journal entries usually dated the last day of the accounting period to bring the balance sheet and income statement up to date on an accrual basis (as required by the matching principle and...










