Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Management, Principles of Management, Project Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
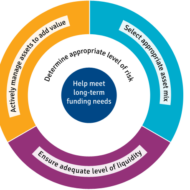
What is Business Risk? It is a term that explains the difference between the expectation of return on investment and actual realization. In CAPITAL BUDGETING, several alternatives of investments are examined before taking an investment decision and only then the Managing Director of the firm along with financial executives gear up for investing in a project that is sound and feasible. Even then the project may not become viable owing to the fluctuations in the economic environment. Money Manipulation So, the million dollar question arises, whether to invest and if invested, will it fetch me profit? See, you cannot have the cake and eat it too. Risk factor prevails in all kinds of environment and we try to over react in a business arena since it involves huge investments. But remember, MONEY WILL MULTIPLY IF YOU MANIPULATE IT WITH CARE. Business firms commit large sums of money each year for capital expenditure. It is therefore essential that a careful FINANCIAL APPRAISAL of each and every project which involves large investments is carried out before acceptance or execution of the project. These capital budgeting decisions generally fall under the consideration of highest level of management. Factors of risk to be considered before investing: Time value of money Pay back period Rate of return on investment(ROI) Uncertainties in the market Cost of debt Cost of equity Cost of retained earnings Factors to be monitored after investing: Maximising profit after taxes Maximizing earnings per share Maintaining the share prices Issue of dividends Ensuring management control Financial structuring Cost of capital refers to the opportunity cost of the funds to the firm I. e., the return on investment to the firm had it invested these funds elsewhere. Servicing the debt and Danger of Insolvency While making the decisions regarding investment and financing, the Finance Manager seeks to achieve the right balance between risk and return. If the firm borrows heavily to finance its operations, then the surplus generated out of operations should be sufficient to “SERVICE THE DEBT” in the form of interest and principal payments. The surplus would be greatly reduced to the owners as there would be heavy Debt Servicing. If things do not work out as planned, the situation becomes worse, as the firm will not be in a position to meet its obligations and is even exposed to the “DANGER OF INSOLVENCY“. Working Capital Management Considering all these factors, we have to come to the conclusion that FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT is like the BACKBONE of a business firm and WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT will be the blood flow infused into the body. Risks are inherent in a business environment whose management is quite possible with the right kind of farsightedness and planning. Luck does not favor anybody who is poor in planning and lack hard...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management
on Feb 25th, 2014 | 0 comments

Venture Capital and Traditional Financing- Comparison of Advantage Venture capital is a new form of financing that has come as a boon for young entrepreneurs and it plays a strategic role in financing small scale enterprises and high technology and risky ventures. In all the developed and developing nations it has made its mark by providing equity capital, so, they are more like equity partners rather than financiers and they are benefited through capital gains. Don Valentine is known as "the grandfather of Silicon Valley Venture Capital". He was one of the original investors in Apple, Atari, LSI Logic, Cisco Systems, Oracle, and Electronic Arts back in the 1970s. So he has a top notch track record. Here are some of his quotes:— Lion (@Lion_Investor1) July 27, 2021 Venture capitalists evaluate the risk using the following factors: Management TeamCompetitive AdvantageMarket PotentialBarriers to entryExit Strategy Banks’ Stand Towards First Generation Entrepreneurs Young and growing businesses need capital at the right time, not only to float their company in the market but also to survive in the long run. When financial institutions like banks and other private financial organizations hesitate to take the risk of early stage financing, since the credibility of the budding firm is not established, venture capital firms comes into the foray to fund the project in the form of equity which can be termed as “high risk capital”. Venture Capitalist is like an Equity Partner Although there is a misconception that the interest of venture capital firms is mainly driven by cutting edge technology in the industry, it is not always the case with all venture capital firms. A venture capitalist associates high risk with huge profits; of course after thoroughly analyzing the prospects and consequences and the viability of the project. The venture capitalist becomes a partner with the entrepreneur in his business. True venture capital financing need not confine itself to high end technology products. Any risky idea with great potential can be financed and venture capital is an all powerful mechanism to promote and institutionalize entrepreneurship. Focus on Growth Mainly venture capital focuses on growth. A venture capitalist is very much interested to see a small business growing into a larger one. He assists in setting up the business, funding it and travels all along to see the firm grow. If it is potential equity participation, the venture capitalist can come out of the partnership once the company becomes profitable and take back his money by selling the shares or convertible securities. If the firm opts for a long term investment from the venture capital finance, the financier has to develop an investment attitude for a long term, say five or ten years to allow the company to make large profits. Active Participant in the Operations of the Firm Another form of financing is that the venture capitalist has his hands on management by which he becomes an active participant in the operations of the firm and his thinking is streamlined as to how to multiply and make quick money which is a win-win situation for both sides. Not only finance, the venture capitalist also contributes to marketing, technology upgradation and management skills to the benefit of the new firm. Venture Capitalist- Banker, stock market investor and an entrepreneur in one. The venture capitalist’s management approach is significantly different from that of a banker whose prime concern is collaterals and securities in the form of assets. He keeps his hands off the management and plays safe. The venture capitalist can also not behave like a stock market investor who invests money without having thorough knowledge about the company’s business and management. He combines the qualities...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Feb 20th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is fund ? Cash, total current assets, net current assets and net working capital are also interpreted as fund. So, it is necessary to clearly define the meaning of fund and demarcate its scope and function. To put it precisely, fund is nothing but, net working capital of a firm. The flow of fund occurs when a business transaction takes place that leads to an increase or decrease in the amount of fund. Firms prepare fund flow statement to explain the sources and applications of fund, which also serves as a technical tool to ascertain the financial condition of a business enterprise. Balance Sheet In a business firm, everyday numerous financial transactions take place. These are summarized into a balance sheet that gives an idea about the assets and liabilities at a specific point of time. When two balance sheets of consecutive periods are compared, we come to know about the inflow and outflow of funds and thereby the net working capital available is ascertained. This is step one. Profit and Loss Statement The next step would be to prepare an adjusted profit and loss account to determine fund inflow or fund lost from business operations. Accounts have to be prepared to ascertain hidden information (for all non-current items of assets and liabilities). Finally fund lost or gained from operations is arrived at and presented in a statement form. It is not that, only accountants could understand these operations and adjustments. Any person with logical reasoning and business acumen can understand the nuances of accounting, of course with some guidance. Few points that highlight the ways in which funds flow outside and inside a business enterprise will give you a better idea on the nature of fund flow: Sources of fund: Sale of fixed assets – sale of land, building, machinery, furniture etc. But you have to take into consideration a factor called “depreciation“. It is nothing but the wear and tear of the assets due to continuous usage, reduction in market value over a period of time, obsolescence, accidents etc. Remember, land is a non-depreciable asset in developing countries like India, whereas it may not be so in certain developed countries where the real estate values are nose diving. Issue of Equity shares – To raise capital free of interest, many big corporate firms go for equity capital from the general public. But the firms should make it a point to declare dividends if it happens to reap enormous profit to retain their market share. Their main aim should be to protect the interests of the equity share holders who are also the owners. Fund that comes into the firm through business operations – through sale of goods and services. Here the firm has to factorise its cost of production and economy of scale in order to make it cost-effective and fix a feasible profit margin. Borrowing of loans from banks and other financial institutions – Although it is a quick way of raising fund, care should be exercised in that, you should be in a comfortable position to “service the debt“. If not, there lurks the danger of bankruptcy where the firm might become insolvent, if it is unable to repay the interest and principal over a period of time. Issue of debentures – Debentures are also a form of equity but it comes with a price. The firm has to pay a percentage as interest on debentures and repayment period is also fixed in advance. The only solace for the firms would be the tax rebate that can be availed on loans and...

Posted by Managementguru in Video Lecturers
on Feb 16th, 2014 | 0 comments
The accounting equation is the basis of accounting. However, the formal equation can be confusing. In this lecture you will learn the simplified equation (What=Who) and how it is the foundation of the accounting profession. By the end of the lecture you will understand the more formal accounting...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Feb 14th, 2014 | 0 comments

Classification of Accounts Accounts are classified as follows: •Accounts in the names of persons are known as “Personal Accounts” •Accounts in the names of assets are known as “Real Accounts” •Accounts in respect of expenses and incomes are known as “Nominal Accounts” Personal Accounts: It deals with accounts relating to persons, firms, companies and man-made institutions. It is further classified into three categories as shown below. PERSONAL ACCOUNTS NATURAL PERSON’S A/C : e.g- David, Customer ARTIFICIAL PERSON’S A/C : e.g- Banks, firms, companies REPRESENTATIVE’S A/C : e.g- Capital, Drawings Real Accounts These are accounts of assets or properties. Assets may be tangible or intangible. Real accounts are impersonal which are tangible or intangible in nature. Eg:- Cash a/c, Building a/c, etc are Real Accounts related to things which we can feel, see and touch. Goodwill a/c, Patent a/c, etc Real Accounts which are of intangible in nature. Nominal Accounts These accounts are impersonal, but invisible and intangible. Nominal accounts are related to those things which we can feel, but can not see and touch. All “expenses and losses” and all “incomes and gains” fall in this category. Eg:- Salaries A/C, Rent A/C, Wages A/C, Interest Received A/C, Commission Received A/C, Discount A/C, etc. DEBIT AND CREDIT Each accounts have two sides – the left side and the right side. In accounting, the left side of an account is called the “Debit Side” and the right side of an account is called the “Credit Side”. The entries made on the left side of an account is called a “Debit Entry” and the entries made on the right side of an account is called a “Credit Entry”. Golden Rules of Book-Keeping Personal Accounts : DEBIT THE RECEIVER & CREDIT THE GIVER Real Accounts : DEBIT WHAT COMES IN & CREDIT WHAT GOES OUT Nominal Accounts : DEBIT ALL EXPENSES AND LOSSES & CREDIT ALL INCOME AND GAINS What is an accounting equation? It is a statement of equality between the debits and the credits. It explains that the assets of a business are always equal to the total of liabilities and capital. It is also called the balance sheet eqaution. Assets = Liabilities + Capital A = L + C ASSETS ARE THE TOTAL VALUE OF PROPERTIES OWNED BY THE BUSINESS LIABILITIES ARE THE RIGHTS OF THE THIRD PARTIES TO THE PROPERTIES OF THE BUSINESS OR THE AMOUNT DUE BY THE BUSINESS TO THE THIRD PARTIES. Basics of accounting – Accounting Equations Made Simple With Solid Clarity from Shyama...









