Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Project Management, Sales
on Feb 3rd, 2015 | 0 comments
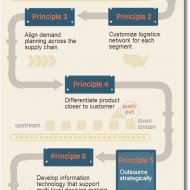
What is Supply Chain Management? Investopedia: Supply chain management (SCM) is the streamlining of a business’ supply-side activities to maximize customer value and to gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. SCM represents an effort by suppliers to develop and implement supply chains that are as efficient and economical as possible. Wikipedia: Supply chain management (SCM) is “the systemic, strategic coordination of the traditional business functions and the tactics across these business functions within a particular company and across businesses within the supply chain, for the purposes of improving the long-term performance of the individual companies and the supply chain as a whole.” Business Dictionary: Management of material and information flow in a supply chain to provide the highest degree of customer satisfaction at the lowest possible cost. SCM requires the commitment of supply chain partners to work closely to coordinate order generation, order taking, and order fulfillment. They thereby create an extended enterprise spreading far beyond the producer’s location. 7 Principles of SCM Supply Chain Management in Simpler Terms: The EFFECTIVE movement and management of materials and information as they flow from their source to the end customer. Supply Chain encompasses purchasing, manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, customer service, demand planning and supply planning. SCM is a daunting task and calls for proper planning and execution. OBJECTIVES OF FORECASTING SCM is the control of the supply chain as a process from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. SCM does not only comprise the passage of a physical product through the chain but also any data that goes along with the product (such as order status information, payment schedules, and ownership titles) and the actual entities that handle the product from stage to stage of the supply chain. There are essentially three goals of SCM: To reduce inventoryTo increase the speed of transactions with real-time data exchange andTo increase revenue by satisfying customer demands more efficiently. When you think of the world’s most efficient and successful performance and supply chains, what comes to mind? For me it is not Wal-mart or Pepsi but Mumbai Dabbawalas – Watch this Video. The Success of Supply Chain of Dabbawalas in Mumbai –Said to be Six Sigma Compliant No over-reliance on technology, all manual operationsCreate an integrated performance chain, the chief, team leaders and delivery men.Acute visibilityKeep it simple. Real simple with a color coding to identify where the food has to be delivered and to whom.Timely Delivery as the shelf life of food is 4-5 hours. Why is it so important for companies to get products to their customers quickly? Faster product availability is significant to increasing sales and there’s a sizeable profit advantage for the extra time that you are in the market and your competitor is not. The earlier and faster you are in the market, the more orders and market share you enjoy. The ability to deliver a product faster also can make or break a sale. If two competitive products appear to be equal and one is immediately available and the other will be available in a week, which would you choose? Supply Chain Management is all about moving goods more quickly to their destination in a strategic and tactical manner. Supply Chain Management Tomorrow: The future for Supply Chain Management looks very bright. Two major trends are benefiting Supply Chain Management operations- Customer service focus and Information technology. Successful organisations must excel in both of these areas, the fundamental objective being to “ADD...

Posted by Managementguru in Marketing, Quotes and Quotes Only
on Jul 14th, 2014 | 0 comments

1. “Good branding without a good business plan is like prettying up a duck with no feathers. It may look good but it ain’t gonna fly.” Paul Provost, August 2010 2. “For a business not to advertise is like winking at a girl in the dark. You know what you are doing but no one else does.” Stuartt H. Britt, US advertising consultant 3. “The objective of all advertising is to buy new customers at a profit. Learn what your customers cost and what they buy…spend all of your ammunition where it counts.” Claude Hopkins-Scientific Advertising (1923) 4. “Nobody counts the number of ads you run; they just remember the impression you make.”– Bill Bernbach 5. “Nobody reads ads. People read what interests them, and sometimes it’s an ad.”- Howard Luck Gossage 6. “The only people who care about advertising are the people who work in advertising”– George Parker 7. “In advertising, not to be different is virtually suicidal” – Bill Burnbach 8. “Don’t find customers for your product. Find products for your customers” – Seth Godin. 9. “Give them quality. That’s the best kind of advertising.” – Milton Hershey 10. “If you can’t explain it to a six year old, you don’t understand it well enough yourself” – Albert Einsteen 11. “If you want to understand how a lion hunts, don’t go to the zoo. Go to the jungle.” – Jim Stengal 12.“The aim of marketing is to know and understand the customer so well the product or service fits him and sells itself.”– Peter Drucker 13. “In our factory, we make lipstick. In our advertising, we sell hope.”-Peter Nivio Zarlenga 14. “I don’t know the rules of grammar… If you’re trying to persuade people to do something, or buy something, it seems to me you should use their language, the language they use every day, the language in which they think. We try to write in the vernacular.”– David Ogilvy 15. “Don’t tell me how good you make it; tell me how good it makes me when I use it.” – Leo Burnett 16. “On the average, five times as many people read the headline as read the body copy. When you have written your headline, you have spent eighty cents out of your dollar.” – David Ogilvy 17. “People spend money when and where they feel good” – Walt Disney 18. “Half the money I spend on advertising is wasted, and the problem is I do not know which half.” Lord Leverhulme, British founder of Unilever and philanthropist 19. “In marketing I’ve seen only one strategy that can’t miss — and that is to market to your best customers first, your best prospects second and the rest of the world last.” – John Romero 20. “The philosophy behind much advertising is based on the old observation that every man is really two men — the man he is and the man he wants to be.” – William Feather 21. “In order for you to profit from your mistakes, you have to go out and make some.”- Unknown 22. “Eighty percent of success is showing up.” – Woody Allen 23. “Vision without action is a daydream. Action without vision is a nightmare.” – Japanese Proverb 24. “They may forget what you said, but they will never forget how you made them feel.” – Carl W. Buechner 25. ”There is nothing more difficult for a truly creative painter than to paint a rose, because before he can do so he has first to forget all the roses that were ever painted.” – Henri Matisse 26. “Simplicity is the ultimate form of sophistication” – Leonardo Da Vinci 27. Business has only...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
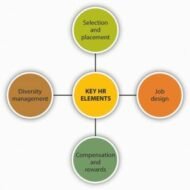
Managing Critical Factors of HR The prerequisite for an organization to excel in all aspects of its business activities is absolute strategic management of its HR functions.Human resource management is an extensive term that covers various aspects of personnel function. This discussion is focused on three main aspects that constitute human resource management. Personnel administration Human resource development Industrial relations Personnel administration: It can be also called as the HR module where policies and programmes are laid down by the HR department for the benefit of the human resource personnel. Employment and compensation are chiefly dealt with in personnel administration. While business firms in the corporate environment are in constant demand of man power, finding the right person for the right job is always a testing task for them. Right from job analysis to HR planning, recruitment, selection, placement, induction and orientation, HR department is held accountable to define and develop these operative functions. Mere acquisition and incorporation of human resource is not adequate, the organizations have to engage themselves in empowering their employees through competent training, motivation and refining their social relations. Job Assessment: Job assessment has to be done for fixing compensation that includes wages and salary administration, incentives, bonus, fringe benefits and social security measures. The shifting business environment and consumer requirements compel the organizations to restructure and re-engineer their organizational functions. These moves can be viewed as strategic responses reflecting from all domains of an organization, namely product, marketing, manufacturing etc., where people are the centre of focus. Human resource development: This is easier said than done. Firms are trying to evolve and employ various methodologies of training to enhance the performance levels to the desired standards. Performance cannot be achieved by coercion or bureaucracy, as the work force is protected by numerous enactment of labor laws enforced by various governments. Training and development is a separate entity by itself and is a continuous process that aims at the development of the organization as a whole and also facilitates employee career planning and development. Industrial relations: The following factors have to be scrutinized by the management to maintain good personal relations with the employees. Motivation Morale Job satisfaction Communication Grievance handling Discipline procedure Quality of work life Employee participation All said and done, the organizational health can be measured by checking the effectiveness of HR management through aspects like HR audit and research that aid the firms to analyze and understand the extent to which they are efficient in utilizing human resource for the benefit of their organization. The experience of a human resource manager comes in handy at situations like these, where he has to don different roles to suit the occasion. Personnel role-advisor for top management, policy maker, counselor to employees, spokesman of the company, change analyst, liaison Welfare role-researcher, catering man, motivator Clerical role-time keeping, wages and salary administration, record maintenance, human engineering Fire fighting legal role-negotiator, trouble shooter, peace maker, problem solver, grievance handling. The management employs scientific, analytical, psychological and social techniques to build the business around human resource, who are the real value additions to the...

Posted by Managementguru in Operations Management, Project Management
on Feb 24th, 2014 | 0 comments

Materials Handling Minimize Movement and Maximize Productivity Manufacturing organizations handle many types of materials in their production environment. Raw materials, materials-in-progress, finished goods, accessories, components, packaging materials, maintenance and repair supplies, scrap and many more must be handled in an efficient manner to make the operations cost-effective and to avoid wastage. The principle behind material handling process is said to be “no handling”, which is not practicable in reality. So it would be appropriate to say, that the objective of materials handling would be, to reduce the number of handlings as well as reducing the distances through which the materials are handled. Why efficient materials handling is inevitable in a manufacturing set-up? The movement of materials from the receiving area to the shipping area through the production line does not add value to the product but only to the cost. Further, plant layout and materials handling are complementary to each other. A production facility must incorporate a good plant layout that enhances the efficiency of movement of materials with ease and should deliver maximum productivity. Principles for Efficient Materials Handling There are certain principles that serve as a guide for efficient materials handling. These provide a framework for selecting specific materials handling equipments that form the core of the production system. Eliminate handling-If not, reduce the distance travelled by the materials Keep moving-If not, reduce the time spent at crucial points Simple patterns of material flow is appreciated-If not, reduce back tracking, cross overs, congestion Carry pay loads Carry full loads Use reliable and inexpensive source of power Materials handling should be considered in the light of movement of men, machines, tools and information. It also depends on the type of product manufactured, quantity, value and size of the organization. Cost effectiveness can be achieved if the firm is able to reduce the manufacturing cycle time through faster movement of materials and thus work-in-progress inventory costs can also be controlled and reduced. Design of the plant layout that facilitates sequential flow of materials through the production facility, improved working conditions, safety in the movement of materials, contribution to better quality by avoiding damage to the materials due to inefficient handling and workers being appraised about the importance of smooth materials handling result in higher productivity at lower manufacturing cost. Interested in being served food by Robots! Factors to considered while deciding on material handling equipments: Adaptability, flexibility, load capacity, power, speed, nature of supervision required, space requirements, ease of maintenance, environment friendliness and cost are some of the factors to be taken into consideration while deciding on the type of material handling equipments. Also the capabilities of manpower to operate the equipment and safety of personnel cannot be overlooked. It is important to select and design, materials handling system that are expensive to purchase and operate. For instance, if overhead cranes are to be used, the structure of the building should be strong enough to support the installation. Spacious aisles are mandatory if the loads are heavy and transported across the shop floors. Equipments used: Elevators, hoists, industrial trucks like fork-lift trucks, pallet trucks, pipelines, automatic transfer devices, automated guided vehicles, and industrial robots are some of the handling equipments that have found their ideal place in this process. Materials handling activity should be evaluated like any other activity to gauge its effectiveness. The focus should be on the manufacturing cycle efficiency, equipment utilization, percentage of time lost, total number of moves and material handling costs as percentage of manufacturing...

Posted by Managementguru in Labor Management, Operations Management
on Feb 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments
What is Operations Management and Why is it Important? Operation is that part of as organization, which is concerned with the transformation of a range of inputs into the required output (services) having the requisite quality level. Management is the process, which combines and transforms various resources used in the operations subsystem of the organization into value added services in a controlled manner as per the policies of the organization. The set of inter-related management activities, which are involved in manufacturing certain products, is called as production management. If the same concept is extended to services management, then the corresponding set of management activities is called as operations management. What is Production? Production is defined as ‘the step-by-step conversion of one form of material into another form through chemical or mechanical process to create or enhance the utility of the product to the user’. Thus production is a value addition process. At each stage of processing, there will be value addition. Pic Courtesy: Minds.com Edwood Buffa defines production as ‘a process by which goods and services are created’. Some examples of production are: manufacturing custom-made products like, boilers with a specific capacity, constructing flats, some structural fabrication works for selected customers, etc., and manufacturing standardized products like, car, bus, motor cycle, radio, television, etc. Characteristics of a Production System 1. Production is an SYSTEMATIZED activity, so every production system has an objective. 2. The system transforms the various inputs to useful outputs. 3. It WORKS IN TANDEM with the other organisation systems. 4. There exists a feedback about the activities, which is essential to control and improve system performance. Evolution of Production Management Why Operations Management is Important? Increases productivity of every organization Leads to economic growth and development Helps employees to receive high wages Earns profit for a company Also plays a strategic role in a firm’s competitive success Want to Learn Some Interesting Operations Management Terms? Capacity planning—The process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products. Different types of capacity exist. For example, design capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period; effective capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period due to constraints such as quality problems, delays, and material management. Efficiency—Performing activities at the lowest possible cost. Enterprise resource planning (ERP)—Large, sophisticated software systems used for identifying and planning the enterprise-wide resources needed to coordinate all activities involved in producing and delivering products. Forecasting—The process of predicting future events, including product demand. Just-in-time—A philosophy designed to achieve high-volume production through elimination of waste and continuous improvement. Lean systems—Sometimes synonymous with just-in-time, it is a philosophy that takes a total system approach to creating efficient operations through the elimination of waste. Location analysis—Identifying the best location for facilities. Mass customization—The ability of a firm to highly customize its goods and services at high volumes through its operations management function. Product design—The process of deciding on the unique and specific features of a product. Process selection—The process of identifying the unique features of the production process that will give the product its unique characteristics. Process selection typically goes hand in hand with product design, as we need to create a process that gives rise to the particular product design desired. An excellent product design is worthless if a process for its creation cannot be developed. Productivity—A measure of how efficiently an organization converts inputs into outputs. It is usually measured by a ratio of output divided by input. Productivity is essentially a scorecard of how efficiently resources are used and a measure of...










