Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Jun 25th, 2014 | 0 comments
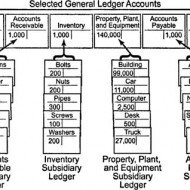
Ledger is a register with pages numbered consecutively. Each account is allotted one or more pages in the Ledger. If one page is completed, the account will be continued in the next page. An index of various accounts opened in the Ledger is given at the beginning of the Ledger for the purpose of easy reference. A general ledger is a complete record of financial transactions that holds account information needed to prepare financial statements, and includes accounts for assets, liabilities, owners’ equity, revenues and expenses. What is meant by Posting? Transactions recorded in the Journal and Subsidiary journal are transferred to the concerned accounts in the Ledger in a summarized and classified form. This process is called posting. “Interesting Statistics on Accounting The first book on double-entry accounting was written in 1494 by Italian mathematician and Franciscan friar Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli. Although double-entry bookkeeping had been around for centuries, Pacioli’s 27-page treatise on the subject has earned him the title “The Father of Modern Accounting. Accounting plays a major role in law enforcement. The FBI counts more than 1,400 accountants among its special agents. The state of New York gave its first certified public accountant (CPA) exam in 1896. Rules for posting: Separate account should be opened in the Ledger for posting transactions relating to separate persons, assets, expenses or losses as shown in the journal. The account concerned which has been debited in the journal should also be debited in the Ledger. However, a reference must be made of the other account which is to be credited in the journal. In other words, in the account to be debited, the name of the other account to be credited is entered in the debit side for giving a meaning to this posting. The debit posting is prefixed by the word ‘To’. Similarly, the account concerned which has been credited in the journal has to be credited in the Ledger, but a reference should be made to the other account which has been debited in the journal. This posting is prefixed by the word ‘By’. Advantages of keeping a Ledger: Ledger provides information regarding all transactions of a particular account whether it is personal a/c, Real a/c or nominal a/c. The final effect, of a series of transactions of a certain customer or a certain property or a certain expense is known at a glance. Ledger provides immediately the totality of certain dealings. E.g., total purchases, Total sales, total expenditure, on a specified head. What is a Ledger account? Give a Proforma of a Ledger account. A Ledger account is nothing but a summary statement of all transactions relating to a person, asset, expense or income, which have taken place during a given period of time showing their net effect. Proforma of a Ledger account: What are the methods of balancing the Ledger account? At the end of the each month or year or any specific day it is essential to determine the balance in an account. To do that, add the totals of both sides (Debit and credit sides) and find out the difference in both the sides. The difference in both the sides is ‘Balance’. If the Debit is greater than the credit side, it is a Debit balance or vice-versa. There are two methods: The bigger total is taken first and is written on both sides of the account. On the smaller side, the balance is Witten above the total next to the last entry on that side. This method is more commonly used. In another method, the totals are written on both sides, one side showing smaller amount and the other showing bigger amount. The difference is...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Apr 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
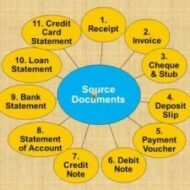
What are the Various Source Documents in Accounting? What is meant by source document? A source document is one used to record the transactions in the books of account. These documents stand as evidence for business transactions. These include Cash Memo Invoice Receipt Debit Note Credit Note Voucher Pay in Slip Cheque etc. 1. Cash Memo: When goods are sold or purchased for cash, the firm gives or receives cash memos with details regarding cash transactions. These documents become the basis for recording these transactions in the books of accounts. 2. Invoice: Invoice is prepared when goods are sold or purchased on credit. It contains the name of the party, quantity, price per unit and the total amount payable. The original copy is sent to the buyer and the duplicate copy is kept as proof of sale and for future reference. Types of Invoice: Inland Invoice – An invoice which is used in internal trade transaction is called as an Inland Invoice. When the goods are sold within a country, the invoice relating to such a transaction is called as an Inland Invoice. Foreign Invoice – An invoice which is prepared for covering an international trade transaction is called as a Foreign Invoice. A number of copies are prepared, maybe even 10 to 12, because a number of authorities require it. Inward Invoice – Inward invoice is received by the buyer from the seller, on receipt of invoice; the buyer stamps it with date of receipt. The inward invoice number is entered in the purchase journal. Outward Invoice – Outward Invoice is a seller’s bill. An invoice which is inward to the buyer is an outward for a seller. It is called outward invoice, because it is sent to the buyer. At least one copy of the invoice is retained by the seller for necessary action and reference. Proforma Invoice – Proforma Invoice is not a real invoice. It is prepared to give a clear idea regarding the amount that would be paid by the buyer if he places an order. This is prepared at the request of the buyer. 3. Receipt: When a firm receives cash from a customer it issues a receipt as a proof of receiving cash. The original copy is handed over to the party making payment and the duplicate is kept for future reference. This document contains date, amount, name of the party and the nature of payment. 5 Kinds of Receipts Small Businesses Should Take Extra Care to Keep Meal & Entertainment Receipts Receipts from Out of Town Business Travels Vehicle Related Receipts Receipts for Gifts Home Office Receipts 4 & 5. Debit and Credit Notes: These are prepared when goods are returned to supplier or when an additional amount is recoverable from a customer. When the purchaser returns the goods to the seller the Purchaser sends a Debit Note to the seller (i.e. the purchaser debits the seller in his books. Purchasers Books) and the Seller sends a Credit Note to the purchaser (i.e. the seller credits the Purchaser in his Books. Sellers Books). Following are the JVs to be passed:- Sales Return inward A/c Dr. To Debtor A/c (Being goods returned by the customer) Creditor A/c Dr. To Goods Return A/c (Being goods sent back to the seller) 6. Voucher: It is a written document in support of a transaction. It is a proof of a particular transaction taking place for the value stated in the voucher. This is necessary to audit the account. In book keeping, voucher is the first document to record an entry. Normally three types of vouchers are used. Receipt voucher Payment voucher Journal voucher RECEIPT VOUCHER Receipt voucher...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Apr 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

Business Policies – Framing and Execution Business policies are the keystone in the arch of management and the life-blood for the successful functioning of business, because without well-laid down policies, there cannot be lasting improvements in the economic condition of the firm and labor-management relations. A policy is a positive declaration and a command to its followers. It translates the goals of an organization into selected routes and provides the general guidelines that prescribe and proscribe programmes, which in turn, dictate practices and procedure. Attainment of Objectives: Buisness policies are general statement of principles for the attainment of objectives which serve as a guide to action for the executives at different levels of management. They pave a broad way in which the sub-ordinates tread along towards accomplishing their objectives. Hierarchy: For each set of objectives at each level, there is a corresponding set of policies. The Board of Directors determine the basic overall corporate policiesThe top management decides on the executive corporate policiesManagers decide on the departments / divisional policiesMiddle managers handle the sectional policies Consistent Decisions contributing to the Objectives: The policies delimit the area within which a decision has to be made; however, they do allow some discretion on the part of the man on the firing line, otherwise, they would be mere rules. At the same time too much of discretion in policy matters may prove harmful to the accomplishment of organizational objectives and hence it is generally within limits. Mutual Application: Policies in general are meant for mutual application by sub ordinates. They are fabricated to suit a specific situation in which they are applied, for they cannot apply themselves. Unified Structure: Policies tend to predefine issues, avoid repeated analysis and give a unified structure to other types of plans, thus permitting managers to delegate authority while maintaining control. Policies for all Functional Areas: In a well-structured and managed organization, policies are framed for all functional levels of management. Corporate planningMarketingResearch and DevelopmentEngineeringManufacturingInventoryPurchasePhysical DistributionAccountingFinanceCostingAdvertisingPersonal SellingSpecial Promotion, are some areas that require clear-cut policies. Clear-Cut Guidelines: Policies serve an extremely useful purpose in that they avoid confusion and provide clear-cut guidelines. This enables the business to be carried on smoothly and often without break. They lead to better and maximum utilization of resources, human, financial and physical, by adhering to actions for...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting
on Apr 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Ratio Calculation From Financial Statement Profit and Loss a/c of Beta Manufacturing Company for the year ended 31st March 2010. Exercise Problem1 Kindly download this link to view the exercise. Given in pdf format. You are required to find out: a) #Gross Profit Ratio b) #Net Profit Ratio c) #Operating Ratio d) Operating #Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio a. GROSS FORFIT RATIO = Gross profit ÷ #Sales × 100 = 50,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 31.25 % b. #NET PROFIT RATIO = Net profit ÷ Sales × 100 = 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 17.5 % c. OPERATING RATIO = #Cost of goods sold + Operating expenses ÷ Sales × 100 Cost of goos sold = Sales – Gross profit = 1,60,000 – 50,000 = Rs. 1,10,000 Operating expenses = 4,000 + 22,800 + 1,200 = Rs. 28,000 Operating ratio = 1,10,000 + 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 86.25 % d. OPERATING NET PROFIT TO NET SALES RATIO = Operating Profit ÷ Sales × 100 Operating profit = Net profit + Non-Operating expenses – Non operating income = 28,000 + 800 – 4,800 = Rs. 32,000 Operating Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio = 32,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 20 % What is a Financial statement? It is an organised collection of data according to logical and consistent #accounting procedure. It combines statements of balance sheet, income and retained earnings. These are prepared for the purpose of presenting a periodical report on the program of investment status and the results achieved i.e., the balance sheet and P& L a/c. Objectives of Financial Statement Analysis: To help in constructing future plans To gauge the earning capacity of the firm To assess the financial position and performance of the company To know the #solvency status of the firm To determine the #progress of the firm As a basis for #taxation and fiscal policy To ensure the legality of #dividends Financial Statement Analysis Tools Comparative Statements Common Size Statements #Trend Analysis #Ratio Analysis Fund Flow Statement Cash Flow Statement Types of Financial Analysis Intra-Firm Comparison Inter-firm Comparison Industry Average or Standard Analysis Horizontal Analysis Vertical Analysis Limitations Lack of Precision Lack of Exactness Incomplete Information Interim Reports Hiding of Real Position or Window Dressing Lack of Comparability Historical...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting
on Feb 14th, 2014 | 0 comments
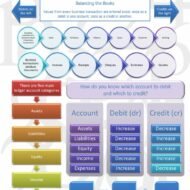
Double Entry System of Book Keeping Accounting is not to be feared Accounting is a subject that is intertwined with our day-to-day lives yet people think it is quite a complicated subject to deal with. The fancy of the subject is such, that many of us fail to understand that it is quite simple, un-complicated and all it talks about is balance. Rather than barging into equations that make us grip with fear, let us start with the basic question of WHAT=WHO? “What” deals with whatever we have in hand or otherwise ASSETS and “Who” deals with the claims, both other’s claims and our own claims on the product we have in hand. Other people’s claims are known as LIABILITIES and our own claim on the product is called Owner’s equity. Now if we take “WHAT=WHO”, it can be translated into the following equation ASSETS= LIABILITIES+OWNER’S EQUITY Accounting: Get Hired Without Work Experience UNDERSTAND WHAT = WHO What = Who Stuff = Who Assets = Who Assets = Who Has Claim Assets = Claims Assets = Other People’s Claims + My Claims Assets = Liabilities + My Claims Assets = Liabilities + My Equity Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Simple Equation to Remember There are two types of claims: other people’s claims and my claims. Assets = Other People’s Claims + My Claims Claims are also referred to as equities. Assets = Other People’s Equities + My Equity. Accountants have a fancy word for other people’s equities. These are known as liabilities. Assets = Liabilities + My Equity Because I am the owner, we will call My Equity Owner’s Equity. Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity This is the formal equation of accounting. The structure of accounting is based on this one perspective. Accounting students memorize it. And try to decipher it. You are way ahead of the game because you understand that what = who! WHAT ARE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES Assets are on the left of the Big T. Asset accounts increase with debits. Liabilities and Owner’s Equity are on the right of the Big T. They increase with credits. Income ultimately increases owner’s equity so it behaves like owner’s equity: it increases with a credit. Expenses increase with debits. The best way to improve your expertise in accounting procedure is to practice; in due course your hand movement and thought process start synchronizing. Examples of Asset accounts – Vehicles, Furniture, Cash Examples of Liabilities accounts- Accounts payable, Owner’s equity Purchasing a TV- Example ASSETS (what) = LIABILITIES + OWNER’S EQUITY (who) Say if you invest Rs.5,000 as down payment from your end and take a loan of Rs.20,000 from the bank to purchase the product. Now, the bank has a claim on your asset to the extent of Rs.20,000 and your claim is Rs.5000. Here liability is Rs.20,000 and Owner’s equity is Rs.5,000. On the asset side we have a TV worth Rs.25,000 You can see that the value of the asset is equal to the value of liabilities, i.e., what = who. ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER’S EQUITY 25,000 = 20,000 + 5,000 Just how you see a hand with five fingered palm on one side and five fingered nails on the other side, this accounting equation has two different perspectives to strike a balance between assets and liabilities. The Big Balancing ‘T’ The Big Balancing ‘T’ BIG “T” FOR PRODUCT PURCHASE WHAT (ASSET) VEHICLES (Rs.25,000) = WHO (LIABILITIES) ACCOUNTS PAYABLE (Rs.20,000) + PAID IN CAPITAL (Rs.5,000) Do I Debit or Credit? When we receive cash for completing a consulting job we know that cash has increased so we debit cash. The corresponding account...










