Posted by Managementguru in Glossary, Strategy
on Mar 5th, 2015 | 0 comments
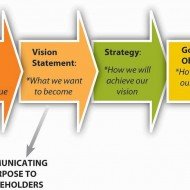
The following is a list of “Key Terms of #Strategic Management” which find their use often when trying to explain the concepts. #Mission An important undertaking that an organization believes it is its duty to do. A specific task or duty assigned to a person or group of people. Missions tend to be long-term and laid out in broad terms, without attempts being made to quantify them precisely. #MISSION STATEMENT Mission statement An open statement of the aims and #objectives of a business or an organization – providing employees with an indication of what they are attempting to achieve through their collective deeds. Mission statements are intended to give substance to the perceived purposes of the organization. Vision Statement A Vision Statement defines what your business will do and why it will exist tomorrow and it has defined #goals to be accomplished by a set date. A Vision Statement takes into account the current status of the organization, and serves to point the direction of where the organization wishes to go. Objective Something which an organization intends to do or achieve; a result that the organization intends to make happen. Long-term or short-term objective, which you hope to achieve within a few years or a few months. Objectives and aims tend to be medium-term and more specific in terms of what is intended to be achieved. SMART OBJECTIVES #Strategy A #plan of future action, usually long-term, in the pursuit of objectives. (e.g.) business strategy; company strategy; financial strategy. The formulation of long-term plans and policies by a firm which inter-connects its various production and marketing activities in order to achieve its business objectives. STRATEGY GENERATION #Aim A result that an organization’s plans or actions are intended to achieve. (e.g.) To try to do something: we aim to be No. 1 in the market in three years’ time. Goal An organization’s aim, objective or purpose. Goals and targets tend to be medium-term or short-term and may be expressed in terms of specific levels of achievements and tend to involve more specific quantification and deadlines. (e.g.) our goal is to break even within twelve months. GOALS VS. OBJECTIVES #Target A level or situation which an organization intends to achieve or aim at. An object or area aimed at the object of an attack or takeover bid. A fixed goal or objective, etc. #Tactics The plans followed to achieve a particular short-term aim. (a) The science and art of disposing and maneuvering forces in combat. (b) The art or skill of employing available means to accomplish an end. (c) A system or mode of procedure TACTICS OR STRATEGY? Plan A set of decisions about how an organization intends to do something, or to ensure that an event or result should happen in the future. Organized way of doing something: contingency plan, government’s economic plans. Plans tend to be quite specific (the shorter-term they are, the more specific they tend to be) and are usually quantified in some detail. They will, in order to ensure that they are complied with, lay out specific deadlines for each key stage. They may also involve the consideration or analysis of priorities and constraints. STRATEGIC PLANNING #Budget A #financial plan, which may be short-term or longer-term, showing probable (planned) #income and #expenditure. Budgets tend to be expressed mainly in monetary terms, although they may focus on the amounts of physical resources (materials, labor time) required. An estimate of income and expenditure for a future period, as opposed to an account, which records financial transactions after the event. BUDGET...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Marketing, Strategy
on Jul 7th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is Portfolio Analysis ? Portfolio Planning is best advised for diversified companies than the more product coherent ones. Portfolio analysis plays a vital role in planning and implementation of various #strategic business units of the organization as a whole. Portfolio planning recognizes that diversified companies are a collection of businesses, each of which makes a distinct contribution to the overall corporate performance and which should be managed accordingly. Companies dealing with a wide #product range and divisions are expected to redefine their strategies for each of the SBU’s or Strategic Business Units. Then they classify these units on a portfolio grid according to the competitive position and attractiveness of a particular product market. What are strategic business units? A strategic business unit is a fully functional and discrete unit of the business that builds its own strategic vision and direction. Within large companies there are smaller specialized divisions that work towards specific projects and #objectives. The strategic business unit, often referred to as an SBU, remains an important element of the company and is accountable to their head office about their operational status. Typically they will operate as an independent organization with a specific focus on target markets and are large enough to maintain internal divisions such as finance, HR, and so forth. Being Strategic: Thinking and Acting with Impact Types of Portfolio Planning: Analytical Planning: Planning is only at the initial level where traditional administrative tools are used. Process Planning: Here planning is a central part of the ongoing #management process and strategic mission is explicit in activities. Advantages of Portfolio Planning: It promotes substantial improvement in the quality of strategies formulated both at the business and corporate levels.It provides a guideline for adopting their overall management process to the needs of each business.It provides selective #resource allocation to the various SBUs.It furnishes companies with a greatly improved capacity for strategic control when portfolio planning is applied intelligently and with attention to its limitations and problems. Since the road to portfolio planning is a long one, companies often face difficulties trying to implement it and cannot realize the full potential of the approach. In implementing portfolio planning, there is a tendency for the focus to be shifted towards #capital investment rather than resource allocation. #Resource Development is the key: Become a Product Manager | Learn the Skills & Get the Job Implementing Corporate Level and Business Level Strategies: Corporate level #strategy is concerned with the strategic decisions a business makes that affect the entire organization. Financial performance, mergers and acquisitions, #human resource management and the allocation of resources are considered part of corporate level strategy.Business level strategy focuses on how to compete in a particular product/market segment or industry. Competitive advantages and distinctive competencies thus become dominant strategic concerns at this level.At the functional level, the primary focus of strategy is efficiency. Boston Consulting Group Matrix: The business policy portfolio models are most popular and useful to understand the firm’s strategic concerns and choices. They define the firm’s scope or domain by highlighting the inter-relatedness of the diverse factors, such as: #Market Growth#Market ShareCash and Cash flow patternsCapital Intensity#Product Maturity BCG Matrix #Stars– Star category represents high growth and high market share– High investments are needed to maintain the share– High cash flow outward movement in this category to maintain status– Usually in the end of the ‘Growth’ #Product Life Cycle stage– Represents emerging and good business for the company, though they need alot of attention and priority #Cash Cows– Represents low growth, high market share– This is the best quadrant of the portfolio as the company basically enjoy the ‘milk’ of success– This is where the...

Posted by Managementguru in Marketing, Principles of Management, Project Management, Strategy, Technology
on Mar 25th, 2014 | 0 comments

Research and Development – Strategic Key for Competitive Advantage Product Innovation and Process Improvement: With the increasing pace of liberalization and ferocity of competition in the corporate business world, it is mandatory for the firms to invest in research and development activities to sustain in the market. In most of the developing countries, scant attention has been paid to research and development activities. A survey indicates that countries like Japan and United States of America spend 2.8 percent of their Gross National Product on R and D, while it is a mere 0.9 percent of the Gross Domestic Product in the case of some Asian countries. What role does research & development play in the industry and economy? Why it is important for the developing countries to invest more on R and D? In spite of the tax rebate offered by most of the governments for R and D, why industries don’t contribute much to indigenous research? Global Competition: It becomes difficult for business organisations to compete in national and international markets both on quality and cost fronts, primarily because of absence of strong base in science and technology. Third world nations are used to buying technology from developed nations, that make them dependent and technology starved. Limited resource is another problem faced by these business firms, the allocation of which becomes difficult owing to rising costs. Invasion of Multinational and Trans national Giants: Another serious aspect to be considered is the invasion of multinational and transnational giants in every sector due to liberalization, globalization and privatization policies of the developing nations. This leads to panic in the industry, as a result of which, the business firms either go for forged alliances or infuse large amounts of funds into R and D activities hurriedly, both of which is a futile exercise to protect themselves from the onslaught of transnational companies. Science and Technological Advancement: The wiser move for the business firms to withstand the competition on an international level, would be to build their empires on a sustainable basis, by honoring the scientific and technological efforts. A thorough knowledge of all the research activities progressing around the world proves useful in managing their activities and operating with limited resources. This demands a long term plan that will support, strengthen and nurture the specified area of science base selected for research and development. Research Management: A well devised research management programme will help the business firms to formulate short and long term technical plans that aid in the research programme. It is very important for a country to encourage the budding population to become more research oriented, that will help the nation prosper in terms of science and technology, besides which, it also helps in the growth of one’s own economy. Chanakya’s 7 Secrets of Leadership The Research and Development strategic management lays emphasis on formulating plans, that support the short and long term objectives of a business firm, by employing innovative minds in the process and periodically reviewing and restructuring strategies in the light of changing demands of the society. The focus of an R and D manager should be on appraisal of technological and competitive environment, assessment of corporate strengths and weaknesses and making strategic decisions, while formulating R and D...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
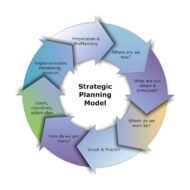
STRATEGIC PLANNING Strategic planning is the primary step in the process of strategic management [Strategic management is a comprehensive topic that covers almost all the functional aspects of the organization] which can be outlined from at least two perspectives: First, strategy is the “broad programme for defining and achieving the objectives of an organization and implementing its mission”. Secondly, “It is the pattern of the organization’s response to the external environment over a period of time”. A strategy that takes a broad and typically long range focus is called strategic planning. MBA Application Strategies for Top Business Schools Strategic planning is the process that classifies the long range goals of the organization and opts for the precise means (strategies and polices) for achieving these goals, allocates resources, and develops long range plans to reach the destination. Watch this Video to Understand the Overview of Strategic Planning Process Time-Horizon: Strategic planning takes into account the extended time horizon. There may not be any immediate impact out of strategic planning, but the consequences in the long-run prove to be gradual and significant as well. It provides with the necessary action plans to make a difference in vital areas concerning development. You can always associate innovativeness with strategy since it explores new paradigms and tries to enhance the impact. When the size of organizations expands, they are broken down into strategic business units (SBU’S) for the purpose of functional excellence. These units are expected to operate as if they were relatively independent businesses. WHY STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP IS IMPORTANT A Tailor Made Approach: A tailor made approach is essential when it comes to strategy development the systematic analysis of the factors associated with customers and competitors (the external environment) helps the organization to meet the challenges of modern society. More and more organizations are focusing on formal approaches and concepts for planning their long range process. Specifically these challenges are a result of increasing rate of change, the complexity of manager’s jobs, the increasing importance of fitting the organization into external environment, and the increasing lag between the preparation of plans and their implementation in future. Resource Allocation: Strategic planning is an organization’s process of defining its strategy or course, and making decisions on resource allocations to pursue this strategy. Managers must be adequately geared up for strategic planning. The goals of the organization must be made plain and not unclear. Each business unit should be categorized based on its performance level to decide on the resource share to be allocated. You need to infuse cash flow into ineffectual units and divest funds from dying units into other profitable ones. The ultimate aim is to build up star performers that will be the perennial source of income or revenue generation. There should be a strong linkage between planning and control. The assessment of strategic plans of the business units must be made periodically and effectively. TOP FIVE REASONS WHY STRATEGIC PLANS FAIL SWOT Analysis: SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses/Limitations, Opportunities, and Threats. Planning is the primary step for control as it provides several standards and benchmarks of control. Planning extracts commitment. Some times planning highlights the objectives only and the planning premises may not be fully reliable. Threats are to be considered as challenges and must be converted into opportunities. Two heads are better than one is the philosophy of brain storming where a group of people with knowledge and expertise assemble to lay out clear plans that will steer the organization smoothly even in times of rough...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Strategic Evaluation: concerns mainly the analysis and judgment of interventions at the level of strategic goals. One of the noteworthy aspects of strategic evaluation consists of the verification of the adopted strategy with respect to the current and likely social and economic situation. How a firm has performed over time and relatively to its competitors, can be determined with the help of the following quantitative measures. Market price of the sharesMarket shareEarnings on capital employedDividend ratesReturn on equityGrowth in sales volumeProduction costs and efficiencyDistribution costs and efficiencyEmployee turnover, absenteeism, and satisfaction indices. Since there is a high correlation between progress and these indicators, we can say that a firm is successful if majority of the factors show a positive signal. But in reality, one cannot expect a business firm to satisfy all the above mentioned criteria, as performance is also affected by unexpected variations in the external environment. One has to trade-off between the positive and negative indicators and find suitable ways to enhance the performance levels. Effectiveness of a Strategy: The strategic importance of any particular criterion may not remain the same at different points of time. The short run and long run effectiveness of strategy cannot be evaluated using the same criteria. There may be difficulties in computation and different methods of computation that may be encountered in measurement. These factors serve as the bases for firms to identify the elements of success. Yet another way of performance evaluation is to identify critical factors that may be regarded as symptoms of decline and can be treated as early warning signals during the implementation of strategy. If they indicate the necessity of a turnaround or retrenchment strategy, the firm should definitely go for a suitable action without further delay. Such factors may be: Declining profit marginDeclining market shareRapidly increasing debtDeclining working capitalIncreasing managerial turnover What is the Need for Strategic Evaluation? You might be curious to know, what is the need for a strategic evaluation at all in the first instance? See, business firms and corporate companies are always in a position to execute their action plans in the wake of severe competition and retention of market share. A plan without a strategy is like life without a soul and decision making is solely dependent upon strategic inputs. Turnaround Strategy The need for feedback, appraisal and reward, check on the validity of strategic choice congruence between decisions and intended strategy all these help in successful culmination of strategic management process and create inputs for new strategic planning. What’s the difference between Strategy and Tactic? The evaluation need not be based only on quantitative terms, but also on qualitative aspects such as: internal consistency, consistency with the environment, appropriateness of the strategy in the light of available resources, acceptability of the degree of risk involved in the strategy, appropriateness of the time horizon of the strategy...










