The following is a list of “Key Terms of #Strategic Management” which find their use often when trying to explain the concepts.
An important undertaking that an organization believes it is its duty to do. A specific task or duty assigned to a person or group of people. Missions tend to be long-term and laid out in broad terms, without attempts being made to quantify them precisely.
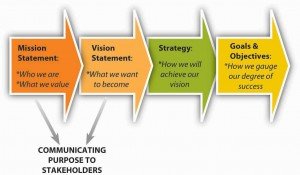
Mission statement
An open statement of the aims and #objectives of a business or an organization – providing employees with an indication of what they are attempting to achieve through their collective deeds. Mission statements are intended to give substance to the perceived purposes of the organization.
Key Terms of Strategic #Management
Vision Statement
A Vision Statement defines what your business will do and why it will exist tomorrow and it has defined #goals to be accomplished by a set date. A Vision Statement takes into account the current status of the organization, and serves to point the direction of where the organization wishes to go.
Objective
Something which an organization intends to do or achieve; a result that the organization intends to make happen. Long-term or short-term objective, which you hope to achieve within a few years or a few months. Objectives and aims tend to be medium-term and more specific in terms of what is intended to be achieved.
A #plan of future action, usually long-term, in the pursuit of objectives. (e.g.) business strategy; company strategy; financial strategy. The formulation of long-term plans and policies by a firm which inter-connects its various production and marketing activities in order to achieve its business objectives.
A result that an organization’s plans or actions are intended to achieve. (e.g.) To try to do something: we aim to be No. 1 in the market in three years’ time.
Goal
An organization’s aim, objective or purpose. Goals and targets tend to be medium-term or short-term and may be expressed in terms of specific levels of achievements and tend to involve more specific quantification and deadlines. (e.g.) our goal is to break even within twelve months.
A level or situation which an organization intends to achieve or aim at. An object or area aimed at the object of an attack or takeover bid. A fixed goal or objective, etc.
The plans followed to achieve a particular short-term aim.
(a) The science and art of disposing and maneuvering forces in combat.
(b) The art or skill of employing available means to accomplish an end.
(c) A system or mode of procedure
TACTICS OR STRATEGY?Plan
A set of decisions about how an organization intends to do something, or to ensure that an event or result should happen in the future. Organized way of doing something: contingency plan, government’s economic plans. Plans tend to be quite specific (the shorter-term they are, the more specific they tend to be) and are usually quantified in some detail. They will, in order to ensure that they are complied with, lay out specific deadlines for each key stage. They may also involve the consideration or analysis of priorities and constraints.
A #financial plan, which may be short-term or longer-term, showing probable (planned) #income and #expenditure. Budgets tend to be expressed mainly in monetary terms, although they may focus on the amounts of physical resources (materials, labor time) required. An estimate of income and expenditure for a future period, as opposed to an account, which records financial transactions after the event.