Posted by Managementguru in Glossary, Strategy
on Mar 5th, 2015 | 0 comments
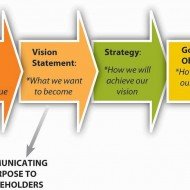
The following is a list of “Key Terms of #Strategic Management” which find their use often when trying to explain the concepts. #Mission An important undertaking that an organization believes it is its duty to do. A specific task or duty assigned to a person or group of people. Missions tend to be long-term and laid out in broad terms, without attempts being made to quantify them precisely. #MISSION STATEMENT Mission statement An open statement of the aims and #objectives of a business or an organization – providing employees with an indication of what they are attempting to achieve through their collective deeds. Mission statements are intended to give substance to the perceived purposes of the organization. Vision Statement A Vision Statement defines what your business will do and why it will exist tomorrow and it has defined #goals to be accomplished by a set date. A Vision Statement takes into account the current status of the organization, and serves to point the direction of where the organization wishes to go. Objective Something which an organization intends to do or achieve; a result that the organization intends to make happen. Long-term or short-term objective, which you hope to achieve within a few years or a few months. Objectives and aims tend to be medium-term and more specific in terms of what is intended to be achieved. SMART OBJECTIVES #Strategy A #plan of future action, usually long-term, in the pursuit of objectives. (e.g.) business strategy; company strategy; financial strategy. The formulation of long-term plans and policies by a firm which inter-connects its various production and marketing activities in order to achieve its business objectives. STRATEGY GENERATION #Aim A result that an organization’s plans or actions are intended to achieve. (e.g.) To try to do something: we aim to be No. 1 in the market in three years’ time. Goal An organization’s aim, objective or purpose. Goals and targets tend to be medium-term or short-term and may be expressed in terms of specific levels of achievements and tend to involve more specific quantification and deadlines. (e.g.) our goal is to break even within twelve months. GOALS VS. OBJECTIVES #Target A level or situation which an organization intends to achieve or aim at. An object or area aimed at the object of an attack or takeover bid. A fixed goal or objective, etc. #Tactics The plans followed to achieve a particular short-term aim. (a) The science and art of disposing and maneuvering forces in combat. (b) The art or skill of employing available means to accomplish an end. (c) A system or mode of procedure TACTICS OR STRATEGY? Plan A set of decisions about how an organization intends to do something, or to ensure that an event or result should happen in the future. Organized way of doing something: contingency plan, government’s economic plans. Plans tend to be quite specific (the shorter-term they are, the more specific they tend to be) and are usually quantified in some detail. They will, in order to ensure that they are complied with, lay out specific deadlines for each key stage. They may also involve the consideration or analysis of priorities and constraints. STRATEGIC PLANNING #Budget A #financial plan, which may be short-term or longer-term, showing probable (planned) #income and #expenditure. Budgets tend to be expressed mainly in monetary terms, although they may focus on the amounts of physical resources (materials, labor time) required. An estimate of income and expenditure for a future period, as opposed to an account, which records financial transactions after the event. BUDGET...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
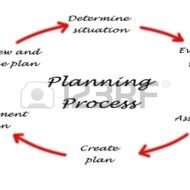
Nature of Organizational Planning What is Planning? “Planning is an intellectual process, the conscious determination of courses of action, and is a continuous process of decision making with built in flexibility.”- Herold Koonz and Weirich Planning is the most basic and primary of all management functions on the premise of which other functions evolve. It would be appropriate to compare planning to the basement or foundation of a building upon which the entire system rests. Planning bridges the gap from where we are to where we want to go. Planning involves selecting the best objectives and deciding on the suitable course of action. When we talk about planning, control is another entity that tags along like inseparable two-sides of a coin. Without planning there is no control and without control planning becomes meaningless. NATURE OF PLANNING: Prime function of management: Planning is the key to all other functions of management like organizing, leading, staffing and controlling. Is a continuous process: Plans need periodic review in the wake of external environment and internal resource potential and thus is a continuous process. Is an intellectual process: What is to be done, when, who and how are the very important questions that loom before a manager before making every decision. He has to use his intellect in order to make the right plans before acting. Is all pervasive: It penetrates right from the top to the bottom level of management, but it is the responsibility of the managers or executives at the top level to make the right moves at the right time. Is flexible: One has to understand that flexibility is restricted when it comes to irretrievable costs already incurred in fixed assets, training, advertising etc. Is goal oriented: Planning starts with setting up of objectives and completely goal oriented. TYPES OF PLANS: Purpose or Missions: Basic task of an organization. For example, teaching and research can be attributed as the basic function of an educational institution; the purpose of business is to produce, distribute goods and make a surplus. Objectives: These are the goals that have to be accomplished by the organization. Corporate companies chart out their production plan well in advance to meet the requirements on time. For this they break the objectives into short term goals i.e., for a quarter based on the sales forecast. This kind of planning gives clarity and direction for the production team to achieve the goals. Strategies: These are the set of action plans designed in order to achieve the future objectives backed up by long term perspective in the wake of environmental analysis and give direction in which the resources have to be channelized. Policies: These are basically the guideline books that direct the course of the organization’s function as what to do and what not to-do. They see to that the decisions made fall well within certain boundaries in order to ensure fair and equitable treatment to all the employees. HR policies govern all the functions related to pay, promotion and other disciplinary mechanisms related to the work force. Procedures: They are programmes designed to carry out the activities of the organization in a specified manner. The procedures for placing a purchase order, payment collection etc., Programmes: A programme is the sum total of goals, policies, procedures, rules, task etc., For example, new product development may be cited as a major programme while promotional campaign may be cited as a supporting programme. Budget: No plan is feasible without a budget allocated to it. A budget is a numberised programme and more of a control device. Revenue budgets, expense budgets, production budgets to name a few. Zero base budget: This kind of budget does not take into account the previous year’s performance record or budget but treats every progarmme afresh and starts working from ground up. Each programme is treated as a separate...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments

What forms the Basis for your Investment Decisions? Profit seeking is the ultimate aim of corporate management and the finance manager acts as the anchor point of the management structure. He has to provide specific inputs into the decision-making process, with respect to profitability. Corporate Investment Decisions Cost control What are the Cost Centres? It is the finance manager’s responsibility to have an eagle’s eye on rising costs by continuously monitoring the cost centers of his organization. Production department where there is always a need for additional resources or inflow of funds, should be his first target of contol. Costs are incurred by each and every department of an organization, namely, the production, marketing, personnel and of course finance and accounting. It is a difficult task to control the rising costs. That is the reason why, big corporate companies go for annual budget formulation at the start of the year and reformulates the finance plan by comparing actual with the projected figures. This kind of evaluation helps the firm to fix responsibilities for various centers of operation. Resource Allocation A finance manager is the first person to recognize rising costs for supplies or production, and he can make immediate recommendations to the management to bring back costs under control. While cost control talks about allocating resources to different responsibility centers in the desired proportion, cost reduction focuses on conserving the resources. Cost reduction can be achieved through modifying product and process designs, cutting down throughput time, doubling labor productivity, mass customization, standardistion etc., Pricing Price Fixation It is always a joint venture between marketing and finance departments when it comes to price fixation of products, product lines and services. Pricing decisions are important in that, they affect market demand and the company’s competitive stand in the market. Pricing strategies have to be evolved in the wake of existing competitor strategies and market preference. The demand forecast is the prerequisite factor of the production process and in-depth market analysis and understanding is inevitable on the part of the executives. Future Levels of Profit The finance manager is also responsible for charting out the future levels of profit, based on the relevant data available. He has to consider the current costs, likely increase in costs and likely changes in the ability of the firm to sell its products at the established selling prices. So, it becomes clear that, such market evaluation cannot be periodical, as the market is highly dynamic and has to be done in a day-to-day basis. Before a firm commences a project, its discounted future fund flow and expected profits must be ascertained which will serve as a basis for comparison. Risk versus Return: Investment decisions always are risky as the gestation period of invested funds is very long and not to return immediately. Further, the firm has to calculate the time period in which its initial investment can be recovered and the feasibility of the rate of return on its investment. Fund Management The finance manager is engaged in activities like, mobilization of funds, deployment of funds, and control over the use of funds and also he is to evaluate the risk return trade-off. Profit maximization is the fundamental objective of any organization and the finance manager plays a key role in restructuring the financial philosophy of a firm to take it to greater...






