Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
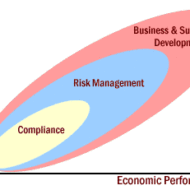
There is no Business Success Without Risk What is the Risk of Taking a Chance in a Business Activity? Business is often viewed as a game or a gamble in which success is always at risk. Think about it, risk is present in every sphere and aspect of our lives and even when you are not running a business. So why the fuss? A thorough knowledge and research of the business activity you are about to perform will give you the needed confidence to go about it. A true business man is an entrepreneur who treats risk as an opportunity rather than a challenge. Business organizations are started with a single purpose, to make profit and then more profit. Only when the organizations grow, there comes the awareness and necessity to think about stakeholders’ interest and working towards a social cause. Initial stages definitely pose threats for the very survival of the organization. Risk is an inherent part of a business as you are not sure about the outcome of your business activity. What are the Chances or Probability? We talk more about probability and chance outcomes when you deal with a particular product. Retail segment is one area where the risk of duplication is high and people have to be cautious and careful in order to protect their copyrights and symbols from being replicated. Mild inflations can benefit the market but recessions put you in doldrums especially if you are dependent on a wholesaler or a manufacturer. Risk can aspect itself in the following ways: Economically- Attrition and effects of global economy Legally- Labor laws and enactments Socially- Expectations from the public in general Government rules and regulations- Government policies and export duties Stakeholder expectations- Wealth maximization and assured profits Environmental – Need to comply with changing standards like waste affluent treatment plants Political scenario- Effects due to changing governments Risk and Uncertainty Risk and uncertainty go hand in hand and you need a risk management template or a model for your reference to solve or manage risks. The first and foremost step would be to identify the risks in your sphere of business activity. Risk documentation or creating a risk profile is an inevitable move for a new organization. This prepares the organization mentally to face challenges in a structured manner and reduces disorientation. It is very important to keep in mind the organisation’s objectives while documenting the risk profile to keep your focus unaltered. Risks evolve continuously and it is the responsibility of the top management to be in line with the market economy to manage the adverse conditions that come in the way. How to Manage Risks? Risk management is an ongoing and continuous process and it cannot be looked upon as a distinct area to be managed by a set of individuals. In a small and upcoming organization the responsibility lies on the shoulders of each and every individual to self assess, evaluate and manage risks and find the right kind of solution that will not be detrimental to the core objectives of the organization. Bigger organizations can afford to have expert opinion by commissioning PROFESSIONALS to identify, assess and manage risks. An overall and broad perspective of risk is what has been analysed here. There are numerous possibilities of risks, whether big or small in magnitude, affecting an organization. A thorough study of the field you are about to venture into, the pros and cons of the business activity, time of launch are few things that will help you to analyse what the market niche warrants for and act accordingly. In further segments, let us look into the factors of risk, identifying and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Management, Principles of Management, Project Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
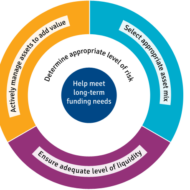
What is Business Risk? It is a term that explains the difference between the expectation of return on investment and actual realization. In CAPITAL BUDGETING, several alternatives of investments are examined before taking an investment decision and only then the Managing Director of the firm along with financial executives gear up for investing in a project that is sound and feasible. Even then the project may not become viable owing to the fluctuations in the economic environment. Money Manipulation So, the million dollar question arises, whether to invest and if invested, will it fetch me profit? See, you cannot have the cake and eat it too. Risk factor prevails in all kinds of environment and we try to over react in a business arena since it involves huge investments. But remember, MONEY WILL MULTIPLY IF YOU MANIPULATE IT WITH CARE. Business firms commit large sums of money each year for capital expenditure. It is therefore essential that a careful FINANCIAL APPRAISAL of each and every project which involves large investments is carried out before acceptance or execution of the project. These capital budgeting decisions generally fall under the consideration of highest level of management. Factors of risk to be considered before investing: Time value of money Pay back period Rate of return on investment(ROI) Uncertainties in the market Cost of debt Cost of equity Cost of retained earnings Factors to be monitored after investing: Maximising profit after taxes Maximizing earnings per share Maintaining the share prices Issue of dividends Ensuring management control Financial structuring Cost of capital refers to the opportunity cost of the funds to the firm I. e., the return on investment to the firm had it invested these funds elsewhere. Servicing the debt and Danger of Insolvency While making the decisions regarding investment and financing, the Finance Manager seeks to achieve the right balance between risk and return. If the firm borrows heavily to finance its operations, then the surplus generated out of operations should be sufficient to “SERVICE THE DEBT” in the form of interest and principal payments. The surplus would be greatly reduced to the owners as there would be heavy Debt Servicing. If things do not work out as planned, the situation becomes worse, as the firm will not be in a position to meet its obligations and is even exposed to the “DANGER OF INSOLVENCY“. Working Capital Management Considering all these factors, we have to come to the conclusion that FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT is like the BACKBONE of a business firm and WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT will be the blood flow infused into the body. Risks are inherent in a business environment whose management is quite possible with the right kind of farsightedness and planning. Luck does not favor anybody who is poor in planning and lack hard...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
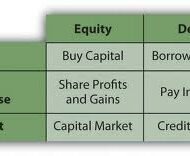
What is your Capital Structure Make up A company in course of charting out its financial schema has to take into account two things. 1) The amount of capital to be raised. 2) Make-up of the capital. Decisions regarding the composition or capitalization are reflected in capital structure. Capital structure of a firm is a combination of debt and equity, which supports long term financing of the firm. The pattern of capital structure has to be planned very carefully by the finance manager in such a way that it minimizes the cost of capital and maximizes value of stocks, thus protecting the interest of the share holders. What is the right capital mix? There needs to be a right mix of different securities in total cpaitalisation that facilitates control, flexibility and maneuverability. From a broad perspective, following are the three fundamental ways in which the schema of capital structure is finalized: Financing purely or exclusively by equity Financing by equity and preferred stock Financing by equity, preferred stocks and bonds. Which of the above most suits a firm depends on multifarious internal and external factors within which a firm operates. Equity: A firm can raise substantially large amount of fund by issuing different types of shares. The money thus raised is a permanent source of resource and without any obligation to refund to the respective owners. Small and growing companies go for equity fund raising as no banks or other financial institutions are prepared to fund these firms in lieu of poor credit worthiness. Even big corporate firms opt for issuing equities when there is a need to raise large sums. But smaller firms, whose major share of capital comprises of common stock, have to be careful, in that, some large concerns might become interested in controlling these stocks. Picture Courtesy : GrowthFunders The one big advantage of equity shareholders is that they are free to trade the shares in the market. They can sell the shares to anybody at any time and if the market warrants, at a higher price. One has really nothing to lose, if he is planning to invest in equities. On the other hand, if the company goes bankrupt, the share holders stand a chance to receive only the residual amount, after the creditors’ claims are cleared and satisfied. What’s in it for Investors? Debt: Debt has a maturity date upon which the stipulated sum of principal is repaid. It places the burden of obligation on the shoulders of the company in the form of periodical interest settlements and principal repayments. Creditors can go for legal action if the company defaults in payment of the assured sum on the specific date. That’s why companies think twice before they go for issuing debentures and other bonds. One good thing for the company is that, it can avail tax rebate on the securities of debt, but at the other end it has to satisfy the interest payments and factorise the cost of capital. Cost and Control Principles Cost principle supports induction of additional doses of debt, but it might prove risky, if the company is not able to service the additional debt. Control principle supports the issue of bonds in order to tighten the rein of ownership, but maneuverability principle discounts this and favors issue of common stock to reduce the interest burden. Four factors are important in the purview of the finance manager, cost, risk, control and timing. He should be able to evolve a pattern that satisfactorily brings a compromise among these conflicting factors, which are then assigned weights in the wake of economic and industrial...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments

What forms the Basis for your Investment Decisions? Profit seeking is the ultimate aim of corporate management and the finance manager acts as the anchor point of the management structure. He has to provide specific inputs into the decision-making process, with respect to profitability. Corporate Investment Decisions Cost control What are the Cost Centres? It is the finance manager’s responsibility to have an eagle’s eye on rising costs by continuously monitoring the cost centers of his organization. Production department where there is always a need for additional resources or inflow of funds, should be his first target of contol. Costs are incurred by each and every department of an organization, namely, the production, marketing, personnel and of course finance and accounting. It is a difficult task to control the rising costs. That is the reason why, big corporate companies go for annual budget formulation at the start of the year and reformulates the finance plan by comparing actual with the projected figures. This kind of evaluation helps the firm to fix responsibilities for various centers of operation. Resource Allocation A finance manager is the first person to recognize rising costs for supplies or production, and he can make immediate recommendations to the management to bring back costs under control. While cost control talks about allocating resources to different responsibility centers in the desired proportion, cost reduction focuses on conserving the resources. Cost reduction can be achieved through modifying product and process designs, cutting down throughput time, doubling labor productivity, mass customization, standardistion etc., Pricing Price Fixation It is always a joint venture between marketing and finance departments when it comes to price fixation of products, product lines and services. Pricing decisions are important in that, they affect market demand and the company’s competitive stand in the market. Pricing strategies have to be evolved in the wake of existing competitor strategies and market preference. The demand forecast is the prerequisite factor of the production process and in-depth market analysis and understanding is inevitable on the part of the executives. Future Levels of Profit The finance manager is also responsible for charting out the future levels of profit, based on the relevant data available. He has to consider the current costs, likely increase in costs and likely changes in the ability of the firm to sell its products at the established selling prices. So, it becomes clear that, such market evaluation cannot be periodical, as the market is highly dynamic and has to be done in a day-to-day basis. Before a firm commences a project, its discounted future fund flow and expected profits must be ascertained which will serve as a basis for comparison. Risk versus Return: Investment decisions always are risky as the gestation period of invested funds is very long and not to return immediately. Further, the firm has to calculate the time period in which its initial investment can be recovered and the feasibility of the rate of return on its investment. Fund Management The finance manager is engaged in activities like, mobilization of funds, deployment of funds, and control over the use of funds and also he is to evaluate the risk return trade-off. Profit maximization is the fundamental objective of any organization and the finance manager plays a key role in restructuring the financial philosophy of a firm to take it to greater...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Training & Development
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
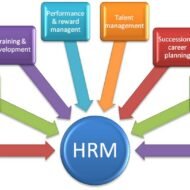
Definitions of Human Resource Management: 1. “A series of integrated decisions that govern employer-employee relations. Their quality contributes to the ability of organisations and employees to achieve their objectives.” (Milkovich & Boudreau, 1997). 2. “Concerned with the people dimension to management. Since every organisation comprises people, acquiring their services, developing their skills, motivating them to higher levels of performance and ensuring that they continue at the same level of commitment to the organisation are essential to achieving organisational goal. This is true, regardless of the type of organisation: viz. government, business, education, health, recreation, or social action.” (Decenzo & Robbins, 1989). 3.”The planning, organising directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, integration, and maintenance of human resource to the end those individual, organisational, and social objectives are accomplished.” (Flippo, 1984). 4. “The organisation function that focuses on the effective management, direction, and utilisation of people; both the people who manage produce and market and sell the products and services of an organisation and those who support organisational activities. It deals with the human element in the organisation, people as individuals and groups, their recruitment, selection, assignment, motivation, empowerment, compensation, utilisation, services, training, development, promotion, termination and retirement.”(Tracey,1994 ) Knowledge Workers Human resource management is therefore understood as the all significant art and science of managing people in an organisation. Increasing research output in behavioral sciences, new trends in managing ‘knowledge workers’ and advances in training methodology and practices have led to substantial expansion of the scope of human resource management function in recent years. HRM is not just an arena of personnel administration anymore but rather a central and pervasive general management function involving specialised staff as assistants to main line managers. Managing employee relationships is the role of the Human Resource department Human Resource Management is a process of valuing and developing people at work, this includes: Recruitment and selection Employee communication and engagement (participation) to increase employee retention Training and development Leadership WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST WEAKNESS Labour turnover & staff retention Labour turnover refers to the proportion of a workforce that leave during a period of time (usually one year) Labour turnover = number of staff leaving during the period x 100 average number of staff Staff retention refers to the ability of a firm to keep its workers. The disadvantages of having a large proportion of staff leaving each year include: The cost of recruiting replacement workers The cost of training the new workers Loss of productivity whilst replacements are found Loss of experienced workers Negative impact on reputation WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST STRENGTH Methods to control turnover: 1. Financial methods of motivation Bonuses Profit share Fringe benefits 2. Non financial methods of motivation Employee engagement and empowerment Training and development Promotion opportunities 3. Improved Human Resource Management procedures Four Fundamental Principles of HRM: Human Resource is the organisation’s most important asset; Personnel policies should be directed towards achievement of ENTERPRISE goals and strategic plans; Corporate culture exerts a major influence on achievement of excellence and must therefore be strengthened with consideration of employee welfare. Whilst integration of corporate resources is an important aim of HRM, it must also be recognised that all organisations are ‘pluralist societies’ in which people have differing interests and concerns, which they defend and at the same time function collectively as a cohesive group. →Evolution of...










