Currently Browsing: Financial Accounting
Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting
on Apr 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
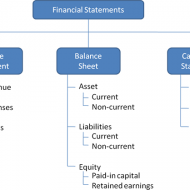
Ratio Calculation From Financial Statement Profit and Loss a/c of Beta Manufacturing Company for the year ended 31st March 2010. Exercise Problem1 Kindly download this link to view the exercise. Given in pdf format. You are required to find out: a) #Gross Profit Ratio b) #Net Profit Ratio c) #Operating Ratio d) Operating #Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio a. GROSS FORFIT RATIO = Gross profit ÷ #Sales × 100 = 50,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 31.25 % b. #NET PROFIT RATIO = Net profit ÷ Sales × 100 = 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 17.5 % c. OPERATING RATIO = #Cost of goods sold + Operating expenses ÷ Sales × 100 Cost of goos sold = Sales – Gross profit = 1,60,000 – 50,000 = Rs. 1,10,000 Operating expenses = 4,000 + 22,800 + 1,200 = Rs. 28,000 Operating ratio = 1,10,000 + 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 86.25 % d. OPERATING NET PROFIT TO NET SALES RATIO = Operating Profit ÷ Sales × 100 Operating profit = Net profit + Non-Operating expenses – Non operating income = 28,000 + 800 – 4,800 = Rs. 32,000 Operating Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio = 32,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 20 % What is a Financial statement? It is an organised collection of data according to logical and consistent #accounting procedure. It combines statements of balance sheet, income and retained earnings. These are prepared for the purpose of presenting a periodical report on the program of investment status and the results achieved i.e., the balance sheet and P& L a/c. Objectives of Financial Statement Analysis: To help in constructing future plans To gauge the earning capacity of the firm To assess the financial position and performance of the company To know the #solvency status of the firm To determine the #progress of the firm As a basis for #taxation and fiscal policy To ensure the legality of #dividends Financial Statement Analysis Tools Comparative Statements Common Size Statements #Trend Analysis #Ratio Analysis Fund Flow Statement Cash Flow Statement Types of Financial Analysis Intra-Firm Comparison Inter-firm Comparison Industry Average or Standard Analysis Horizontal Analysis Vertical Analysis Limitations Lack of Precision Lack of Exactness Incomplete Information Interim Reports Hiding of Real Position or Window Dressing Lack of Comparability Historical...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments

Management Vs. Financial Accounting Management Accounting : The process of preparing management reports and accounts that provides accurate and timely financial and statistical information to the management Financial Accounting : The purpose of accounting is to provide the information that is needed for sound economic decision making concerned with classifying, measuring and recording the transactions of a business. What is Management Accounting: Management accounting is the updated version of what you call financial accounting and the most circulated term in corporate business arena. Management involves planning, organizing, staffing, leading and controlling the resources available in an organization, namely the physical and human resources. Much importance is given to personnel management as they are the priceless assets of any organisation.But it is equally important for a firm to record all its business transactions for future reference and tax audits. Thus the necessity of accounting comes into the fray. Financial Statements Made Easy Functional Difference: Well, accounting means something to do with finance. So, what is the big difference, if it is financial or management accounting? One difference is in the title, and the other in their function. The rationale behind financial accounting is statutory, done for the benefit of shareholders, customers, government regulatory agencies, other external agencies, potential investors and the like. It records all business transactions that are purely monetary in nature and no further analysis is done. Essential for Management Planning: Management accounting is voluntary and reports are prepared to meet the internal needs of management. We talked about planning, for which interpretation and analysis of such quantitative data and other inputs becomes necessary to plan for future needs of management. The main functions being attention direction and problem solving, management accounting is primarily concerned with providing information relating to the various aspects of a business, like cost or profit associated with some portions of business operations. It employs techniques such as standard costing, budgeting, marginal costing, break- even analysis and so on., Inputs also stem from industry data, competitor data, published reports by public and private agencies and research studies findings, thus widening its scope for improvement in business operations. Financial Accounting: Financial accounting is restricted to deal only with “generally accepted accounting principles” and any deviation is considered to be errors for correction. Though it provides valid and authentic information, it lacks timeliness. The former restricts the accountant to a mere book-keeper while the latter transcends the role of the accountant to that of total business information technologist. Here he becomes an evaluator of different functional areas like marketing, production, purchase and personnel. As modern business is huge in size, complex, diversified and decentralized in terms of operations, financial accounting just does not fill the bill, as information is required as when an event happens at various hierarchical levels of an organisation. This infographic from Goodaccountants.com details the industries that employ the most accountants and auditors, and the results are very interesting! Management accounting is inter disciplinary in character and derives inspiration from organizational theory, economics, behavioral sciences, statistics and management. Although the paraphernalia required for management reporting is complex and expensive, it is worth the try, as it tries to compare and contrast the actuals with the standards and bring out variances if any. This is quite useful in determining the cost-effectiveness of a particular project or to be prepared for suitable action. Management accounting is nothing but a management information system where the managers have to be techno-savvy in order to handle the total information resource and project it suitably to the management to take timely actions for the increase in growth, profit and sustainability of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments

An Analysis to Understand the Art of Accounting Objectives of an Accountant: The pure objective of an accountant would be to record all business transactions that are monetary in nature, in order to ascertain if the company has earned profit or suffered loss during a financial year. The financial position of the company as on a particular date can thus be understood from the accounting journals and ledgers. We are talking about the conventional purpose of accounting. But with the lapse of time, more and more is being expected from accounting, in that, it has to meet the demands and requirements of tax authorities for the purpose of income tax and sales tax returns, government regulations, investors, owners and the management. Thus it can be aptly defined as the art of recording, classifying and summarizing events in a significant manner, that involve money transactions and/ or events that are of financial character, for interpretation. Systematic records for future reference: Book keeping is an accounting practice that tells us how to keep a record of financial transactions. A firm deals with its customers and suppliers, where numerous business transactions take place every day. It is not possible for us to remember every transaction, which we might need it for our reference at a future date. Especially, if it happens to be a credit sale, definitely the necessity of systematic book keeping arises. The owner would like to know, what amount is due from whom, from time to time. To know the financial position of the firm: Every merchant is in business to earn profits. So systematic recording of factual and financial information will facilitate the owner to understand where he stands financially at the end of a financial year, what is his net profit and to pull the ropes tight if credit margin is wide. Further more, he can also understand the nature of his business growth by comparing the accounting records of two consecutive years. Taxation purposes: Some people evade tax, but no one can avoid tax. The main source of revenue generation for government is tax payments from business merchants and corporate companies. You need to pay a percentage as tax, in accordance with profit arising from sales. The accounting records that you maintain contain facts that are taken into account by the taxation authorities as a basis for assessment. https://amzn.to/2sl5aL7 Good evidence in the court of law: To prove your genuinity, in case of some disputes between yourself and the customer or supplier, your records and vouchers, if authentic and valid, are going to speak for you in the court of law as solid evidence. Accounting also answers some of these questions: How well the different departments of business have performed all along? What is the most profitable product line? What are the products whose production has to be increase and what is to be stopped in order to avoid losses? Is the cost of production reasonable or excessive? Is there a need to revise policy decisions to improve the profitability? What will be the future plans of business in the wake of existing results presented to the management? Overall, is the firm proceeding towards the right direction in terms of productivity, profitability and growth? Accounting is not only about recording and classifying, the interesting features being analysis and interpretation, which are the key factors for the development of the organization as a whole. Note: The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG),is the head of the Supreme Audit Institution of India (SAI) CAG is the sole auditor of the accounts of the Central (Union) Government and the State Governments. CAG is also responsible for the audit...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
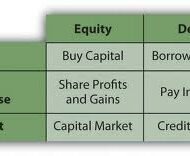
What is your Capital Structure Make up A company in course of charting out its financial schema has to take into account two things. 1) The amount of capital to be raised. 2) Make-up of the capital. Decisions regarding the composition or capitalization are reflected in capital structure. Capital structure of a firm is a combination of debt and equity, which supports long term financing of the firm. The pattern of capital structure has to be planned very carefully by the finance manager in such a way that it minimizes the cost of capital and maximizes value of stocks, thus protecting the interest of the share holders. What is the right capital mix? There needs to be a right mix of different securities in total cpaitalisation that facilitates control, flexibility and maneuverability. From a broad perspective, following are the three fundamental ways in which the schema of capital structure is finalized: Financing purely or exclusively by equity Financing by equity and preferred stock Financing by equity, preferred stocks and bonds. Which of the above most suits a firm depends on multifarious internal and external factors within which a firm operates. Equity: A firm can raise substantially large amount of fund by issuing different types of shares. The money thus raised is a permanent source of resource and without any obligation to refund to the respective owners. Small and growing companies go for equity fund raising as no banks or other financial institutions are prepared to fund these firms in lieu of poor credit worthiness. Even big corporate firms opt for issuing equities when there is a need to raise large sums. But smaller firms, whose major share of capital comprises of common stock, have to be careful, in that, some large concerns might become interested in controlling these stocks. Picture Courtesy : GrowthFunders The one big advantage of equity shareholders is that they are free to trade the shares in the market. They can sell the shares to anybody at any time and if the market warrants, at a higher price. One has really nothing to lose, if he is planning to invest in equities. On the other hand, if the company goes bankrupt, the share holders stand a chance to receive only the residual amount, after the creditors’ claims are cleared and satisfied. What’s in it for Investors? Debt: Debt has a maturity date upon which the stipulated sum of principal is repaid. It places the burden of obligation on the shoulders of the company in the form of periodical interest settlements and principal repayments. Creditors can go for legal action if the company defaults in payment of the assured sum on the specific date. That’s why companies think twice before they go for issuing debentures and other bonds. One good thing for the company is that, it can avail tax rebate on the securities of debt, but at the other end it has to satisfy the interest payments and factorise the cost of capital. Cost and Control Principles Cost principle supports induction of additional doses of debt, but it might prove risky, if the company is not able to service the additional debt. Control principle supports the issue of bonds in order to tighten the rein of ownership, but maneuverability principle discounts this and favors issue of common stock to reduce the interest burden. Four factors are important in the purview of the finance manager, cost, risk, control and timing. He should be able to evolve a pattern that satisfactorily brings a compromise among these conflicting factors, which are then assigned weights in the wake of economic and industrial...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
Characteristics and Objectives of Accounting What is Accounting: According to American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money transactions and events which are, in part at least, of a financial character and interpreting the results thereof.” American Accounting Association (AAA) has defined accounting as “the process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed judgements and decisions by users of the information.” Characteristics of Accounting: i. Accounting is the art of recording and classifying different business transactions. ii. The business transactions may be completely or partially of financial nature. iii. Generally the business transactions are described in monetary terms. iv. In accounting process, the business transactions are summarized and analyzed so as to arrive at a meaningful interpretation. v. The analysis and interpretations thus obtained are communicated to those who are responsible to take certain decisions to determine the future course of business. The Small Biz Doers’ Guide to Small Biz Accounting Objectives of accounting: a. To record the business transactions in a systematic manner. b. To determine the gross profit and net profit earned by a firm during a specific period. c. To know the financial position of a firm at the close of the financial year by way of preparing the balance sheet d. To facilitate management control. e. To assess the taxable income and the sales tax liability. f. To provide requisite information to different parties, i.e., owners, creditors, employees, management, Government, investors, financial institutions, banks etc. ...










