Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 11th, 2014 | 0 comments

Spirituality and Management The purpose of correlating spirituality and management might present a weird picture to some. Research of the old Hindu scriptures, epics and Vedas disclose the secrets of management etiquettes coated with spiritual sugar which serves as a road map for us to cherish and follow. As an ardent follower of the BHAGAVAT GITA, THE UNIVERSAL BOOK OF SPIRITUAL SCIENCE, it was really amazing for me to know that the core principles of management have already been defined and dealt with that were formulated at a later date by MANAGEMENT GURUS like PETER DRUCKER, HENRY FAYOL, C. K. PRAHALAD and the like. I would like to present four qualities that struck me while I was comparing and contemplating. PERCEPTION AND UNDERSTANDING THE INNER SELF SELF MOTIVATION AND SELF TRANSCENDENCE DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES LEADERSHIP The Leader and the Manager: The LEADER IS BEING FOLLOWED willingly, but a manager has to command individuals in order to adhere to his instructions. So, being a good leader starts from soul searching or understanding the nature of one’s inner self. SELF CONCEPTION gives a different dimension to approach problems. Spiritual experiences induce clarity in thinking that leads to ethical decision making. The spiritual experiences of Arjuna, one of the PANCHA PANDAVAS with LORD KRISHNA made him stronger (at will) and sharper (right perception). Decision Making: “I am the strength of those who are devoid of personal desire and attachment. O Arjuna, I am the legitimate desire in those, who are not opposed to righteousness, “says Lord Sri Krishna. At the war front, Arjuna the GREAT WARRIOR is not sure whether to fight against his own kith and kin. The inspiring words of Krishna motivated him to come out from the state of INERTIA and enter RIGHTEOUS ACTION. It is a testimony of what philosophers call the transcendence from alienation to self confidence to reach ethical decision making. One can never forego his duty or responsibility, be it his personal life or in the management arena. EFFECTIVENESS IS DOING THE RIGHT THINGS EFFICIENCY IS DOING THINGS RIGHT Management Lessons from Mahabharata from Parth Acharya Forming a VISION, planning the right Strategies, pooling the resources, hiring right people for the right job, setting goals and objectives, reviewing by MANAGEMENT BY OBJECTIVES, MANAGEMENT BY EXCEPTION, rewards and recognition, all have been dealt with a masterly excellence in MAHABARATHA which talks about the GURUKSHETRA WAR between the PANDAVAS and KAURAVAS or to simply put it, between THE GOOD AND THE EVIL. “The Supreme Lord is situated in everyone’s heart, O Arjuna, and is directing the wanderings of all living entities, who are seated as on a machine, made of the material energy.”Mind can make you LIBERATED OR BONDED that depends upon your WILL to master it or be a slave. Controlling your mind in turn controls your actions and thought process that leads to well augured efforts that proves fruitful to the human race. Leaders are born and not made goes the saying. But if you are able to be THE MASTER OF YOUR MIND, you are a leader made. Management Lessons from THE BHAGAVAT GITA Applicable to both western and Indian school of management, THE BHAGAVAT GITA deals with problems at the GRASS ROOT LEVEL relating to THE HUMAN PSYCHE. Management lessons from Bhagvad gita from singhm91 It enlightens us on all managerial techniques, goading us towards a serene atmosphere and state of affairs in place of the conflicts, stress, and lack of co-ordination, common in most of the enterprises world wide. “Do your duty perfectly, and the results will follow suit”, is the crux of GITA. How many of us...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
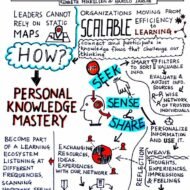
Profile of a successful leader Adaptive Capabilities: Leaders need to radically change their mindset so as to stand the test of time; but the core leadership attributes like vision or creativity, intelligence, commitment, and a healthy dose of luck still continue to define the pre-requisites of success. Integrity of Character is most important when talking about successful leadership. The philosophical undercurrent is that “Be Good, Do Good” and you will be good. The motive must be devoid of mistakes though there is room for mistakes in judgment. Leaders must have a clear vision and be able to communicate this vision to others so that it becomes a shared vision and everybody willingly contributes in fulfilling the vision. Six ‘C’s or six criteria that determine a leader’s credibility Conviction Character Care Courage Composure Competence Cross-Functional Expertise – Acquisition of knowledge should make a leader humble and flexible and gaining knowledge must be seen as a life long experience rather than collection of voluminous data or skills. A leader will try to apply his broad functional knowledge and expertise in the right places and the results will be definitely magnificent. A leader must look into the possible options rather than to plan, the possible rather than the perfect, involvement instead of obedience. Change is the only entity that remains unchanged and it is inevitable for the leaders to consider change as the core element of growth. With accelerated pace of change in the economic, political and socio-cultural environment, leaders not only need to acquire new knowledge and skills but they also need to unlearn many of the things that have out-grown their purposes. Leaders should follow the CODE OF PRIDE to motivate the workforce. P– PROVIDE FOR A POSITIVE WORKING ENVIRONMENT R– RECOGNISE EVERYONE’S EFFORTS I– INVOLVE EVERYONE D– DEVELOP SKILLS AND POTENTIAL E– EVALUATE AND MEASURE CONTINUOUSLY In large corporate organizations, the leader must be willing to share power and control so that leadership is encouraged at various levels. Successful leaders are those who are self-motivated by setting their own standards and compete with themselves. Innovation is the need of the hour What do you mean by innovation? Creating something new or modifying the old one. Here the term innovation implies the change in the “THOUGHT PROCESS” of leaders who are able to turn a crisis into an opportunity. Also called as “THINKING OUT OF THE BOX” where a leader finds new application for old ideas which cannot be discarded or dis-regarded. “You must learn from your past mistakes but not Lea(r)n on your past successes”. High achievers take moderate risks calculating the circumstances and they rely on their own abilities unlike low achievers who invariably like to minimize risks or take wild and irrational risks. Running a corporate business has become more like an experiment since we cannot control or predict the future. It is highly unstable and unpredictable. So leaders have to cope up with this non-linear force acting in the external environment building up pressure. Leaving things as they are can be just as predictable as changing everything, you lose or win both ways. Now let us look at some of the definitions of Leadership 1. “Leadership is generally defined as influencing people so that they will strive willingly towards the achievement of group goals.”- Koontz and O’Donnell 2. “Leadership is the lifting of man’s visions to higher heights, the raising of man’s performance to higher standards, the building of man’s personality beyond its normal limitations.”- Peter F.Drucker 3. “Leadership is the ability to secure desirable actions from a group of followers voluntarily without the use of correction.”- Alford and Beatty 4. “Leadership refers to the quality of the behavior of individuals where by they guide people on their activities in organized efforts.”- Chester I.Bernard Behavioral Commitments of a Leader: Challenging the process Challenging the status quo and act as radical change agents Inspiring others by being pioneers, instigators, navigators and learners Showing risk-taking ability,...

Posted by Managementguru in Decision Making, Principles of Management, Project Management
on Mar 7th, 2014 | 0 comments
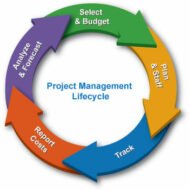
Meticulous Project Management Fundamental Aspect of a Project: Planning is the fundamental aspect of any management system as it sets the direction or pathway, which the firm has to follow in order to accomplish the goals and objectives of an organization. In a project management or a process management, planning is the key function followed by preparation of a proposal or a report that analyses and defines the resources necessary to carry on the project. This project report can then be sent for evaluation by an expert consultant to determine the feasibility and viability of the project. Organising to Get the Desired Result: A project undertaken has to be meticulously planned and organized to achieve the desired result in the given time frame. One has to understand that a project differs from a process in that, it involves fixed time fame and cost frame.Say,for instance, your firm is rewarded with a project to design ERP solutions for a big corporate company. What will be step one? You will try to gather all the details regarding organization structure and hierarchy, people involved and their designations, availability of physical resources, whether the corporate firm is technically equipped, product portfolio, strategic business units and their viability, distribution channels and so on., As one is aware, enterprise resource solution software integrates production, marketing and human resource departments to facilitate even flow of information and quick execution of orders without any time delay. Picture Courtesy: Project Management and Leadership Champions Data Collection: Data collection is inevitable and has to be precise to attain your set goals. The next logical step will be deciding the time frame and allocating resources (human and other physical resources) to carry on the project. If you feel that the delivery deadline cannot be met with, you have to immediately inform your sponsors about the time delay and extend your time frame for the project to materialize. On -Time Delivery: Projects that involve production and delivery of goods depend on the manufacturing cycle time and delivery lead time. Implementation becomes a cake walk if your business plan has incorporated, 1) well laid down step by step procedures, 2) leverage for uncertainty in the external environment and 3) focus on proper communication. Communicating the entire project plan as per the intentions to the people concerned is very vital for the success of a project, because people should understand, what needs to be done, what is one’s role, and the strategies evolved by the management. PERT and CPM: Program evaluation and review techniques (PERT) and critical pathway method are some of the tools that help in ascertaining the progress rate of projects. These tools help in identifying specific milestones and activities that are to be carried out in a sequential manner and also to estimate the time required for each activity, with a help of a network diagram. A very interesting and simple video explaining how to determine project duration using critical path…. Success of a project management is determined by Decision making ability Communication skills Negotiation techniques and Time management skills, of the project manager and also depends on how well it protects the interests of the stakeholders involved. A project is a comprehensive team effort with the budget and time well within the scope of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 7th, 2014 | 0 comments
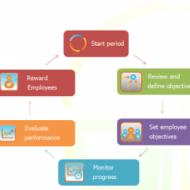
MBO BY PETER DRUCKER Peter Ferdinand Drucker was an influential writer, management consultant, and self-described “social ecologist. Harvard Business Review honored Drucker in the June 2004 with his seventh McKinsey Award for his article, “What Makes an Effective Executive”, the most awarded to one person. The Concept of MBO: Management by objectives was a concept introduced by the doyen of management, Peter Drucker. This concept involves formulation of objectives for the entire organization and which are then broken down into divisional, departmental and finally individual objectives. Objectives are decided on the basis of mutual consultation between managers and employees at the departmental and divisional levels and thus it can be appropriately called an integration of top down and bottom up approaches in management. The specific aim is to make the employees participate in decision making and thus motivate them to perform better. Management by objectives follows a step-by-step procedure that ensures the feasibility of the action plans decided upon. Realistic and achievable plans are set. Activities to be preformed are identified. Logical relationship between the sequences of activities is laid down. Time frame and cost frame are fixed. Resources to be allocated are decided upon. Salient features of the process: Self control and Self direction: The workers exhibit keen self control in that, they self appraise their performance that results in intrinsic motivation. Setting short goals and periodical review to match the current performance with the expected standards greatly boosts the performance of each and every individual and gives him the necessary drive to accomplish the assigned tasks. Periodic progress review: This helps to correct errors and deviations if any. This review is done by managers of higher levels in a constructive way and adequate counseling and guidance can be given to the subordinates to bridge the shortfall if any, in performance. This is possible only when there exists a mutual understanding between the superior and subordinates to find reasons and solve problems together. Reviews need not necessarily pinpoint errors but also revise future plans and actions. The major emphasis of management by objectives lies in its result oriented approach. What is the relationship between management by objectives and motivation? Motivation of an employee can be brought about by financial incentives such as bonus, increments, pay and perks or non-financial incentives such as recognition, appreciation and additional responsibilities. But nothing can equal self-motivation which makes an employee perform with aplomb. As management by objectives is directly linked with goal-setting, performance becomes better and better as the goals are set at a higher level. It involves complete participation from the employees’ end and when specific goals are set by mutual consent of workers and management, the results are magnificent. Many firms practice management by objectives to promote harmony and sense of belonging in the minds of employees as a result of which there is remarkable improvement in performance and productivity. The focus is on improving the job design and work module to make the jobs more meaningful, interesting and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 7th, 2014 | 0 comments

Performance Optimization Through Effective Management An organization is a network of people striving to achieve their targets. So it is a wise thing to synchronize their activities in-order to enhance the harmony and build a strong team as well that protects the network from crumbling by means of mutual trust and behavior. It is imperative for the management to define the structure and hierarchy as well as the techniques that help the organization to efficiently function. Here are some means to make your organization to function efficiently and you’re your team stand apart from the crowd. Training of Subordinates: The better the training of subordinates, the fewer the number of necessary supervisors. Well trained subordinates require not only less of their manager’s time but also less contact with their managers. ‘On the job’ training programmes have found to be more effective in industries which are labor intensive. Coaching and mentoring improve the understanding and efficiency of the workforce and help them to maximize their effort and in turn productivity. Clarity of Delegation of Authority: The most serious symptom of poor organization affecting the span of management is inadequate or unclear authority delegation. If a manager clearly delegates authority to perform a well defined task, a well trained subordinate can get it done with the minimum of manager’s time and attention. But if the subordinate’s task is not clearly defined, either the task will not be performed or it will be a colossal waste of time for the manager to supervise and guide the subordinates’ effort. Clarity of Plans: The character of a subordinates‘ job is defined by the plans to be put into effect. If these plans are well defined, if they are workable, if the authority to undertake them has been delegated, and if the subordinate understands what is expected, little of a supervisor’s time will be required. Such is often the case with a production supervisor, who bears the responsibility of achieving targets within the stipulated time period. If the plans cannot be drawn accurately, subordinates must do much of their own planning where they may lack direction. On the other hand if the superior has setup clear policies to guide decisions and has made sure they are consistent with the operations and goals of the department, work becomes simple and easy for the subordinates to follow. Communication Techniques: If every plan, instruction, order or direction has to be communicated by personal contact and every organization change or staffing problem has to be handled orally, it slows down the managerial activity. The ability to communicate plans and instructions clearly and concisely also tends to increase a manager’s span. At the same time the subordinate’s job is greatly facilitated by superiors who can express themselves well. A manager’s casual easy style may please subordinates, but it reduces the effective span of management and lowers morale as well. Amount of Personal Contact Needed: Many situations cannot be completely handled with written reports, memorandums, policy statements, planning documents and other communication techniques that do not involve personal contact which an executive find it valuable. There are other situations in which the best way of communicating a problem, instructing a subordinate, or “getting a feel” of how people really think is to spend time in personal contact . The high percentage of time spent in meetings and committees might be reduced some what by better training, better policy making and planning, clearer delegation, more thorough staff work, better control system and objectives standard. Studies have revealed that, effective spans were narrower at lower and middle levels of organization but were increased at upper levels and size had little...










