Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
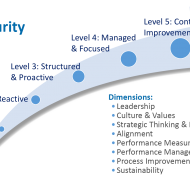
STRATEGIC PLANNING Strategic planning is the primary step in the process of strategic management [Strategic management is a comprehensive topic that covers almost all the functional aspects of the organization] which can be outlined from at least two perspectives: First, strategy is the “broad programme for defining and achieving the objectives of an organization and implementing its mission”. Secondly, “It is the pattern of the organization’s response to the external environment over a period of time”. A strategy that takes a broad and typically long range focus is called strategic planning. MBA Application Strategies for Top Business Schools Strategic planning is the process that classifies the long range goals of the organization and opts for the precise means (strategies and polices) for achieving these goals, allocates resources, and develops long range plans to reach the destination. Watch this Video to Understand the Overview of Strategic Planning Process Time-Horizon: Strategic planning takes into account the extended time horizon. There may not be any immediate impact out of strategic planning, but the consequences in the long-run prove to be gradual and significant as well. It provides with the necessary action plans to make a difference in vital areas concerning development. You can always associate innovativeness with strategy since it explores new paradigms and tries to enhance the impact. When the size of organizations expands, they are broken down into strategic business units (SBU’S) for the purpose of functional excellence. These units are expected to operate as if they were relatively independent businesses. WHY STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP IS IMPORTANT A Tailor Made Approach: A tailor made approach is essential when it comes to strategy development the systematic analysis of the factors associated with customers and competitors (the external environment) helps the organization to meet the challenges of modern society. More and more organizations are focusing on formal approaches and concepts for planning their long range process. Specifically these challenges are a result of increasing rate of change, the complexity of manager’s jobs, the increasing importance of fitting the organization into external environment, and the increasing lag between the preparation of plans and their implementation in future. Resource Allocation: Strategic planning is an organization’s process of defining its strategy or course, and making decisions on resource allocations to pursue this strategy. Managers must be adequately geared up for strategic planning. The goals of the organization must be made plain and not unclear. Each business unit should be categorized based on its performance level to decide on the resource share to be allocated. You need to infuse cash flow into ineffectual units and divest funds from dying units into other profitable ones. The ultimate aim is to build up star performers that will be the perennial source of income or revenue generation. There should be a strong linkage between planning and control. The assessment of strategic plans of the business units must be made periodically and effectively. TOP FIVE REASONS WHY STRATEGIC PLANS FAIL SWOT Analysis: SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses/Limitations, Opportunities, and Threats. Planning is the primary step for control as it provides several standards and benchmarks of control. Planning extracts commitment. Some times planning highlights the objectives only and the planning premises may not be fully reliable. Threats are to be considered as challenges and must be converted into opportunities. Two heads are better than one is the philosophy of brain storming where a group of people with knowledge and expertise assemble to lay out clear plans that will steer the organization smoothly even in times of rough...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
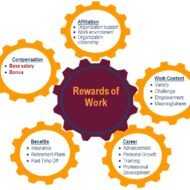
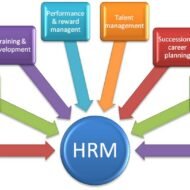
Operative Functions of HRM Staffing Staffing is one of the managerial functions. But this function is normally performed by the HR managers for all the departments of the firm. In most organizations, the HR department establishes personnel policies and coordinates the HR functions of all the departments. This function is also called the operative function or HRM function. It includes, amongst others, the processes of hiring, training, compensating, appraising and retaining employees, and attending to their labour relations, health and safety, and equality concerns. Procurement Procurement refers to a string of activities undertaken by the HR managers for filling the present and future vacancies of the organization. The activities include job analysis and designing, HR planning, recruitment and, finally, the selection of suitable employees. Here, job analysis refers to both the determination of specific tasks and responsibilities connected to a job and identifying the skills, knowledge and abilities required for the job holder. HR planning involves choosing and placing the right person at the right job and at the right time. Recruitment involves gathering a pool of applicants from which suitable employees may be selected. Lastly, selection involves screening, testing, interviewing and hiring the most suitable employees for the organization. SCOPE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF HRM Development Development here refers to both employees’ training and management development. HR managers are accountable for conducting and supervising training and development programmes for employees. The very purpose of a training and development programme is to increase the employees’ competencies in their job by improving their knowledge, skills and abilities. Training and development is widely accepted as a method for enhancing the employee skills, increasing the individual and organizational performance, improving the employee morale, and achieving the business growth and success. Compensation Compensation refers to the determination of the pay scale and other benefits for the employees. Establishing and maintaining the pay system of an organization is one of the principal jobs of the HR managers. They must devise ways to ensure fair and equitable pay rates. In addition, HR managers should regularly manage the performance evaluation system of the organization, and continuously design reward systems such as performance-linked incentive plans and bonus and flexible work schedules. Maintenance The maintenance function aims at retaining efficient and experienced employees in the organization. This calls for creativeHR practices. In this regard, HR managers are responsible for offering a wide range of HR programmes covering occupational safety, health promotion and physical fitness, canteen facilities, recreation activities, transportation programmes, employee suggestion schemes, career counselling and growth for creating a positive work environment. OBJECTIVES AND FUNCTIONS OF HRM Integration It consists mainly of industrial relations and aims at ensuring good relations between the management and the employees. HR managers have to implement industrial relations programmes that would ensure ethical and fair treatment in disciplinary action, grievance redressal, and career management processes. They should also counsel the employees and the management to prevent and, when necessary, resolve disputes over labour agreements or other labour relation issues. It is to be understood here that the functions of HRM can vary widely from one organization to another, depending upon its nature, size, and objectives. For instance, a smaller organization may follow a shorter HRM process with a greater emphasis on functions like procurement and compensation and little or no priority for activities like training and development and industrial relations maintenance. On the contrary, large organizations may pursue a longer and more comprehensive HRM process to meet the requirements of both the management and the workforce. WANNA TAKE A HR QUIZ N CHECK YOUR HR IQ? 1. The development and application of employees’ skills and energies to accomplish the goals and objectives of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Training & Development
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
Definitions of Human Resource Management: 1. “A series of integrated decisions that govern employer-employee relations. Their quality contributes to the ability of organisations and employees to achieve their objectives.” (Milkovich & Boudreau, 1997). 2. “Concerned with the people dimension to management. Since every organisation comprises people, acquiring their services, developing their skills, motivating them to higher levels of performance and ensuring that they continue at the same level of commitment to the organisation are essential to achieving organisational goal. This is true, regardless of the type of organisation: viz. government, business, education, health, recreation, or social action.” (Decenzo & Robbins, 1989). 3.”The planning, organising directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, integration, and maintenance of human resource to the end those individual, organisational, and social objectives are accomplished.” (Flippo, 1984). 4. “The organisation function that focuses on the effective management, direction, and utilisation of people; both the people who manage produce and market and sell the products and services of an organisation and those who support organisational activities. It deals with the human element in the organisation, people as individuals and groups, their recruitment, selection, assignment, motivation, empowerment, compensation, utilisation, services, training, development, promotion, termination and retirement.”(Tracey,1994 ) Knowledge Workers Human resource management is therefore understood as the all significant art and science of managing people in an organisation. Increasing research output in behavioral sciences, new trends in managing ‘knowledge workers’ and advances in training methodology and practices have led to substantial expansion of the scope of human resource management function in recent years. HRM is not just an arena of personnel administration anymore but rather a central and pervasive general management function involving specialised staff as assistants to main line managers. Managing employee relationships is the role of the Human Resource department Human Resource Management is a process of valuing and developing people at work, this includes: Recruitment and selection Employee communication and engagement (participation) to increase employee retention Training and development Leadership WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST WEAKNESS Labour turnover & staff retention Labour turnover refers to the proportion of a workforce that leave during a period of time (usually one year) Labour turnover = number of staff leaving during the period x 100 average number of staff Staff retention refers to the ability of a firm to keep its workers. The disadvantages of having a large proportion of staff leaving each year include: The cost of recruiting replacement workers The cost of training the new workers Loss of productivity whilst replacements are found Loss of experienced workers Negative impact on reputation WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST STRENGTH Methods to control turnover: 1. Financial methods of motivation Bonuses Profit share Fringe benefits 2. Non financial methods of motivation Employee engagement and empowerment Training and development Promotion opportunities 3. Improved Human Resource Management procedures Four Fundamental Principles of HRM: Human Resource is the organisation’s most important asset; Personnel policies should be directed towards achievement of ENTERPRISE goals and strategic plans; Corporate culture exerts a major influence on achievement of excellence and must therefore be strengthened with consideration of employee welfare. Whilst integration of corporate resources is an important aim of HRM, it must also be recognised that all organisations are ‘pluralist societies’ in which people have differing interests and concerns, which they defend and at the same time function collectively as a cohesive group. →Evolution of...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Management Accounting
on Feb 14th, 2014 | 0 comments

Advantages of Management Accounting It helps to increase the efficiency of all functions of management.It helps in target-fixing, decision-making, price-fixing, selection of product-mix and so onForecasting and Budgeting help the concern to plan the future and financial activities.Various tools and techniques provide reliability and authenticity to carry out the business functions.It is useful in controlling wastage and defects.It helps in complete communication between all levels of management.It helps in controlling the cost of production thus increasing the profit percentage.It is proactive-analyses the governmental policies and socio-economic scenario which helps to assess the external environmental impacts on the organization. Limitations of Management Accounting It is concerned with financial and cost accounting. If these records are not reliable, it will affect the effectiveness of management accounting.Decisions taken by the management accountant may or may not be executed by the management..It is very expensive. Only big concerns can adopt this method of accounting.New rules and regulations are to be framed, hence there is a possibility of opposition from the employees.It is only in the developing stage.It provides only data and not decisions.It is a tool to the management and not an alternative of management. These are the advantages and limitations of management accounting. Characteristics of management accounting Following are the characteristic features of management accounting: First and foremost characteristic is that it provides the necessary information to the management. It might be any data- numbers, gross profit, net profit, comaparitive financial statements, profit and loss account etc.,It is purely analytical.The interpretations help the management in timely decision-making.It adopts a selective technique to arrive at the results.Helps to chart-out the future course of action.Also helps to know the present financial condition of the firm and the respective implications on the stake holders. Various tools of management accounting: MARGINAL COSTINGSTANDARD COSTINGBUDGETARY CONTROLRATIO ANALYSISFUND FLOW ANALYSISCASH FLOW ANALYSIS...








