Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management, Project Management, Strategy
on Mar 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategy Implementation Organizational objectives must be accomplished by strategic planning and thinking that makes your organization unique and also helps to have a competitive edge. What are the elements that are part of this planning strategy? Proper allocation of resources An appropriate organization structure Efficient human resource personnel An effective management information system A feasible budgeting system A good reward system Periodic strategy review system There are many more aspects that can be attributed to broadly define strategic planning and execution. The success or failure of this exercise is in the hands of managers, who should be adequately prepared for the planning process. The objectives of the organization must be well defined and clear so that the people in the organization can evolve the necessary plans to accomplish those objectives. The action plans are then formulated based on these initially formed plans. So, the planning premises form the base on which the organization is built. Strategic business units must be identified and nurtured to add value to the organization. Why strategic planning becomes a failure in some of the organizations? Lack of proper training in strategic planning, and the key persons are the managers at all levels. Vague goals and objectives don’t make them meaningful and strategic excellence cannot be achieved. Long term goals not subjected to periodic review. If there is fluctuation in the political, economic or social environment, that is detrimental to the industry in which the firm operates, the goals can be reviewed and a revised strategic plan can be devised for the long term health of that organization. Poor budget planning. To enjoy a sustainable competitive advantage in the market, you need to have a good financial backup to give shape to your plans. The strategic plans must be supported by specific action plans. It is a pity that in many organizations, there is neither co-ordination nor co-operation between the peers to make the strategic plans successful. Integrating these various functional groups becomes a tough task for the management. Simple but effective measures: Above all odds, a company can make things work, if the management is wise enough to follow these First and foremost thing to be done is to communicate the strategic plans to all the managers who are key decision makers. The management must make sure that everybody involved in the strategic implementation understand those strategies. Well devised action plans that contribute to the accomplishment of the firm’s objectives must be laid down. A well defined span of management that makes communication flow easy and simple. Revising the strategies in lieu of the contingencies. A conducive organizational climate that is devoid of conflicts and pressure Involvement of top management to ensure success. Thinking Out of the Box: You need “thinking managers“, to make your organization grow. The modern business management lays great emphasis on “getting people together” to accomplish the goals and objectives. How do you get people to work together? They should have a common business ideology that binds them to work for the upliftment of the organization. Although top level management cadre is responsible for formulating strategic plans, organizations must understand that the idea also reaches the lower level management in the right sense. That facilitates smooth execution delivering the expected result. Benefit from this Free Udemy Course on Marketing Strategies https://www.udemy.com/one-minute-marketing-lessons-30-quick-marketing-strategies/...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
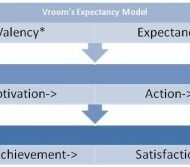
Herzberg and Victor’s Motivation Models Herzberg’s Hygiene Factor Theory Psychologist Fredrick Herzberg asked a basic question to 200 accountants and engineers in firms in and around Pittsburg-“What do people want from their jobs’? He used the critical incident method of obtaining data for analysis. “Think of a time when you felt exceptionally good or exceptionally bad about your job, either your present job or any other job you have had”. The responses obtained were fairly consistent in that, good feelings were associated with job content and bad feelings with job context. The ones on the right side of the table are intrinsic factors leading to job satisfaction and acted as motivators and ones on the left side lead to job dis-satisfaction and were termed as hygiene factors. Hygiene Factors: One has to understand that hygiene factors need not always cause dis-satisfaction; when the managers handle the situation in an amicable manner in terms of company policy, supervision, working conditions, salary and administration, things will be in the right direction but, even if they are adequate, people are never satisfied. These are called Hygiene factors and managers must try to eliminate factors that create discontent among the workers. If we want to motivate people, the real motivators are achievement, recognition, responsibility and growth. We must change the job design in such a way that the work arising out of the job should be challenging, exciting and should offer them a sense of achievement, recognition and growth. HYGIENE FACTORS MOTIVATORS Company policy Achievement Relationship with superiors Recognition Working conditions Work itself Salary Responsibility Relationship with peers Advancement Personal life Growth Relationship with subordinates Status Security CRITICISM: The factors which one particular group of individuals finds to be dis-satisfying may not be applicable for everybody. Factors which are beyond the scope of employees such as policy formulations cannot be considered as hygiene factors. VICTOR H. VROOM’S EXPECTANCY MODEL Valency*Expectancy=Motivation By increasing the positive value of the outcomes through such means as better communication about the outcomes, values and actually increasing them, i.e., the rewards and also by increasing the expectancy of the person by making him believe that the work will really lead him to the desired outcome, organizations can make a strong connection between the work and the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

Theory of Management History and Evolution To understand the concept of management, a recap of its history and its slow but steady evolution is absolutely necessary. After the advent of machines, thanks to the industrial revolution of the eighteenth century, management has become an entity by itself. Pic Courtesy: Management Theories Since business activity is increasing by leaps and bounds globally, a more organized set up is called for, which has led to the development of different management concepts. Whether you consider management an art or a science, one definite thing is that, science and art complement each other and not mutually exclusive. Management gurus like Peter Drucker, Henry Fayol, Taylor and others have classified the essential features of management, for the benefit of the industry. Theory comes first followed by practice. Management knowledge certainly improves your style of working. How long do you think, luck, intuition or experience can be relied on, without a scientific knowledge of management. It is a thought to be pondered. Hypotheses Practical experimentation and analysis of theoretical hypotheses, yield better results and in course of time you tend to gain more scientific knowledge. Management is a process of planning, organizing, staffing, leading and controlling. Picture Courtesy: Technofunc.com The management process is applicable to all kinds of organizations and firms, be it a private firm, a government institution, a hospital, a school, a college, an university and other financial, profit making or non profit making NGO’s. This clearly indicates that management is a process that involves individuals who work in groups to accomplish their objectives in an effective and efficient manner. Levels of Management Does management pertain only to the top level management? A big no! It applies to managers at all levels. It is a chain reaction and a successful management totally depends on the synergistic activities of the people belonging to that organization. So, care must be taken by the managers to create and design an internal environment that is conducive for the smooth operations of the firm thus increasing the productivity. This does not mean that the external environment can be overlooked. A manager has to respond to the periodic changes, be it social, technological, economic or political in the external environment also. Management styles Management is a must for every organization and the style of management may vary according to the nature and size of business. Large organizations now-a-days prefer a “flat structure“, as it brings their employees closer and reduces the span of management, thus making communication faster. The more the number of levels, the more the conflict and improper communication. Although management pervades the entire organization, it is the duty of the top management cadre to initiate and maintain consistency in the process of management. All managers (by the term “manager “which is a much generalized term, we denote persons who hold authority to get things done; he may be a financial, administrative, human resource or a production executive) have a common aim, that is to create surplus. To increase productivity, create a suitable environment for the effective performance of their group and to solve crisis situations, they must be capable of seeing the “big picture”. Recent Developments A sea of changes has swept the theory of management area in recent times, owing to the development of different approaches. Management theory is criticized to have all the characteristics of a jungle as numerous management practitioners have recorded their findings in the management history. This led to severe confusion as to what management is, and how things should be organized; however, in modern corporate business world, the managerial activity is directed towards growth, thanks to the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Centralization and De-Centralization Concepts CENTRALIZATION: The term “centralization” has several meanings: Centralization of Performance: Say, if the operations of a company is restricted to a single geographical location, it characterizes centralization of performance. Departmental Centralization: Specialized activities are carried out by a single department, say, maintenance of a whole plant, staff recruitment by HR department etc., Centralization as an aspect of management: This implies restricted delegation and exclusivity of decision-making by the top management. According to Allen, “Centralization is the systematic and consistent reservation of authority at central point in an organization.” According to Weihrich and Koontz, “Centralization (as an aspect of management) is the tendency to restrict delegation of decision-making. What are the special circumstances that force the managers to reserve authority and centralize decision making powers? 1. To facilitate personal leadership 2. To provide for integration 3. To handle emergencies 4. To utilize resources effectively and instantaneously. DECENTRALISATION: It is the tendency to disperse decision making authority in a structured and organized manner. It can be viewed as a philosophy rather than a principle where-in “discretion” plays a major role in deciding which decisions to push down into the organization structure and which to hold near the top. Capital expenditure, Investment analysis and major policy decisions have to be dealt with, by the top management. It is the systematic effort to delegate to the lowest levels of authority except that which can be exercised at central points. TYPES OF DECENTRALIZATION: Three approaches to the concept are: 1. PROFIT CENTRES 2. COST EXPENSE CENTRES 3. INVESTMENT CENTRES Profit Centre: Here the organization is split into divisions on a “product basis” and is given full authority to handle its own scheduled operations, right from placing orders to negotiating the sale of its finished products. Cost Expense Centre: Whenever it is easy to determine the cost of operations, cost centres are established. Cost centres run on “budgets” which acts as a control tool to run the units within the specified budgetary limits. Investment Centre: Useful in the case of big multi-product enterprises where product performance is measured by decentralizing the investment aspect. Each strategic business unit is responsible for the acquisition, use and disposition of fixed resources. Advantages of Decentralization: Managers and executives are relieved form excessive work pressure Even low level employees are involved in decision making thus bringing the decision making process closer to the scene of action. It facilitates product-diversification Creates an opportunity for learning Ensures effective control When a big organization is divided into relatively smaller units, it becomes flexible and also effects close control. Disadvantages of Decentralization: · Conflict arises between people belonging to different levels of the organization · Rising cost · Lack of co-ordination between production and marketing departments · No defined leadership Contingency Factors in Decentralizing: 1. Organizational goals 2. Organizational size 3. Geographical dispersion 4. Technical complexity of tasks 5. Time frame of discussions and decisions 6. Subordinates’ take on issues 7. Planning and control procedures 8. Environmental factors 9. Knowledge and experience of managers Effective Decentralization can be accomplished by · Establishing appropriate centralization · Developing efficient managers · Proper provision for communication and co-ordination · Establishing adequate controls Top management must be willing to delegate authority towards decision making; Middle management must be willing to accept responsibility that is being delegated. Only then effective decentralization is...








