Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
Executive Development – Options are Wide Open Who is an Executive: A person or group having administrative or managerial authority in an organization. While “executive” and “manager” and “leader” are often used interchangeably, “executive” is commonly used to signify the top 5% to 10% of the organization. Executive Development : aimed at developing the skills and competencies of those that (will) have executive positions in organisation. Capabilities of a Good Manager: A good manager can make an organization grow, survive and shine amidst tough competition, if he is bestowed with corporate competencies such as perseverance, capacity to put in hard work, sense of loyalty and responsibility, all of which may be inherited or acquired qualities. Loyalty stems from internalized morality that may be a result of his value system. Executive success is what the organizations should aim for, and firms should try to figure out the fundamental components that make up the success formula or equation. Road to Self-Development: In less developed countries, employees are more than satisfied if they are provided with a job that offers safety and security. Their thinking is restricted to mere physical and biological comforts and does not go beyond that point, where self development and self-actualization come into the picture. In developed countries, the situation is quite different, where the workers aim for empowerment and look for reasons that motivate them to do a job. Money also has its due role to play, and people whose wages are very meager cannot be expected to aim for empowerment, where their single motive is mere survival. Abraham Maslow’s Point of View: Abraham Maslow puts forward the hierarchical needs theory, arguing that, there are five levels of needs for people in general, right from physiological needs at the bottom of the pyramid and need for self actualization at the top, and safety, security and esteem needs coming in between. He points out that, once a need is satisfied, it ceases to be a motivator. This is so evident in our day to day lives, where wants and needs never cease to exist and once a want is satisfied, human mind wanders to catch hold of another. So, organizations should understand and analyze, what factors best motivate their employees, particularly their managers (who might serve as a source of inspiration to their subordinates).It should be remembered that non-availability of jobs leads to dissatisfaction whereas availability of jobs need not motivate employees. Some factors which have been proven to be real motivators are as following: Recognition Opportunities for self development Additional responsibilities(lateral expansion) Timely rewards(in terms of money and appreciation) Security Inculcating a sense of belongingness Conducive corporate atmosphere Corporate culture Good human relations Economic burden makes people less enthusiastic and anxious in developing countries and this hinders them from delivering to their fullest potential. Also the bureaucratic approach followed by conservative firms, autocratic leadership style and lack of supportive atmosphere make people work like automatons devoid of creativity. Such firms may show good results in terms of productivity initially, but in due course has to pay the price, in terms of absenteeism, high attrition rates and less efficiency. It has been proven that job satisfaction is directly proportional to efficiency. When people find a job tedious and monotonous, they tend to lose interest, which will be evident from their lack lustrous performance. Performance management has its bearing on executive success and by providing with ample scope for career advancement and autonomy; managers prove their mettle even within limited scope of resources. Acceleration of executive change implies the development of the executive mind for performing managerial activities in a better way. Note : A survey of CEOs in Fortune 500 enterprises indicated that executives spend little time with their...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
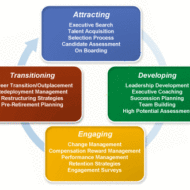
Operative Functions of HRM Staffing Staffing is one of the managerial functions. But this function is normally performed by the HR managers for all the departments of the firm. In most organizations, the HR department establishes personnel policies and coordinates the HR functions of all the departments. This function is also called the operative function or HRM function. It includes, amongst others, the processes of hiring, training, compensating, appraising and retaining employees, and attending to their labour relations, health and safety, and equality concerns. Procurement Procurement refers to a string of activities undertaken by the HR managers for filling the present and future vacancies of the organization. The activities include job analysis and designing, HR planning, recruitment and, finally, the selection of suitable employees. Here, job analysis refers to both the determination of specific tasks and responsibilities connected to a job and identifying the skills, knowledge and abilities required for the job holder. HR planning involves choosing and placing the right person at the right job and at the right time. Recruitment involves gathering a pool of applicants from which suitable employees may be selected. Lastly, selection involves screening, testing, interviewing and hiring the most suitable employees for the organization. SCOPE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF HRM Development Development here refers to both employees’ training and management development. HR managers are accountable for conducting and supervising training and development programmes for employees. The very purpose of a training and development programme is to increase the employees’ competencies in their job by improving their knowledge, skills and abilities. Training and development is widely accepted as a method for enhancing the employee skills, increasing the individual and organizational performance, improving the employee morale, and achieving the business growth and success. Compensation Compensation refers to the determination of the pay scale and other benefits for the employees. Establishing and maintaining the pay system of an organization is one of the principal jobs of the HR managers. They must devise ways to ensure fair and equitable pay rates. In addition, HR managers should regularly manage the performance evaluation system of the organization, and continuously design reward systems such as performance-linked incentive plans and bonus and flexible work schedules. Maintenance The maintenance function aims at retaining efficient and experienced employees in the organization. This calls for creativeHR practices. In this regard, HR managers are responsible for offering a wide range of HR programmes covering occupational safety, health promotion and physical fitness, canteen facilities, recreation activities, transportation programmes, employee suggestion schemes, career counselling and growth for creating a positive work environment. OBJECTIVES AND FUNCTIONS OF HRM Integration It consists mainly of industrial relations and aims at ensuring good relations between the management and the employees. HR managers have to implement industrial relations programmes that would ensure ethical and fair treatment in disciplinary action, grievance redressal, and career management processes. They should also counsel the employees and the management to prevent and, when necessary, resolve disputes over labour agreements or other labour relation issues. It is to be understood here that the functions of HRM can vary widely from one organization to another, depending upon its nature, size, and objectives. For instance, a smaller organization may follow a shorter HRM process with a greater emphasis on functions like procurement and compensation and little or no priority for activities like training and development and industrial relations maintenance. On the contrary, large organizations may pursue a longer and more comprehensive HRM process to meet the requirements of both the management and the workforce. WANNA TAKE A HR QUIZ N CHECK YOUR HR IQ? 1. The development and application of employees’ skills and energies to accomplish the goals and objectives of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, International Business, Marketing, Project Management
on Mar 11th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is Trade? Trade is the exchange of commodity and services. International trade represents business transactions taking place at the global level, and it is fundamentally different from domestic trade. Trade at international level demands huge investments, network of franchisees and proficient people to run the show. Many corporate giants are trying to capture Asian markets, especially Indian market, which has become the industrial hub for such economic activities. Economic liberalization has been the focus of many developing countries for the past two decades and this has allowed multinational companies with huge investment potential to enrich the weaker economies. What is International Trade? International trade tries to generate more foreign exchange, which is always good for the economy. Say, if a country has rich resources of petroleum, naturally it will try to sell the surplus to countries not endowed with such natural resources. That is why Middle East nations are prosperous and economically independent. The diversity in productive possibilities in different countries is due to the presence of limited natural resources. When a country gets a head start in a particular product, it can become the high volume, low cost producer. The economies of scale give it a significant advantage over other countries, which find it cheaper to buy from the leading producers than to manufacture the product themselves. Barriers for Effective Trade Every nation must try to specialize in the production and export of those commodities, which are available in plenty and must import such products in the production of which they have a resource deficiency. It should be remembered that there are severe man made barriers in international trade such as, export duties, quotas, exchange restrictions etc.,that hinder the free movement of products. International Trade and Finance Nevertheless, it is not also possible for a country to produce domestically every kind of product. In spite of all these restraining factors, global trade is thriving, thanks to the advanced technological aspects introduced in communication and faster means of transportation. Distance is no more a constraint and the world has become one small global village. Foreign Exchange Issues All domestic transactions, say in a country like India take place in rupees, which is the legal tender in the country. However, in its trade with other countries like USA, Germany, Japan, France and Britain, the payments have to be made in terms of dollars, marks, yens, francs and pound sterling respectively. The mechanism through which payments are effected between two countries having different currency systems is called foreign exchange. It may be also defined as the exchange of money or credit in one country for money or credit in another. Foreign exchange rates can affect relative prices and net exports. A rise in the a nation’s foreign exchange will depress that nation’s net exports and output, while a fall in the foreign exchange rate will increase net exports and output. Because of the significant impact of exchange rates on national economies, countries have entered into agreements on international monetary...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 10th, 2014 | 0 comments
Dimensions of Human Resource Management I would like to brief you on some of the key aspects that mark the paradigm shift in the HR environment towards better management prospects. 1. The Human Resource function has shifted its focus to a much wider canvas that includes Empowerment of EmployeesRestructuring the Organisation and so on. 2. A range of HR sub-systems are involved in Planning The NumbersTypes And Skills Of HrEnsuring Their AvailabilityPlacing In The Right JobPromoting And Nurturing Their Mental HealthHelping Them Develop Special Talent And Skills 3. Human Resource is considered as an “investment” and no more an “expenditure”. Investment in TrainingRe-Training AndContinuous Learning On The Job develops the skills and competences of managers and employees and prove to be an useful investment. 4. The concepts of Learning Organisations AndTeam-Building serves a basis for “Competitive advantage” and “Motivating the employees.” 5. Values that are stressed upon are Co-OperationHarmonisationSynergyTrustBeing Pro-ActiveCollaboration 6. Strategy: VisionMissionObjectivesGoals– How these can be achieved? The techniques that are basically holistic in nature can solve the purpose. Such techniques involve SEWA– Self mastery, Empathy for workers, Worker-directedness and Achievement in performanceABO-Action by Objective Nine Dimensions of an Effective HR Department: What is the reputation of the HR department?What are the criteria (deliverables) that shape HR work?What is the mission or strategy of the capabilities – focused HR department?How is the HR department organised? How does HR facilitate the definition and creation of organisation capabilities?How do we make better HR investment and choices?How do we create HR practices?How does HR go about doing its work? What do HR professionals need to be, know, and do to be effective? Let us make a sincere comparison between the past and the present in terms of HR perspective These techniques produce performers who find their way through any set of given problems, manage themselves and lead the team to a stae of self- realisation. Old model vs New model 1. Job was the basic unit/ Team is the basic unit 2. Relations with environment there handled by the individuals/ Densely networked with environment 3. Information flow was vertical/ now it is vertical, horizontal and holistic 4. Many layers of management / Organisations have become flat 5. Emphasis on structures/ Emphasis on process and literally virtual organisations have evolved 6. Career path upward and linear/ career path lateral and flexible 7. Standardised evaluation and reward system/ Customised evaluation and reward system 8. Ethnocentric/ International 9. Single strong culture/ Multicultural and diversity of viewpoints and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 10th, 2014 | 0 comments

Motivation is one area where periodical updates are necessary for an organisation to gauge the morale and mood of their employees. Companies sometimes act very smart in that they break their hands by patting their own back. If you wish to propel your organisation forward, you need to satisfy your work force first. The million dollar question is a big “HOW?” Well, a problem properly diagnosed is half done. And this motivation thingy is not a problem at all. Keen observation and understanding is what is needed on a manager’s part to steer things in the right direction, that is good for the company. Man, even your kid will turn his back if you want to take control by unleashing your power. The right thing to do is to find out exactly how motivated they are. There are several things that come into the purview of motivation.Let us do this in a questionnaire format so that things might fall in place. Question No 1: What is that, that motivates an employee, to be more precise your employee? (This turns out to be the hot dissertation topic for many young MBA’s) Is it any one of the following? Financial rewards Clear Goals Connecting with others Rank Appreciation and Recognition Throat neck competition Job security Fear Results Excitement Variation or Diversity Principle of Motivation: Well, the principle of motivation is pretty much the same for all individuals. I 100 % go with Maslow’s hierarchial needs theory which travels right from physical needs at the base of the pyramid upto self realisation at the top. If this is the case,how come there is a disparity when everybody is subjected to the same kind of influence at the work place? For some it stops somewhere in the middle who are very much satisfied with the pay check figure and the perks that go with it. For some there is an inner drive that makes them unstoppable until they reach the pinnacle. This is the very thing that differentiates a manager from a subordinate. This is the very thing that distinguishes a CEO from a manager. This is the same thing that generates top business guns and management gurus who fall a genre apart form the rest of the crowd. Well, there are other factors such as the family background and the environmental influence that shaped up your personality all through. Motivation Surveys: Motivation surveys are not only important in getting to know your employees but also it showers a immaculate image on the company. It feels good for your workforce when they are involved and consulted with, on issues related to themselves. A recent Harvard review has stated that most of the managers feel that they really get motivated when there is : “Recognition for Good Work.” But folks, you will be surprised to know that the same review reveals another side of the coin, the top motivation for workers is when they make “Progress.” Again, call it the inner drive, impulse, motive, ambition, fire in belly, vigor, vitality…Getting to know your work force makes you “BOND WITH THEM” and it aids you in plugging the holes at the right place and at the right time. See, there is no bench mark for motivation, you respect your work force, treat them with dignity, communicate well and give them what they want and that’s it, you are defintely a winner. If you are a person capable of motivating your work force, you automatically become a source of inspiration. My humble suggestions to managers goes thus: 1. Make your employees understand what motivates them.( Kindly find what flares your temper before venturing into this exercise.!) 2....










