Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Stress Management, Training & Development
on Mar 19th, 2014 | 0 comments
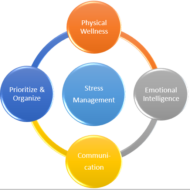
Did you know that without your knowledge, your health might be deteriorating due to pressure at work. Effective stress management is the only way out to become happier, healthier, and more productive. Whatever we do or say has a direct effect on our physiological processes as it affects our psyche-both positive and negative. While positive vibes act as a booster to our health, enhances the morale causing increased productivity which is “THE CONTRIBUTION FACTOR” in corporate organisations, negative vibes causes distress to the party affected and in-turn the organisation. Though in a small way, which is enough to cause great distress waves amonsgt the entire organisation through grapevine. Morale Surveys Therefore, it becomes necessary that every organisation takes some time to understand and analyse the mind-set of their employees to maintain the entire health of their firm. This can be done through surveys or questionnaires which serve as best platforms that shoulder employees’ opinion. On the side of the individual, he also should spare some time, from time-to-time to analyse his attitude towards the organisation and his/her colleagues and how it affects his/her performance. Management scholars say that “SELF-APPRAISAL” is the best tool for enhanced organisational performance and productivity. What is Stress? It is very important to understand what stress is, to combat it. Stress is nothing but a condition where people get excited emotionally or in other words ” a disturbed mental state” affecting the well-being. The causal agents may be physiological which can be medically treated or emotional which we are more worried about as emotionally unstable individuals cannot think properly which again leads to physical distress. It becomes therefore vital to know how we perceive and interpret things through our cognitive skills, again influenced by environmental factors to a considerable extent. People, particularly working in corporate environment and IT industry are subjected to much stress and they don’t know how to find a vent to their feelings or when there is no adequate support from the family side. What are the Ways Out? So, what is it we do at times like these? Not to bother. The mantra is “RELAX” to the maximum possible extent. First thing extract yourself away from the scene of action so that you could breathe some fresh air. Then think calmly and try to isolate the bug that is bothering you. Here the problem is the bug and analyse how far you have become vulnerable to the situation. Gauge the amount of damage done and rate the problem in terms of ” recoverable by myself- no help needed”, ” recoverable- but with external support”. Remember, for every problem there is a solution. It may not be tailor- made, but definitely passable with little bit of compromise from our end if necessary. 10 Yoga Poses You Should Do Everyday to Combat...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
Employee Training – Train Your #Employees to Tone up their Spirit What is Training & Development: process to obtain or transfer #knowledge, #skills and abilities needed to carry out a specific activity or task. Human Resource training is not at all a complex process; with the right kind of supervisors, who impart training and their subordinates being enthusiastic about learning, it seems to be quite an easy job. But, some firms fail to achieve the desired productivity, in spite of good training programmes and availability of efficient workers. The biggest problem being, the failure to impart relevant training, by identifying and analyzing the training needs which too often is not the case. To be successful, firms have to adopt a systematic approach to training process. Training fills the gap between what someone can do and what he should be able to do. The first aim of training is to ensure that, as quickly as possible people can reach an acceptance level in their jobs. Training then builds on this foundation by enhancing skills and knowledge as required to improve performance in the present job or to develop potential for the future. Steps involved in systematic approach of training: 1) Identifying and analyzing training needs: Training should always fall in line with the #objectives of the organization to be achieved and it should be relevant to the context. Running training programmes just for the sake of running it, without defining the purpose, or sending the trainees for a workshop that has nothing to do with what the trainees really need to learn -all these are inappropriate methods of training and it makes the trainees lose their focus and direction. Another problem you will meet in the off-the job training is that, transferring the knowledge to action in the work place. If the objectives are not specified and appraised properly to the trainees, they will not be able to satisfy your expectations. So, a thorough analysis of what people need to know as trainees at different functional levels proves useful in saving much time and labor of the firm. 2) Job analysis-a basis for identification of training needs: The basis for training starts from job analysis, where the organization has to be quite prudent about its specifications and expectations well defined. The indicated specifications may be about, Knowledge -what the worker needs to know in terms of professional, technical, technological, commercial aspects. Skills-Manual, intellectual, perceptual, analytical or social which depends on the nature of the job. A top level employee needs to possess more analytical skills backed up by rational thinking, whereas a lower level employee is only expected to deliver his technical skills properly. Attitudes: The disposition to behave or to perform in accordance with the requirement of the work. This is one of the most important aspects that is neglected by most of the organizations by sheer oversight. If a customer is not properly received in a boutique shop or a restaurant, think what will be the response and reaction of the customer? If a worker does not pay due respect to his superior or boss, what are the chances of his career advancement? Whether it is a production environment or a market environment, firms must teach the trainees to conform to the guidelines regarding #attitude. 3) Prepare your training plans based on the objectives: Decide on the content of the course, as established by job and task analysis and information from performance appraisals. Decide on the training techniques, which may be, Job instruction On-the -job training Coaching Lecturing Computer based training Action learning Interactive video etc., which are a combination of on- the job and off-the job training...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
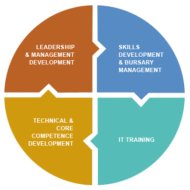
Executive Development – Options are Wide Open Who is an Executive: A person or group having administrative or managerial authority in an organization. While “executive” and “manager” and “leader” are often used interchangeably, “executive” is commonly used to signify the top 5% to 10% of the organization. Executive Development : aimed at developing the skills and competencies of those that (will) have executive positions in organisation. Capabilities of a Good Manager: A good manager can make an organization grow, survive and shine amidst tough competition, if he is bestowed with corporate competencies such as perseverance, capacity to put in hard work, sense of loyalty and responsibility, all of which may be inherited or acquired qualities. Loyalty stems from internalized morality that may be a result of his value system. Executive success is what the organizations should aim for, and firms should try to figure out the fundamental components that make up the success formula or equation. Road to Self-Development: In less developed countries, employees are more than satisfied if they are provided with a job that offers safety and security. Their thinking is restricted to mere physical and biological comforts and does not go beyond that point, where self development and self-actualization come into the picture. In developed countries, the situation is quite different, where the workers aim for empowerment and look for reasons that motivate them to do a job. Money also has its due role to play, and people whose wages are very meager cannot be expected to aim for empowerment, where their single motive is mere survival. Abraham Maslow’s Point of View: Abraham Maslow puts forward the hierarchical needs theory, arguing that, there are five levels of needs for people in general, right from physiological needs at the bottom of the pyramid and need for self actualization at the top, and safety, security and esteem needs coming in between. He points out that, once a need is satisfied, it ceases to be a motivator. This is so evident in our day to day lives, where wants and needs never cease to exist and once a want is satisfied, human mind wanders to catch hold of another. So, organizations should understand and analyze, what factors best motivate their employees, particularly their managers (who might serve as a source of inspiration to their subordinates).It should be remembered that non-availability of jobs leads to dissatisfaction whereas availability of jobs need not motivate employees. Some factors which have been proven to be real motivators are as following: Recognition Opportunities for self development Additional responsibilities(lateral expansion) Timely rewards(in terms of money and appreciation) Security Inculcating a sense of belongingness Conducive corporate atmosphere Corporate culture Good human relations Economic burden makes people less enthusiastic and anxious in developing countries and this hinders them from delivering to their fullest potential. Also the bureaucratic approach followed by conservative firms, autocratic leadership style and lack of supportive atmosphere make people work like automatons devoid of creativity. Such firms may show good results in terms of productivity initially, but in due course has to pay the price, in terms of absenteeism, high attrition rates and less efficiency. It has been proven that job satisfaction is directly proportional to efficiency. When people find a job tedious and monotonous, they tend to lose interest, which will be evident from their lack lustrous performance. Performance management has its bearing on executive success and by providing with ample scope for career advancement and autonomy; managers prove their mettle even within limited scope of resources. Acceleration of executive change implies the development of the executive mind for performing managerial activities in a better way. Note : A survey of CEOs in Fortune 500 enterprises indicated that executives spend little time with their...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
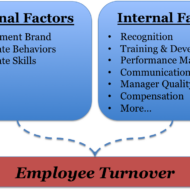
Smart Retention Strategies: Before going into the details of how to handle attrition, the first thing you must understand and realize is this. Each person working for you will have different expectations, perspectives and demands about his job, work environment and compensation respectively. Right at the time of recruiting and selecting the employee, his ideas must be taken into consideration and then it becomes the prerogative of the management whether to hire the person for that particular job. So the first step will be the right person for the right job, giving due importance to the anticipation of the employee who is going to become a member of your business family. Udemy Best Sellers:New Manager Training in Essential SkillsLeadership: Practical Leadership Skills Need for Open Conversation: In case of a small firm or company, it is easy for the manager to have a one on one conversation with each employee to settle his score of grievances then and there. Managers must have an open conversation without room for any ambiguity in the minds of his workers. The manager should try to protect the interest of the employees by representing their demands to the management at the right time. Many employees quit their positions because they have a nagging feeling at the back of their minds that their immediate boss is not the right kind of person to whom they can look up to and ask for support. In big corporates it is not easy to go for a one on one approach. A unique corporate culture that Trains the employees to have an uniform approach to all the systems of routineLed by an effective leader who controls and monitors the behavior and attitude of the workersPossesses sound management practices that make the employees come out with their suggestions freely and induce them to participateProvides satisfactory compensationIncorporates an open door policy catering to the different needs of people and also to the different levels of management, will help the managers to have a healthy relationship with the employees. Human Wants and Needs: Human wants are unlimited and when one want is satisfied, we want more of the same or yet another of a higher order. Approach your workforce to satisfy their craving either in terms of compensation or recognition which will also help to retain your workforce to a greater extent. There should be room for growth, especially for entrepreneurial minds and minds that have parallel thinking. Pic Courtesy: CuteHR Self-Motivation is the Key: Although motivation brings cheer amongst your workforce, self-motivated employees produce better results. Job satisfaction is a relative term; it differs with individuals, some like challenges and some are easily satisfied with an increase in salary quotient. A comprehensive appraisal on the personality of your workforce will give you a clear picture of the IQ (Intelligence Quotient) and EI (Emotional Intelligence) range of your employees which helps in designating employees in the appropriate slots. Such human rationing saves you a lot of time, energy and money as the employees are guaranteed satisfaction in their jobs. Contracts and Agreements: Contracts and agreements bind the employees to the firm only legally. How is that going to help you in terms of productivity? If one of your employees is going to work with discontent, he becomes a problem source spreading the same kind of feeling to others working with him. So it is also necessary for the management to spot out these problem persons either to bring them back into the groove or fire them without any further delay. Rising costs of living and unemployment ratios are really of economic concern, but still we find employees just like that quitting...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
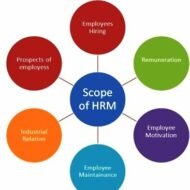
Scope and Characteristics of HRM 1. Personnel aspect: concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, lay off and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity, etc.; 2. Welfare aspect; dealing with working conditions and provision of amenities such as canteens, crèches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health, safety, recreation facilities, etc.; and 3. Industrial Relations aspect: the legal part which covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance redress and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc. Small Business Management and Marketing Essentials CHARACTERISTICS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. It is an art and a science: The art and science of HRM is indeed very complex. HRM is both the art of managing people by recourse to creative and innovative approaches; it is a science as well because of the precision and demanding application of theory that is required. 2. It is pervasive: Development of HRM covers all levels and all categories of people, and management and operational staff. No discrimination is made between any levels or categories. All those who are managers have to perform HRM. It is pervasive also because it is required in every department of the organisation. All kinds of organisations, profit or non-profit making, have to follow HRM. 3. It is a continuous process: First, it is a process as there are number of functions to be performed in a series, beginning with human resource planning to recruitment to selection, to training to performance appraisal. To be specific, the HRM process includes acquisition (HR planning, recruitment, selection, placement, socialisation), development (training and development, and career development), utilisation (job design, motivation, performance appraisal and reward management), and maintenance (labour relations, employee discipline, grievance handling, welfare, and termination). Second, it is continuous, because HRM is a never-ending process. 4. HRM is a service function: HRM is not a profit centre. It serves all other functional departments. But the basic responsibility always lies with the line managers. HRM is a staff function – a facilitator. The HR Manager has line authority only within his own department, but has staff authority as far as other departments are concerned. 5. HRM must be regulation-friendly: The HRM function has to be discharged in a manner that legal dictates are not violated. Equal opportunity and equal pay for all, inclusion of communities in employment, inclusion of tribal’s and farmers in the benefits and non-violation of human rights must be taken care of by the HRM. 6. Interdisciplinary and fast changing: It is encompassing welfare, manpower, personnel management, and keeps close association with employee and industrial relations. It is multi- disciplinary activity utilising knowledge and inputs from psychology, sociology, economics, etc. It is changing itself in accordance with the changing environment. It has travelled from exploitation of workers to treating them as equal partners in the task. 7. Focus on results: HRM is performance oriented. It has its focus on results, rather than on rules. It encourages people to give their 100%. It tries to secure the best from people by winning the whole hearted cooperation. It is a process of bringing people and organization together so that the goals of each are met. It is commitment oriented. 8. People-centred: HRM is about people at work both as individuals and a group. It tries to help employees to develop their potential fully. It comprises people-related functions like hiring, training and development, performance appraisal, working environment, etc. HRM has the responsibility of building human capital. People are vital for achieving organizational goals. Organizational performance depends on the quality of people and employees. 9. Human relations philosophy: HRM is a philosophy and the basic assumption is that employees are human beings and not a factor of production like...










