Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Decision Making, Management Accounting, Project Management
on Apr 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
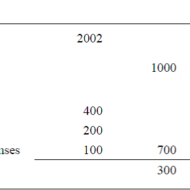
ACCOUNTING AND DECISION MAKING – IDENTIFYING THE PROBLEM SITUATION Learn accounting and finance basics so you can effectively analyze business data to make key management decisions. Business owners are faced with countless decisions every business day. Managerial accounting information provides data-driven input to these decisions, which can improve decision-making over the long term. Fig 1.1- ACCOUNTING INFORMATION FOR A SINGLE PRODUCT The above illustration clearly depicts that there has been a loss of Rs.100 in one year’s time for this particular product. The reason can be attributed to the increase in the “cost of goods” whereas other expenses have remained the same in both the years. For a single product manufactured, the problem is identifiable and solvable. But when the organization is producing a range of products, you need to apply some accounting technique by which the product losing money is identified and suitable measures are taken to cut down the escalating cost. Fig 1.2- Accouning Information for a Product Range The above illustration compares and contrasts the relationship of three products a company manufactures. It is seen that products P1 and P2 are doing well. Though the cost of sales has gone up for P1 and P2, the sales volume has also increased thus increasing the gross profit over the period of time. Here the product that has to be dealt with is P3 whose sales volume has drastically gone down, yet with the same cost of sales. When there is an increase in cost of sales, two things have to be considered. Identifying the problem-product Either cut down the production cost or increase the selling-price if the product has a real demand in the market. Uses of Accounting Data: Accounting information helps the management to arrive at make or buy decisions, to outsource production of certain components to cut down or control costs, to expand the production, to increase the sales volume or to downsize their project capacity. Techniques like Break-Even Analysis, Costing and Budgeting aid in going for the right production-mix, marketing-mix and sales target plans for the respective financial years. Aggregate Planning: As we all know planning is the key to the future and financial planning has to be given utmost importance for a production process. Aggregate planning involves translating long-term forecasted demand into specific production rates and the corresponding labor requirements for the intermediate term. It takes into consideration a period of 6 to 18 months, breaking it into work modules weekly or monthly and planning for the specific period in terms of men, material and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Decision Making, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments

Evaluating the Importance of Decision Making Successful decision making is one that is devoid of any ambiguity or tentativeness. Although there is a wide range of choice and alternative techniques to arrive at a decision, timely decision making is what adds value to the decision. The objective is to execute the action plan immediately to avoid delays that might prove costly in terms of productivity. Defensive behavior of managers: Managers who are the key figures to make decisions sometimes play defense to avoid action, blame or change. They exhibit a variety of defensive behaviors which is a wasted effort; this also makes the workers lethargic in their attitude. Avoiding action is considered to be the best political strategy. Some managers always talk about the rules and regulations that have been followed for ages in that company and want every action to be rigidly adhered to the precedence and neither allows nor admits the need to consider the nuances of a particular case. Policies and Procedures: Policies and procedures are of course the prerogative of the top level management, but it is the duty of the manager to suggest reforms in those policies that are obsolete by bringing it to the perusal of the ultimate authorities. How long will you sing the same song “The rules clearly state that”! Also don’t try to pass the buck or play duals, that clearly showcases your inability to handle things and nobody nowadays is prepared to believe false pretense. Expectation of Sub-Ordinates from the Superiors: Subordinates look up to their superiors for support as well as quick solutions for problems of any kind that comes their way; only a person who is quick in reacting to situations with presence of mind and consideration is well liked by and approved of. If you distance yourself from problems or try to prolong a task in lieu of your inability to make a decision, in the short run it might prove helpful in covering up making you look busy and productive. But what happens in the long run? It leads to organizational rigidity and stagnation in terms of productivity and a sag in the morale of the employees. Fifty Models for Strategic Thinking Playing it Safe is not Always Safe: Playing safe is not always safe. Some managers always like to lead a team that has taken up viable projects with a high probability of success. There is no pain but lots of gain. This tactics makes you devoid of risk taking -which according to me is the prime and supreme quality that a manager or a team leader must possess or at least try to develop. Also taking a neutral position in #conflict situations makes you a dull leader and not a person to be much sought after. What is the result of Poor Decision Making? The first and foremost thing that managers have to understand and admit is that, poor decision making is the root cause of failed course of action. They should have the guts to admit and take up the responsibility for the negative outcome and not to seek some strategically helpless defense mechanisms. Making others a scapegoat for your helplessness doesn’t shield you for long but puts you in the defending territory forever. Ddefensiveness delays decisions, affects organizational success, sets a bad precedence, increased group conflicts, interpersonal tensions and leads to unreliable evaluations. The long and short of the discussion clearly highlights the importance of recruiting not only a qualified manager but a committed and reliable person who has the ability to take risks and tackle crisis situations with ease and steer the organization smoothly without any hitches by greasing it...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Decision Making, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership
on Mar 30th, 2014 | 0 comments
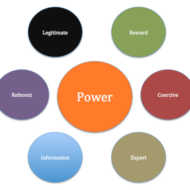
Power and Balance in Corporate Governance Power has the ability to disorient a person’s behavior and attitude. When properly used it leads to height of efficiency, when misused it calls for calamity and disorientation in the entire business firm. It is nothing but the authority that comes with your job which has to be utilized for constructive purpose and at the same time to ascertain that things are “going in the right direction.” Precise use of power leads to a congenial atmosphere in your business arena”. Otherwise in course of time you might have to tackle warfare with your subordinates and the “undercurrent of animosity” might ruin your business success. How it affects Inter-Personal Relationship: When we talk about POWER it usually fits well into the top level management cadre, as managers and senior managers are assigned with huge powers in order to lead the firm in times of crisis as well as maintain the consistency of the nature of the firm. So when there is abuse of power consciously or unconsciously, people create a space between themselves and that particular person who misuses the power. So the result would be a lack of interpersonal relationship between the manager and the employees. Managers generally acquire and use influence that has its impact not only on the behavior of the individuals, but also on the organizational effectiveness as a whole which in turn affects productivity. Use Power as a Constructive Tool: In fact, authoritative behavior is often misunderstood by most of the managers in the business setup; there is a need for the managers to skillfully use their power in order to extract work from their teams as well as to maintain a balance between the extent to which authority must be used and the tolerance level of the employees’ (mind set). So it is more of a psychology which involves much critical analysis on the part of the manager to understand the constructive aspects of his authority and how employees at a lower level will always look up to him for support and guidance and not indifference. Power covers and affects the following important aspects, Discretion Crisis management Dependence of employees Responsibility Leadership Governance Interpersonal relationship Change management Environmental influences Reward systems Collaborative management Success of the firm and so on. In order to maintain his own integrity as well as the organisations’ the manager must be able to appreciate the relevance of power in management just by not looking into the literature but act in accordance with the situation. A detailed analysis of power dynamics makes the manager more effective in dealing with behavior inconsistencies in the organization. Try to be more open in your communication and make your employees feel that “You are always there” to support and guide them. This in turn will make your “Boss to have a second look at you” for a promotional pay. This discussion is from the manager’s perspective and there is more to be discussed and considered from an employee’s...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Financial Management, Human Resource, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 30th, 2014 | 0 comments
What is Turnaround Strategy Distress signals start flying around when a particular company, whether multinational, corporate or medium sized, is subjected to financial pressure and is at the brink of bankruptcy. What was happening all along? No body knows and nobody wants to be held responsible. The CEO has to bear the brunt and alas, extermination! Aim of Turn-around Strategy: The overall aim of a turn around strategy is to bring back a firm to normalcy which has been under distress in terms of acceptable levels of profitability, solvency, liquidity and cash flow. Turn around strategies should be very carefully formulated so as to stabilize the firm in distress, i.e., to bring the company out of the hole and then go for long term planning. Turn around can be in the form of operational efficiency management, financial restructuring, marketing management or savings in the form of cost reduction or liquidity in the form of asset reduction. Facebook Marketing: A Step-by-Step to Your First 1000 Fans! Turn around to see what is around: We have seen so many such occurrences at the global level and micro level. Some companies rejuvenate like a phoenix bird from the ashes, some go haywire, and some dissolve into thin air. It all depends how well you handle the situation with either the help of an external expert consultant or you might want to go for joint venture or collaboration in order to save you skin from mounting interest payments or you right royally sell the company if somebody is ready to takeover. Either way you have to do something! “Turn around to see what is around”. Don’t see what you want to see See what has to be seen Change the CEO (He is the Ideal Victim!) Resurrect your employees’ confidence Cut down costs Look for Alternatives Lie low for Sometime(till the situation favors) Slowly capture the market by innovative Campaigns and ads Paint a new picture about your company Review your Mission and Vision statements Work on targets Bang on the right target customers and clients Strengthen your Channel of Distributors Go smooth with the bankers (You need them always!) Have confidence in yourself Crisis management is necessary Stress busters like yoga and meditation mandatory Evolve Strategies One step at a time (Slow and steady) Fear and Panic grips the organization in situations of crisis. So the first step would be to stay cool to assess the situation by calmly reviewing the damage with all the concerned people. The next step would be to stop the bleeding by cutting all unwanted costs, unnecessary overheads, and the final stage would be renaissance, recovery, renewal or by whatever name you want to call it, even if it means negative investment or profit. Proper Planning, Inventory Control, Strategic prepositions, Renewal of old strategies in accordance with the situation, Tightening finance controls, Defining the credit management limits, all these are precautionary measures which will hold you from falling into the danger of handling a crisis situation, as” recovery of damaged integrity is going to cost you more than ploughing back your profits....

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Decision Making, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 30th, 2014 | 0 comments
TURNOVER RATIO OR ACTIVITY RATIO or ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIO Turnover ratios are also known as activity ratios or efficiency ratios with which a firm manages its current assets. The following turnover ratios can be calculated to judge the effectiveness of asset use. Inventory Turnover Ratio Debtor Turnover Ratio Creditor Turnover Ratio Assets Turnover Ratio 1. INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO This ratio indicates whether investment in stock is efficiently used or not, in other words, the number of times the inventory has been converted into sales during the period. Thus it evaluates the efficiency of the firm in managing its inventory. It helps the financial manager to evaluate the inventory policy. It is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by average inventory. Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of goods sold / Average Inventory (or) Net Sales / Average Stock Cost of goods sold = Sales-Gross profit Average Stock =Opening stock + Closing stock/2 2. DEBTOR TURNOVER RATIO Debtors play a vital role in current assets and to a great extent determines the liquidity of a firm. This indicates the number of times average debtors have been converted into cash during a year. It is determined by dividing the net credit sales by average debtors. Debtor Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Trade Debtors (or) Net Credit Sales / Average Debtors – Average Bills Receivable Net credit sales = Total sales – (Cash sales + Sales return) Total debtors = [ Op.Dr. + Cl.Dr. / 2 + Op.B/R + Cl. B/R / 2] When the information about credit sales, opening and closing balances of trade debtors is not available then the ratio can be calculated by dividing total sales by closing balances of trade debtor Debtor Turnover Ratio = Total Sales / Trade Debtors Note: Bad and doubtful doubts and their provisions are not deducted from the total debtors. The higher ratio indicates that debts are being collected promptly. 3. CREDITOR TURNOVER RATIO This is also known as “Creditors Velocity”. It indicates the number of times sundry creditors have been paid during a year. It is calculated to judge the requirements of cash for paying sundry creditors. It is calculated by dividing the net credit purchases by average creditors. Creditor Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Purchases / Average Trade Creditor (or) Net Credit Purchases / Average Creditors + Average Bills Payable Net credit purchases = Total purchases – (Cash purchase + Purchase return) Total Creditors = [Op.Cr. + Cl.Cr. / 2 + Op. B/P + Cl. B/P / 2] The higher ratio should indicate that the payments are made promptly. Net credit purchases consist of gross credit purchases minus purchase return. When the information about credit purchases, opening and closing balances of trade creditors is not available then the ratio is calculated by dividing total purchases by the closing balance of trade creditors. Creditor Turnover Ratio = Total purchases / Total Trade Creditors 4. ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO The relationship between assets and sales is known as assets turnover ratio. Several assets turnover ratios can be calculated depending upon the groups of assets, which are related to sales. a) Total asset turnover. b) Net asset turnover c) Fixed asset turnover d) Current asset turnover e) Net working capital turnover ratio a. TOTAL ASSET TURNOVER This ratio shows the firms ability to generate sales from all financial resources committed to total assets. It is calculated by dividing sales by total assets. Total asset turnover = Total Sales / Total Assets b. NET ASSET TURNOVER This is calculated by dividing sales by net assets. Net asset turnover =Total Sales / Net Assets Net assets represent total assets minus current liabilities. Intangible and fictitious assets like goodwill, patents, accumulated losses, deferred expenditure may be excluded for...










