Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Dec 14th, 2016 | 0 comments

Income Tax and PAN Card Info What is meant by Income Tax? A percentage of income earned by an individual or a company (complying to Indian laws) is paid in the form of tax to the government. This is called Income Tax. This comes under Income Tax Act constituted by Parliament of India. Department of income tax operates under Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, Government of India. This is responsible for checking and collecting tax. Where should I pay Income Tax? Income tax should be paid to the I.T deparment. This is called income tax filing which is done at the end of July every year. What is the period for which a person’s income is taken into account for purpose of Income Tax? The income earned from April 1st to March 31st is considered for calculating income tax. This period is called a financial year. For example April 1, 2015 to March 31, 2016 is a financial year. This is also called previous year. What is an assessment year? The 12 month period that comes after the previous year is called an assessment year. This is the period to file income tax return for the previous year. For example, for the financial year 2015-16, the assessment year is 2016-17. During this period, a person files his return for the income earned in the previous year. How to file income-tax returns online What is PAN Number or Permanent Acount Number? PAN is a ten digit number issued by the Income Tax deparment. It also serves as a valid identity proof for an Indian citizen. PAN number is demanded at many places now-a-days. When you file income tax returns When you open a bank account or Demat account It is useful in applying telephone connection and credit card When you want to register for service tax and sales tax When you buy or sell a vehicle When you deposit or withdraw money to the tune of Rs.50,000 in the bank or post office, PAN is a must If you want to invest in mutual funds If you are buying a property worth more than 5 Lakhs When you exchange large volume of foreign currency (over and above Rs.25,000), you need to submit your PAN CARD. Even when you buy GOLD , giving your PAN number has become mandatory after the DEMONETIZATION EFFORTS taken by the government recently on November 8, 2016. PAN card Dont’s… Same person having more than one PAN card is an offence. You have to submit any one card to the income tax department and update your info. You can be charged a fine of upto Rs.10,000 if you are found to have more than one PAN card. If somebody puts the PAN card to mis-use he might be fined and subject to imprisonment too. You can view your PAN card details in their website. If you apply for PAN card through private agents, kindly check whether your details are updated in the government website. Issue of PAN card PAN card issuing has been made very simple. You will be asked to fill up FORM 49-A and attach your address proof (Aadhar card or Ration card). The form can be downloaded from the following addresses online: www.tin-nsdl.com http://www.incometaxindia.gov.in/Pages/form-pan.aspx Also you get these forms issued by the IT PAN and TIN service centres. Having a PAN card doesn’t mean that you have to pay Income Tax. It is to facilitate people to pay Income Tax when their income levels warrants for paying tax. A Complete Tutorial on Financial Markets and...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Oct 24th, 2016 | 0 comments

Types of accounting information may be classified into four categories: Operating informationFinancial accounting informationManagement accounting information andCost accounting information 1. Operating Information: This is the kind of information which is required to conduct the day-to-day activities. Examples of operating information are: Amount of wages paid and payable to employeesInformation about the stock of finished goods available for sale andEach one’s cost and selling priceInformation about amounts owed to and owing by the business enterpriseInformation about stock of raw materials, spare parts and accessories and so on. By far, the largest quantity of accounting information provides the raw data (input) for financial accounting, management accounting and cost accounting. Spend Wisely 2. Financial Accounting: Financial accounting information is meant both for owners and managers and also for the use of individuals and agencies external to the business. This accounting is concerned with the recording of transactions for a business enterprise and the periodic preparation of various reports from such records. The records may be for general purpose or for a special purpose. Focus on the Long Term 3. Management Accounting: Management accounting makes use of both historical and estimated data in assisting management in daily operations and in planning for future operations. It deals with specific problems that is faced by enterprise managers at various organizational levels. The management accountant is often concerned with finding alternative courses of action and then helping to select the best one. For e.g. The accountant may help the finance manager in preparing plans for future financing or may help the sales manager in deciding the selling price to be fixed on a new product by providing suitable data. Generally management accounting information is used in three important management functions: ControlCo-ordination andPlanning 4. Marginal costing This is an important technique of management accounting which provides multi dimensional information that helps in decision making. Specialised Accounting Fields A number of specialized fields in accounting also have evolved besides financial accounting. Management accounting and cost accounting are the result of rapid technological advances and enhanced economic growth. The most important among them are explained below: 1. Tax Accounting: Tax accounting is all about the filing of tax returns and the consideration of the tax implications of proposed business transactions or alternative courses of action. Accountants specializing in this branch of accounting are familiar with the tax laws affecting their employer or clients and are up to date on administrative regulations and court decisions on tax cases. 2. International Accounting: This accounting is concerned with the special issues associated with the international trade of multinational business organizations or MNC’s. Accountants specializing in this area must be familiar with the influences that custom, law and taxation of various countries bring to bear on international operations and accounting principles. 3. Social Responsibility Accounting: This branch is the newest field of accounting and is the most difficult to describe. Social responsibility accounting is so called because it not only measures the economic effects of business decisions but also their social effects, which have previously been considered to be immeasurable. Social accounting is also known as social accounting and auditing, social and environmental accounting, corporate social reporting, corporate social responsibility reporting, non-financial reporting or accounting. Benefits of Social Accounting 4. Inflation Accounting: Inflation accounting is a term describing a range of accounting models designed to correct problems arising from historical cost accounting in the presence of highinflation and hyperinflation. Inflation accounting is used in countries experiencing high inflation or hyperinflation. 5. Human Resources Accounting: Human resource accounting is the process of identifying and reporting investments made in the human resources of an organization that are presently unaccounted for in the conventional accounting practices. It is an extension of standard accounting principles. This system of accounting...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Startups
on Jan 22nd, 2016 | 0 comments

The Key Functions of a Finance Manager Finance manager is one of the important role-players in the domain of finance function. He must have a complete know-how on the areas of accounting, finance, economics and management. His position calls for judicious capability and analytical approach to solve various problems related to finance. A person who deals with finance related activities may be called finance manager. “Focus on a few key objectives … I only have three things to do. I have to choose the right people, allocate the right number of dollars, and transmit ideas from one division to another with the speed of light. So I’m really in the business of being the gatekeeper and the transmitter of ideas.” – Jack Welch The Finance Man Finance manager performs the following major functions Forecasting Financial Requirements It is the principal function of the Finance Manager where he is required to estimate the financial obligations of the business concern. He should evaluate how much finances are required to procure fixed assets and forecast the amount needed to meet the working capital requirements in future. Acquiring Necessary Capital The next step of a finance manager is to focus on how the finance is deployed and where it will be available. Investment Decision Best investment alternatives have to be considered to assure reasonable and stable return from the investment. He must be competent in the field of capital budgeting techniques to govern the effective utilization of investment. The finance manager must attach more importance to the principles of safety, liquidity and profitability while investing capital. Cash Management Cash management plays a major role in the area of finance because proper cash management also helps to meet the short-term liquidity position of the concern. Inter-relation With Other Departments Finance manager handles various functional departments such as marketing, production, personnel, system, research, development, etc. He must maintain a good rapport with all the functional departments of the business organization. “Rule No. 1 : Never lose money. Rule No. 2 : Never forget Rule No. 1.”― Warren...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting
on Apr 25th, 2015 | 0 comments
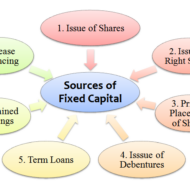
What is Long Term Financing? It is a form of financing that is provided for a period of more than a year to those business entities that face a shortage of capital. Before delving into the advantages of long term financing I would like to present you few fascinating facts on the economy that will blow your mind. Dell “has spent more money on share repurchases than it earned throughout its life as a public company,” writes Floyd Norris of The New York Times.According to Forbes, if a Google employee passes away, “their surviving spouse or domestic partner will receive a check for 50% of their salary every year for the next decade.”Start with a dollar. Double it every day. In 48 days you’ll own every financial asset that exists on the planet — about $200 trillion. Wow…According to Bloomberg, “Americans have missed out on almost $200 billion of stock gains as they drained money from the market in the past four years, haunted by the financial crisis.The “stock market” began in May 17th, 1792 when 24 stock brokers and merchants signed the Buttonwood Agreement.The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 creates the Securities and Exchange Commission, charged with the responsibility of preventing fraud and to require companies provide full disclosure to investors.Wall Street was laid out behind a 12-foot-high wood stockade across lower Manhattan in 1685. The stockade was built to protect the Dutch settlers from British and Native American attacks. Sources of Long Term Finance Long-term loans (External)Issue of shares or equitySale and leaseback (Internal)Retained profit Examples of long-term financing include – a 30 year mortgage or a 10-year Treasury note. Financial Markets and Securities Purpose of Long Term Finance To finance fixed assets.To finance the permanent part of working capital.Expansion of companies.Increasing facilities.Construction projects on a big scale.Provide capital for funding the operations. Factors determining Long-term Financial Requirements Nature of BusinessNature of Goods producedTechnology used Long term finance for businesses A Clear Perspective on Break Even Analysis Let us look at some of the Advantages of going for a Debt Financing Option Debt is the cheapest source of long-term financing. It is the least costly because interest on debt is tax-deductible, bondholders or creditors consider debt as a relatively less risky investment and require lower return.Debt financing provides sufficient flexibility in the financial/capital structure of the company. In case of over capitalization, the company can redeem the debt to balance its capitalization.Bondholders are creditors and have no interference in business operations because they are not entitled to vote.The company can enjoy tax saving on interest on debt. Disadvantages of Long Term Debt Financing Interest on debt is permanent burden to the company: Company has to pay the interest to bondholders or creditors at fixed rate whether it earns profit or not. It is legally liable to pay interest on debt.Debt usually has a fixed maturity date. Therefore, the financial officer must make provision for repayment of debt.Debt is the most risky source of long-term financing. Company must pay interest and principal at specified time. Non-payment of interest and principal on time take the company into bankruptcy.Debenture indentures may contain restrictive covenants which may limit the company’s operating flexibility in future.Only large scale, creditworthy firm, whose assets are good for collateral can raise capital from long-term debt. Financing through Debt Vs Equity There are a number of ways to finance a business using debt or equity. Though the first choice of many small-business owners would be equity, they may also prefer to utilize some type of debt to fund the business rather than take on additional investors. When done the right way, long-term debt financing provides a number of advantages to the business and its owner. Term Loans from Banks Most banks provide term loans,...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting
on Feb 24th, 2015 | 0 comments

What are known as Final Accounts? Trading, profit & loss account and balance sheet, all these three together, are called as final accounts. Final result of trading is known through Profit and Loss Account. Financial position is reflected by Balance Sheet. These are, usually, prepared at the close of the year hence known as final accounts. They serve the ultimate purpose of keeping accounts. Their purpose is to investigate the consequence of various incomes and expenses during the year and the resulting profit or loss. 1. Trading and Profit and Loss A/c is prepared to find out Profit or Loss. 2. Balance Sheet is prepared to find out financial position of a concern. Trading Account Trading refers buying and selling of goods. Trading A/c shows the result of buying and selling of goods. This account is prepared to find out the difference between the Selling prices and Cost price. Profit and Loss Account Trading account discloses Gross Profit or Gross Loss. Gross Profit is transferred to credit side of Profit and Loss A/c. Gross Loss is transferred to debit side of the Profit Loss Account. Thus Profit and Loss A/c is commenced. This Profit & Loss A/c reveals Net Profit or Net loss at a given time of accounting year. Trading Profit And Loss CMD from knoxbusiness Balance Sheet Trading A/c and Profit & Loss A/c reveals G.P. or G.L and N.P or N.L respectively; besides the Proprietor wants i. To know the total Assets invested in business ii. To know the Position of owner’s equity iii. To know the liabilities of business. Definition of Balance Sheet The Word ‘Balance Sheet’ is defined as “a Statement which sets out the Assets and Liabilities of a business firm and which serves to ascertain the financial position of the same on any particular date.” On the left hand side of this statement, the liabilities and capital are shown. On the right hand side, all the assets are shown. Therefore the two sides of the Balance sheet must always be equal. Capital arrives Assets exceeds the liabilities. BUY “ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS AND CONCEPTS” OBJECTIVES OF BALANCE SHEET: 1. It shows accurate financial position of a firm. 2. It is a gist of various transactions at a given period. 3. It clearly indicates, whether the firm has sufficient assents to repay its liabilities. 4. The accuracy of final accounts is verified by this statement 5. It shows the profit or Loss arrived through Profit & Loss A/c. PREPARATION OF FINAL ACCOUNTS Preparation of final account is the last stage of the accounting cycle. The basic objective of every firm maintaining the book of accounts is to find out the profit or loss in their business at the end of the year. Every businessman wishes to find out the financial position of his business firm as a whole during the particular period. In order to accomplish the objectives for the firm, it is essential to prepare final accounts which include Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. It is mandatory that final accounts have to be prepared, every year, in every business. Trading and profit & loss accounts are prepared, after all the accounts have been completely written and trial balance is extracted. Before preparing final accounts, it becomes obligatory to scritinize whether all the expenses and incomes for the year for which accounts are prepared have been duly provided for and included in the accounts. Form of Final Accounts: There is a standard format of final accounts only in the case of a limited company. There is no fixed prescribed format of financial accounts in the case of a proprietary concern and partnership...










