Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource
on Jun 25th, 2014 | 0 comments
Smith et al. describe management as “Making Organizations perform”. Management is concerned with Individuals who are delegated authority to manage others – Let me call them ‘People with Power’. Activities for achieving goals – ‘Real Action Plans’. A body of knowledge represented by theories and frameworks about people and organizations – ‘Policy Framework’. What do managers do? As we all know they are involved in general management functions like Forecasting Planning Organizing Motivating Co-ordinating Controlling Are you aware of the ‘hidden’ dimensions of a manager’s job? Modern management theories, although highlighting the complexity of the role, have yet to provide sufficient empirical research and advice into key areas that enable both managers and organizations to increase their effectiveness. For example Dealing competently with organizational politics (“You can ignore it, but it won’t go away” – This is how surveyed employees said they viewed office politics) Successfully managing change (Adaptability is about the powerful difference between adapting to cope and adapting to win) Controlling ethical issues and demands (It takes 20 years to build a reputation and five minutes to ruin it. If you think about that, you’ll do things differently.) Developing the role of women managers (Women can be better managers than men because they tend to be more conservative and do their homework. Men tend to take more risk without the research) Ensuring personal ‘survival’ and career success in organizations (A successful man is who lays a firm foundation with the bricks others throw at him.) Safeguarding personal health in a stressful environment (Manage stress before it manages you). How to achieve a more comprehensive view of development? Frameworks for setting, linking, and balancing individual and organizational objectives. Systems for identifying and selecting managers Structures to support, motivate and reward Plans to enable career progression Mechanisms to measure and evaluate performance. HRM and Management Development Human resource management as the name suggests is about the effective management of people in organizations. HRM involves the integration of people with business goals and strategies HRM views people as assets to be developed and utilized in a productive way rather than costs to be minimized or eliminated. The philosophies, ideologies, values and beliefs of management that operate and dominate within the organization have an impact on people management. The practices, policies and management styles that managers employ in their managerial role also align people’s behavior towards organizational goals. Senior managers determine the extent to which people are integrated into the organization’s strategic plans. They set the agenda and create the culture climate of prevailing values, attitudes and behavior. Middle and junior managers translate and ‘operationalize’ broader human resource strategies and policies. They give HRM its meaning and reality. It is their perfect management style and actual behavior that decided how the human resources is deployed and managed and thus what people experience as human resource management. The way managers themselves are managed and developed is a significant influencing factor in the way people are subsequently...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Interview Questions, Strategy
on Jun 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments

Social Media Recruiting Finding the right job is a herculean task and it reminds me of this saying, “When you want to have something you’ve never had, You have to do something you’ve never done.” Job Hunting: I would rather use the term ‘Job Hunting’ than ‘Job Searching’ because competition is so much so that you feel lost in the crowd. The job market scenario does not look very appealing in spite of being well-qualified for the respective positions. Everybody talks about ‘Cracking the Jobs with Hacking the Resumes’ and ‘Preparing a killer resume that is likely to pull you towards a dream job’. The sad part of the story is, “Dream jobs never exist and how can you land on something that is not there?” Of course, I go with you, ‘Resumes are indispensable for kick-starting the process; yet you need that extra something, which I would like to call the ‘J’ factor (people are getting bored of ‘X’ factor ‘J’ stands for job factor). Social Media Networking: Let me put it simply; you have to get noticed to capture the plum job. Market yourself in such a way that recruiters can never say no. Well, you guessed it right, “SOCIAL MEDIA NETWORKING” within quotes is the need of the hour and NOW-A-DAYS recruiters gauge the personality of the prospective candidates through social media networking sites like FACEBOOK, TWITTER AND LINKEDIN. Are you a people-person? Social media recruiting has become indispensable and most of the recruiting agencies overlook traditional channels like employment exchanges and classifieds and prefer the former source as the approach is more direct and focused. If you have a well-built profile in Facebook or LinkedIn your chances of landing on an enterprising job is guaranteed. Further. if you are an active member of a LinkedIn group or a Google Community, you stand a bright chance to capture the attention of big recruiters searching for the right talent. How prepared are you? The question is ‘How prepared are you to link a bait’ and ‘What are your chances?’ Social media recruiting has become a routine process in most of the ‘top-most’ companies and if you are not aware of the significance, you have everything to lose. Try to understand that, 40% of people socialize more online than they do face-to-face, 100.000 tweets are sent, 2 million queries are searched on Google and 684.478 pieces of content are shared on Facebook every minute. (Statistics courtesy- http://www.onrec.com/) Bumper Benefits for the recruiter: By using social media as a recruiting source companies straight away Cut the exorbitant outsourcing bill payments to external HR agencies as this is completely free Direct contact with the candidate and can assess his personality first hand Word of mouth referrals through social media (Social media is modern day word of mouth marketing) do the companies and employers Himalayan good by making prospective candidates stand in queue before them which otherwise proves to be a tough and expensive task. There is less spam as the communication is transparent that proves to be a win-win situation for both, the employer as well as the potential candidate Employers can bang on their potential targets by clear-cut job specifications and LinkedIn proves to be the top most destinations for social media recruiters. Social media recruiting fits companies of varying sizes and spheres In a single click the employers and recruiters have access to almost all information needed to write an authentic ‘Biography’ about you. If LinkedIn profile supplies professional information, Facebook shows your personal side. It raises a question though, ‘Are you social media-responsible?’, In other words ‘Are you behaving properly in the virtual...

Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour
on May 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
Organizational Climate – An Analogy Organizational climate is a measure of the feel of the internal environment of an organization which is perceived by an outsider and/or an employee according to their business with the organization. Organizational climate has a great effect on employees’ behavior. If the climate of an organization is open and friendly, employees feel relaxed and if it is very formal, then such a comfort level may not be felt. Climate for an organization is somewhat like personality for a person. “Just as every individual has a personality that makes him/her unique, an organization has a climate that clearly distinguishes its personality from other organizations. Human religionists introduced the concept of organizational climate in the late 1940’s. Now this has become a very useful metaphor for thinking about and describing the social aspects of a firm. Some definitions: “A set of characteristics that describe an organization and that i. Distinguish one organization from another ii. Are relatively enduring over a period of time and iii. Influence the behavior of people in the organization.” – Forehand and Gilmber “A mutually agreed internal (or molar) environmental description of an organization’s practices and procedures.” – Benjamin Schneider (1975) “A relatively ending quality of the internal environment that is experienced by the members, which influences their behavior and can describe in terms of values of a particular set of characteristics of the organization.” – Renato Tagiuri (1968) Features: It is an abstract and intangible concept. But it exercises a significant impact on the behavior and performance of organization members. It is the perceived aspect of organization’s internal environment. It refers to the relatively enduring characteristics which remain stable over a period of time. It gives a distinct identity to organization and differentiates it from others. It is a total expression of what the organization is. It is the summary perception which people have about organizations. It is a multi-dimensional concept. It consists of all organizational factors – authority pattern, leadership pattern, communication pattern, control etc. Elements of Organizational Climate: Individual Autonomy: The extent to which employees are entrusted with to make decisions, the degree to which they are free to manage themselves and have the freedom to exercise their responsibility come under the purview of individual autonomy. Position Structure: It means the extent of direct supervision, formalization and centralization in an organization. Reward Orientation: The degree to which an organization rewards individuals for hard work or achievement. It will be high when an organization orients people to perform better and rewards them for doing so. Task Orientation: If the outlook of the top management is task oriented, the employees will have to speed up the pace of work to please their bosses. Relations Orientation or Consideration: Here the climate is conducive and supportive where the managers are relations-oriented while dealing with their sub-ordinates. The needs and aspirations of the workers will be given due importance resulting in enhanced team spirit. Job Satisfaction: The workers feel happy if the jobs are designed to allow the worker to use their innovative skills. Morale: Morale represents a composite of feelings, attitude and sentiments of organizational members towards the organization, superiors and fellow workers. If it is high, there will be an atmosphere of co-operation and if it is low, there will be conflicts and poor co-operation among the workers. They will also feel dis-oriented in their work. Control: The control systems may be either rigid or flexible. An impersonal or bureaucratic atmosphere is seen in the former situation where the scope of self-regulation will be minimum. DOWNLOAD THE PDF...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Training & Development
on Apr 25th, 2014 | 0 comments
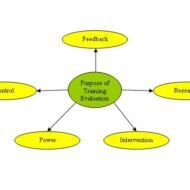
The process of Training Programme Evaluation Evaluation of training programme is basically critical examination of appraisal of training programmers. Appraisal of training programme is necessary for improvement and evaluation is a continuous process. “Learning from mistakes” and transforming them into experience and knowledge is the crux of training evaluation. Areas of Evaluation: The participant’s opinion about the programme Knowledge, attitude, skills learned during the training sessions Behavioral change, if any, as a result of training Pay off and benefits that accrue to the organization resulting from the change in behavior of the trainees. What should the evaluation process consider in the planning stage? Attributes of training programme to be evaluated Standard for evaluation Measuring various aspects of the programme and feedback on the effectiveness of the same Implementation of the programme results Scrutinizing the changes that need to be done in the training session Method of dealing with the change – Who will do it, how will the changes be made, how quickly the changes can be implemented. Steps in the Evaluation Process: Establish acceptable standards and bench marking Data collection Analysis of data, interpretation and drawing conclusions Feedback of the results 1. Establish acceptable standards Standards may be set in any one of the following methods; Setting standards through best practice Setting standards through bench marking 2. Data Collection Data may be collected using any one of the following techniques: Questionnaire Interview Written Test Observation 3. Analysis of Data and Interpretation Raw data should be tabulated – Histogram and frequency distribution yield basic information on the shape of dispersal of data around the mean and standard deviation. Relevant statistical tools must be employed depending upon the purpose of evaluation. 4. Evaluating and Feedback The steps involved in this process are: Design valuation – Includes clear objectives backed up by proper content Evaluation of content – Value and usefulness of the programme content may be measured by seeing the reaction of the trainees. An animated discussion in the classroom is a clear indication of the value the content offers. Usefulness may be known by interviewing the trainees and by comparing the performance impact of training with individual job descriptions. Evaluating the presenters – By taking feedback from the trainees the training quality of the presenter or lecturer may be evaluated. Evaluation of trainees – Three aspects that have to be considered on the part of the trainees are, feeling and opinion, learning and attitudinal changes. Evaluating on the job results and productivity changes – A number of factors affect productivity and pre and post measurement of some of the below mentioned aspects shall throw light on the effect of the training programme. Factors affecting Productivity: Cost Reduction ,grievance reduction, productivity after versus before training, work quality, quantitative results, accident rates, absenteeism, employee suggestions, supervisory rating, profits, sales volume, turnover rates, customer complaints, worker efficiency, training time required for proficiency, cost per untrained employee, new product development, new customers and public relations. Behavioral Factors: Some of the specific behavioral changes listed as follows can be observed before and after the training programme – application of new knowledge, use of new skills, high standards, courtesy, adherence to safety regulations, teamwork, perseverance, honesty, co-operation, quality of work, punctuality, effort, initiative. Useful Information: Sample Training Evaluation Questionnaire 5 evaluation methods to evaluate staff training...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource
on Apr 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Entrepreneurs are the mechanism by which our economy turns demand into supply. They create new ventures that provide new, improved products and services. Here we list some of the principal qualities of entrepreneurs and how those qualities help in shaping up our economy. Productivity Accelerators: Entrepreneurship raises productivity through technical and other forms of innovation. Entrepreneurs as risk bearers find resources and fill market gaps that would be missed by larger, more bureaucratic organizations. They allow a country to extract every last bit of marginal capacity out of whatever resources exist within the society. Brilliant Tips on Productivity by some Popular Entrepreneurs: Focus on one thing at a time: It may seem like a no-brainer, but multitasking can actually cut back on your productivity. Instead of juggling multiple projects at once, schedule out blocks of time — or even entire days — during which you only focus on one task or one project. Steph Auteri, @stephauteri, Word Nerd Pro Outsource, outsource, outsource: Everything may be a priority, but you are not equally brilliant at everything. Eliminate the unnecessary tasks and outsource your weaknesses so your time and focus is directed to where you’ll make the biggest impact for the business. Kelly Azevedo, @krazevedo, She’s Got Systems Define roles and divide work: Make sure everyone on the team has distinct roles defined, and divide work accordingly. Everyone on a proactive team will want to do everything, and clearly defined roles make it clear who should do what. David Gardner, @david_gardner, ColorJar Job Creators: It is a powerful tool of job creation –Entrepreneurship as a whole contributes to social wealth by creating new markets, new industries, new technology, new institutional forms, new jobs and net increases in real productivity. The jobs constructed through their activities in turn lead to equitable distribution of income which leads to higher standards of living for the population. Entrepreneurship facilitates the transfer of technology. Entrepreneurs play a strategic role in commercializing new inventions and products. They play a critical role in the restructuring and transformation of economy. Their behavior breathes vitality into the life of large corporations and governmental enterprises. Market Competitiveness: They make the markets more competitive and thereby reduce both static and dynamic market inefficiencies. Micro-preneurs working in the informal sector circumvent established government authority when governments and their programmes inhibit economic development. They stimulate redistribution of wealth, income and political power within societies in ways that are economically positive and without being politically disruptive. Social Welfare: They improve social welfare of a country harnessing dormant, previously overlooked talent. They create new markets and help in expansion into international markets. The unique feature of entrepreneurship – that it is a low cost strategy of economic development, job creation and technical innovations. Technology Innovation: Technology entrepreneurship is also important for sustainable development as Nobel Prize Laureate prof. Dan Schechtman puts it: “Technological entrepreneurship is a key to the well-being of the world”. India has been the first among the few developing countries to have assigned a significant and categorical state role to small scale industries from the first Five Year Plan itself, and the small scale sector has emerged as a dynamic and vibrant sector of the economy during the eighties. If the country develops pucca infrastructure and removes the hurdles in the operative environment politically and legally, no doubt the Indian economy will be scaling to greater heights. Surplus manpower (educated and un-educated), which has been a great liability can become an asset once those with potential are selectively groomed for self-employment and enterprise formation, leading to further job...










