Science of Macro Economics: Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole. The part of economics concerned with large-scale or general economic factors, such as interest rates and national productivity.

The sales and profit quotient of business enterprises in a market is dependent on the vigor of the overall economy to a greater extent.
During expansion, the real GDP can accelerate to 4 to 5 % a year and during recessions the pace of growth declines for an extended period.
The overall economic growth is subject to many cyclical fluctuations and the reasons for change in the pace and pattern of economic scenario still remains a mystery.
Business cycles are rhythmic patterns of expansion and contraction due to inflations and recessions.
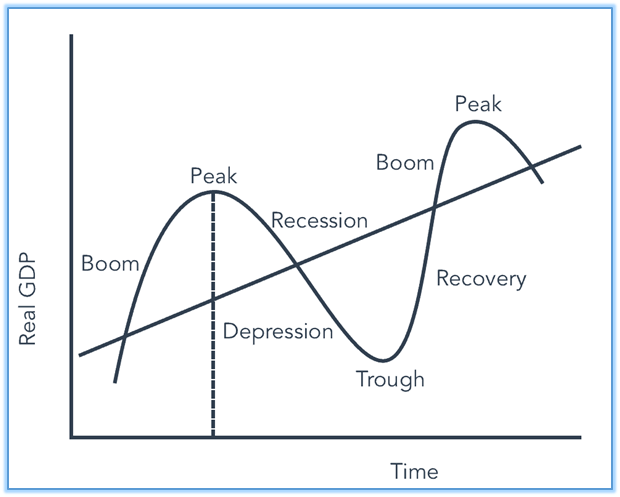
It is still an intriguing factor that unemployment persists even during times of expansion and production of goods and services fall down during cyclical downturn making millions of people lose their job.
If macroeconomics can find the appropriate solution to these problem situations, better will be the prospects of many people’s lives and fortunes.
Monetary and fiscal policies should be formulated in the light of reducing the severity of business cycles.
The purpose of monetary policies is to stabilize the prices by managing the expansion and contraction of the volume of money in circulation, full employment and stability of exchange rates.
Fiscal policy is linked with the government’s stand on public revenue, expenditure and debt.

The idea is to reduce inequalities in income and wealth and develop a socially optimum investment pattern.
Resources available in a country influence the kind of investment pattern. Developing countries like India has its focus of activity centered on telecommunication and power generation through information technology and alternate fuel resources.
Availability of skilled labor is an additional plus in countries like India and China and many countries prefer to outsource their business processes to offshore companies present here.
Tax structure is a source of revenue generation aimed at economic stability.
During inflation, an increase in tax rates will reduce the buying power of people thereby reducing the prices in the economy.
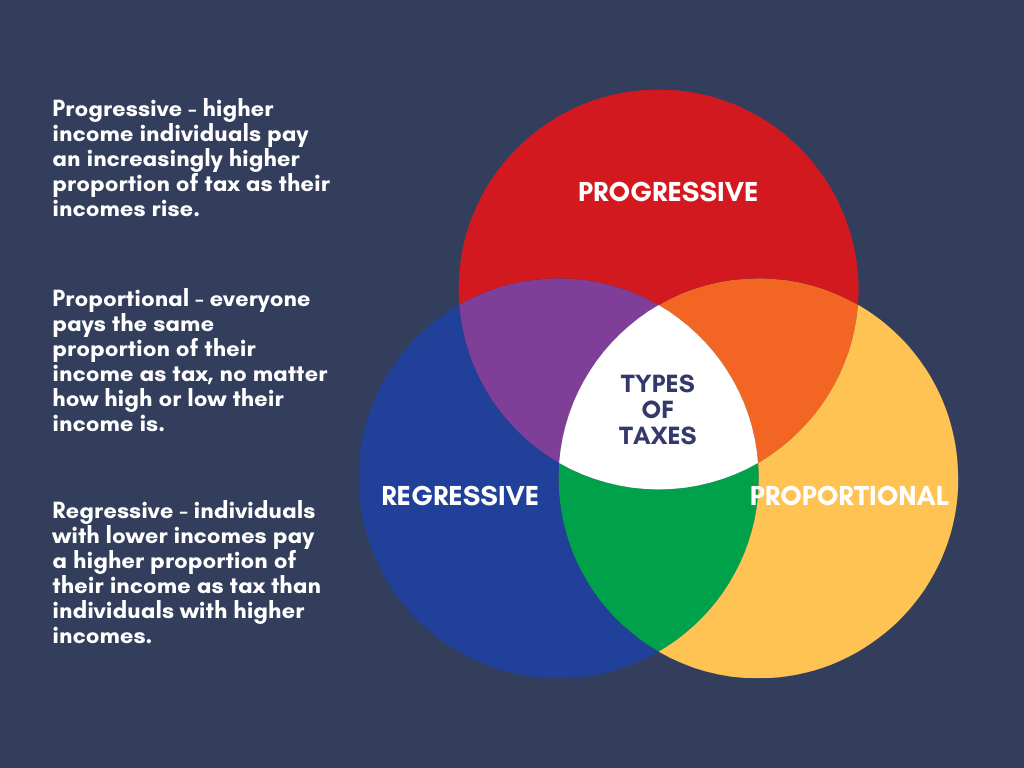
A reduction in tax rates during depression will encourage economic investment and consumption. Generous subsidies and reforms in industrial policies alone cannot bring about the desired growth in the economy.
A nation should aspire to increase its growth ratio by providing the necessary infrastructure.
Economic scholars of each nation have to vigilantly analyze the previous patterns of business cycles for the benefit of the society and this kind of review will lead to dependable forecasts on the basis of which proactive measures could be devised.
Note:
What is VAT: VAT is a multi-point levy where the tax paid on local purchases from the registered dealer can be set off against the tax payable on the sale of goods, other than special goods.