Posted by Managementguru in Glossary, Human Resource
on Dec 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments

This HR Glossary pertains to ‘A’ series terminologies Ability Aptitude or competence, the skill or proficiency needed to perform certain tasks. Ability test An assessment instrument used to measure an individual’s abilities, mental or physical skills level (i.e. problem solving, manual dexterity, etc.). Absenteeism Referred to as the habitual failure of employees to report for work when they are scheduled to work. Absolute ratings A rating method where the rater assigns a specific value on a fixed scale to the behavior or performance of an individual instead of assigning ratings based on comparisons between other individuals. Abstract reasoning The process of perceiving issues and reaching conclusions through the use of symbols or generalizations rather than concrete factual information. Acceptance theory of Authority A manager’s authority rests on his or her subordinate’s acceptance of his or her right to give orders and to expect subordinate’s compliance with them. Accessibility The extent to which a contractor’s or employer’s facility is readily approachable and does not inhibit the mobility of individuals with disabilities, particularly such areas as the personnel office, worksite and public areas. Accessible format Materials that are designed in alternate formats such as Braille, audiotape, oral presentation or electronically for individuals with visual impairments. Accident and Health Benefits Employee fringe benefits paid usually through employer funded insurance plans. Accountability The responsibility placed on an individual or group for their own or others’ actions, conduct, performance, projects, etc. Accreditation A process of external quality review and certification by a recognized body that evaluates individuals, colleges, universities and educational programs to assure they are performing the functions that they claim to be performing in a competent manner. Achievement test A standardized testing instrument used to measure how much an individual has learned or what skills he or she has attained as a result of education, training or past experience. Acquisition The process of acquiring control of another corporation by purchase or stock exchange. Action learning A learner-driven, continuous learning process where learning revolves around the need to find solutions to real problems. Active learning The process of learning new knowledge, skills and behaviors through taking specific actions or performing specific tasks. Active listening A manner of listening that focuses exclusively on what the other person is saying and validates understanding of both the content of the message and the emotions underlying the message to ensure exact understanding. Activities of daily living (ADL) The personal care activities which are essential to an individual’s everyday living, including eating, bathing, grooming, dressing, mobility and toileting. Action-centered Leadership A theory of leadership which focuses on what leaders actually have to do in order to be effective,rather than on the personal qualities that they need to be good leaders, and which believes that leadership can be taught. Adjunct program A supplemental training tool that applies programming principles to existing instructional modules, materials, texts, manuals, etc., that are designed to direct the learner to specific areas within the module. Adjudicator: Aa person who gives a decision on a problem, an adjudicator in an industrial dispute. Administrative service organization (ASO) A term used to define an organization that provides outsourced solutions to meet the administrative and HR needs of the client with the client retaining all employment-related risks and liabilities. Administartive Officer Office employee responsible for managing the office, running errands and assisting the executive or boss, typing, filing, and other office related duties as required by the specific job. Adverse action Any act by an employer that results in an individual or group of individuals being deprived of equal employment opportunities. Adverse impact A substantially different rate of selection in hiring, promotion or other employment decision that works...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Apr 5th, 2014 | 0 comments
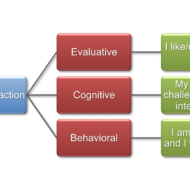
Attitude and Job Satisfaction What is attitude? Attitudes are evaluative statements or judgments concerning objects, people or events –Stephen Robbin. They also represent an ‘affective orientation towards an object.’ It simply means what one feels and thinks about something. Elements of attitude: Cognitive components – opinion or belief Affective components – emotion or feeling Behavioral components – intention to behave The interaction of these three components determines the way in which an individual develops an attitude towards something. Sources: Society Friends Teachers Family Members It also forms on the basis of the level of admiration we have over an object or persons. People also try to imitate others and attitudes are gradually formed on that basis also. In some attitudes formed are less stable, in some they even dominate the whole life. Types: Organizational behavior uses the concept of attitudes in relation to nature of the job and its influence on the performance of the persons. Accordingly, Job Satisfaction Job Involvement and Organizational Commitment, are the three kinds of attitude a person could have with respect his / her job or organization. Job Satisfaction: In “Job Satisfaction “, Stephen P. Robbins writes about five factors which make a person satisfied with his or her job. These factors are Mentally challenging work Equitable rewards Supportive working conditions Supportive colleagues and Personality-job fit. Cranny, Smith and Stone define job satisfaction as employees’ emotional state concerning the job, considering what they anticipated and what they actually got out of it. In fact, an employee with low expectations can be more satisfied with a certain job than someone who has high expectations. If one’s expectations are met or surpassed by the job, then one is happy and satisfied with the job. Job Involvement: Job involvement has been defined as an individual’s psychological identification or commitment to his / her job. As such individuals who display high involvement in their jobs consider their work to be a very important part of their lives- In other words for highly involved individuals performing well on the job is important for their self esteem. Organizational Commitment: Three important elements of a committed individual would be Identification with the organization’s goals and/or mission Long-term membership in the organization and intention to remain with the organization, often termed loyalty High levels of extra role behavior- behavior beyond required performance- Often denoted to as citizenship behavior or pro-social behavior. Cognitive Dissonance Theory: Leon Festinger developed this theory which explains the relationship between attitude and behavior. It refers to”any incompatibility that an individual might perceive between two or more of his or her attitudes, or between his or her behavior and attitudes.” Attitude Surveys: This is a tool that helps to collect information about the levels of attitude among the people. In most companies these kinds of surveys are conducted with the help of different rating scales like Likert scale offering five or seven alternative choices for each of the statement developed for attitude measurement. Summary: Research conducted on attitude and job satisfaction in Indian workers has made clear certain points as given below: Attitude is positively correlated with efficiency Absenteeism will bring down satisfaction levels Unions, negatively affect the employee attitude and job satisfaction Attitude researches and surveys will improve...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
India often looks at Japanese or American models to comprehend the concepts of management. In reality, Indian scriptures can be considered as treasuries of management. The Bhagavat Gita, the Vedas and the Epics highlight the true spirit of working together and the need for de-stressing the self for enhanced performance levels. The idea of NISHKAMYAM (to perform one’s own work without expecting a result) is truly said to be the highest ideology preached by Lord Krishna. What Induces Stress? A dynamic condition in which an individual is presented with an opportunity or confronted with a demand, related to what she or he desires and for which the outcome is uncertain but important, can be called a stressful situation. The consequences of stress in an organizational set up express themselves in the form of physiological, psychological or behavioral symptoms, which are harmful to the individuals who experience high levels of stress. Symptoms of stress: AnxietyDepressionIncreased job dissatisfactionAbsenteeismDecline in productivityRapid turn overHigh blood pressureHeart diseasesHead aches Stress Can be Motivating: While long term stress is harmful to the individual and organization as well, it is said that short term stress serves the purpose of task accomplishment by individuals or groups, within the stipulated time. It serves as a motivation factor rather than a causative agent of frustration. It has been proved by scientists and medical researchers that stress has a direct effect on the metabolism of a person, that causes increase in heart and breathing rates, increase in blood pressure, thus inducing heart attacks. Equally important are the behavioral and attitudinal changes that are created by stress, which cannot be overlooked. Job Satisfaction: Psychological symptoms arise due to job-related dissatisfaction, boredom, work pressure, irritability and procrastination. Sometimes forceful involvement may also lead to decreased job satisfaction. The job to be carried out can be finished at the particular time if the individual is able to give one’s best shot. But when it is performed under stress, they complete the job with dissatisfaction. When the incumbent is asked to perform a task that lacks clarity, naturally ambiguity arises in his mind followed by anxiety. Behavioral Symptoms of Stress Changes in productivity levels, absence, and rapid staff turnover are stress symptoms of behavioral nature. It might be expressed even in the form of increased smoking, consumption of alcohol etc., Say for instance, in production department, when there is a need to supply a product in a very limited time, the workers may be active initially, but the performance slows down when they get totally tired or dissatisfied with the work. Again the demand by the superior adds additional stress that reaches unmanageable levels. Similarly, people taking care of administration, banking, marketing and other office related works fall a prey to stress. How to manage stress? From an organization view point, it is believed that a limited amount of stress may work wonders in terms of performance, with stress acting as a “positive stimulus”. But even low levels of stress are likely to be perceived as undesirable from an individual’s stand point. How could be the notion of management and individuals be different on the acceptable levels of stress? It does not solve the purpose. Individuals have to understand that, they have to live up to the expectations of the management in order to enhance their credit ratings, in terms of promotion and pay. They have to understand that challenges are to be perceived as opportunities to prove their mettle. Self and situational analysis, work analysis, time management and physical well- being are some techniques that practically solve problems of stress. “De-stressing the Self” Techniques for Employees Organisations can reduce stress of the employees...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Strategic Evaluation: concerns mainly the analysis and judgment of interventions at the level of strategic goals. One of the noteworthy aspects of strategic evaluation consists of the verification of the adopted strategy with respect to the current and likely social and economic situation. How a firm has performed over time and relatively to its competitors, can be determined with the help of the following quantitative measures. Market price of the sharesMarket shareEarnings on capital employedDividend ratesReturn on equityGrowth in sales volumeProduction costs and efficiencyDistribution costs and efficiencyEmployee turnover, absenteeism, and satisfaction indices. Since there is a high correlation between progress and these indicators, we can say that a firm is successful if majority of the factors show a positive signal. But in reality, one cannot expect a business firm to satisfy all the above mentioned criteria, as performance is also affected by unexpected variations in the external environment. One has to trade-off between the positive and negative indicators and find suitable ways to enhance the performance levels. Effectiveness of a Strategy: The strategic importance of any particular criterion may not remain the same at different points of time. The short run and long run effectiveness of strategy cannot be evaluated using the same criteria. There may be difficulties in computation and different methods of computation that may be encountered in measurement. These factors serve as the bases for firms to identify the elements of success. Yet another way of performance evaluation is to identify critical factors that may be regarded as symptoms of decline and can be treated as early warning signals during the implementation of strategy. If they indicate the necessity of a turnaround or retrenchment strategy, the firm should definitely go for a suitable action without further delay. Such factors may be: Declining profit marginDeclining market shareRapidly increasing debtDeclining working capitalIncreasing managerial turnover What is the Need for Strategic Evaluation? You might be curious to know, what is the need for a strategic evaluation at all in the first instance? See, business firms and corporate companies are always in a position to execute their action plans in the wake of severe competition and retention of market share. A plan without a strategy is like life without a soul and decision making is solely dependent upon strategic inputs. Turnaround Strategy The need for feedback, appraisal and reward, check on the validity of strategic choice congruence between decisions and intended strategy all these help in successful culmination of strategic management process and create inputs for new strategic planning. What’s the difference between Strategy and Tactic? The evaluation need not be based only on quantitative terms, but also on qualitative aspects such as: internal consistency, consistency with the environment, appropriateness of the strategy in the light of available resources, acceptability of the degree of risk involved in the strategy, appropriateness of the time horizon of the strategy...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
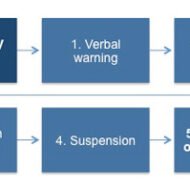
Organizational Discipline – A Way of Life Organizational Discipline: Discipline is the force that prompts individuals or groups to observe rules, regulations, standards and procedures deemed necessary for an organization. Discipline is one word that instills fear in the minds of individuals. The very word sounds autocratic when uttered by your boss and creates a feeling that you are being forcibly controlled. If you do not live up to the expectations of the management, definitely you are going to get listed for disciplinary action. Why is that discipline always gets enforced to gain obedience?Why people get intimidated when subjected to disciplinary action?Why streamlining your behavior becomes so difficult some times? Have you ever given a thought on how we always try to put the blame on management for being a father figure? We have to see things from a broader perspective. When you work for somebody, it is their prerogative to develop some rules and standardize some norms which they think is suitable for the mode of operations. Policies and procedures are formulated for the effective functioning of the organization. It is your responsibility to make them satisfied with your conduct to gain trust and confidence. Organizations are real time schools where you can learn a lot about proper social behavior and develop high standards of discipline. Learning Induces Change in Behavior Learning, an ongoing process is a wonderful experience and individuals must use the opportunity to fit themselves well in the human network when they work for big corporates. The objective of discipline is “orderly behavior”. How many of you maintain a cordial relationship with your peers in the organization?Are you sure they are not talking behind your back for some unpleasant quality of yours?Are you alienating yourself from the rest of the group? Self appraisal is the best way to rank yourself against various critical factors of interpersonal relationship with your team members. Things which we have to consider that might be the causes for indiscipline and misconduct stems from psychological, social and personality oriented factors. Absenteeism Pic Source: Dominion Systems Absenteeism is one thing that no superior can withstand as it directly affects the productivity and vitality of the company. The reasons if presented are weird, he becomes more agitated. Dishonesty is not a thing to be tolerated by the management. Insubordination also causes clashes between the executives and the employees as their “egos are battered.” Carrot and Stick Policy Considering from the employees’ point of view, the carrot and stick policy of the management alone do not make them committed to the firm. Challenging tasks, sense of participation, favorable work climate etc. makes them more responsible and faithful. Immediate rewards and recognitions are more appealing than deferred benefits like pension or gratuity. The emotional aspects of the employees must not be handled in a conservative but in a flexible manner by the management. This will create a feeling of trust and openness between the two. Democracy Hard and fast rules may not solve the purpose when there is no room for any humanism or democracy. This might even be the cause for employees to work against the interests of the company. This leads to disciplinary actions which prove hectic to both the parties. The management on its part has to definitely shed its autocratic attitude and adapt to more participative style of leadership. Personnel department has to play their administrative role in acting as a link factor between the employees and their superiors. Although managers exercise the authority of punishment, it is the HR department’s duty to develop proper procedures of administration of discipline and assist the management in conducting enquiries and solicit the cooperation...










