Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Decision Making, Management Accounting, Project Management
on Apr 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
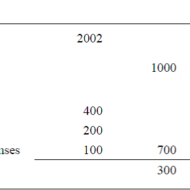
ACCOUNTING AND DECISION MAKING – IDENTIFYING THE PROBLEM SITUATION Learn accounting and finance basics so you can effectively analyze business data to make key management decisions. Business owners are faced with countless decisions every business day. Managerial accounting information provides data-driven input to these decisions, which can improve decision-making over the long term. Fig 1.1- ACCOUNTING INFORMATION FOR A SINGLE PRODUCT The above illustration clearly depicts that there has been a loss of Rs.100 in one year’s time for this particular product. The reason can be attributed to the increase in the “cost of goods” whereas other expenses have remained the same in both the years. For a single product manufactured, the problem is identifiable and solvable. But when the organization is producing a range of products, you need to apply some accounting technique by which the product losing money is identified and suitable measures are taken to cut down the escalating cost. Fig 1.2- Accouning Information for a Product Range The above illustration compares and contrasts the relationship of three products a company manufactures. It is seen that products P1 and P2 are doing well. Though the cost of sales has gone up for P1 and P2, the sales volume has also increased thus increasing the gross profit over the period of time. Here the product that has to be dealt with is P3 whose sales volume has drastically gone down, yet with the same cost of sales. When there is an increase in cost of sales, two things have to be considered. Identifying the problem-product Either cut down the production cost or increase the selling-price if the product has a real demand in the market. Uses of Accounting Data: Accounting information helps the management to arrive at make or buy decisions, to outsource production of certain components to cut down or control costs, to expand the production, to increase the sales volume or to downsize their project capacity. Techniques like Break-Even Analysis, Costing and Budgeting aid in going for the right production-mix, marketing-mix and sales target plans for the respective financial years. Aggregate Planning: As we all know planning is the key to the future and financial planning has to be given utmost importance for a production process. Aggregate planning involves translating long-term forecasted demand into specific production rates and the corresponding labor requirements for the intermediate term. It takes into consideration a period of 6 to 18 months, breaking it into work modules weekly or monthly and planning for the specific period in terms of men, material and...

Posted by Managementguru in Operations Management, Project Management
on Feb 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
Significance of Operations Management: Business firms need to formulate brilliant operations strategies in order to survive in the market for long. Focus on finance and marketing alone is not sufficient to compete in the global market. The emergence of innovative products and processes from leading companies in different parts of the world is a clear-cut evidence to prove the significance of operations function. Operations management is gaining importance, thanks to public awareness on quality and its applicability in service operations too. Advent of Industrial Revolution: Until the advent of machinery, each and every nation was dependent on agriculture, which was the prime economic activity. After the industrial revolution of the eighteenth century, mechanization in a large scale converted agricultural economy to an industrial economy. Slowly scientific principles were introduced into production activities to make it more systematic and thus “Production Management” evolved. Now service operations have also gained momentum and since the concepts and techniques of production management are applicable to service operations too, it is rightly called as “Operations Management.” Operations management functions at three different levels. Strategic levelTactical levelOperational level Strategic level: At the strategic level, the operations manager must have a long term vision, as to shape up the company’s success in the light of strategic decisions taken, with the approval of the top management. His area of concern would be, New product developmentNew process developmentProduct re-designProcess re-designProcess layoutProduct layoutFacility locationAggregate capacity planningPlanning co-ordination with finance and marketing departments Tactical level: At the tactical level, the operations manager is concerned about the planning and scheduling operations of the desired output. His area of concern would be: Designing a suitable inventory systemPlan for the work force and train them effectivelyQuality control systemMaintenance andReliability assurance system. Operational level: At the operational level, the job of the operations manager is to accomplish the “set targets”, by performing various coordinating and controlling functions. His area of concern would be: Ordering materials at the right timeScheduling productionScheduling workers as per production requirementControlling quality of goods and services producedFollow up of various schedules for proper implementationMaintaining and updating equipment and system reliabilityOn the job skill development of workers, etc. These functions are by no means exhaustive, but only indicative. The process of planning and control operations is not done in water tight compartments, but are interactive and integrative feeding on one another and also aligned in line with the overall corporate objectives. The strategies are evolved for the purpose of efficient utilization of the available resources as well as to predict the changes in the external business environment that calls for suitable action to limit their impact on the goals of the organization, in terms of cost, quality and...




