Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
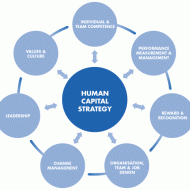
Human Capital is the skill sets, knowledge and experience of human resource put to effective use to increase productivity. The term capital indicates the resource value of humans in which organizations invest their time, energy and money. The much pondered subject in recent times in big corporate organizations is about managing human capital.

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

New Paradigms in Employee Retention What is Employee Retention: It refers to the various policies and practices which let the employees stick to an organization for a longer period of time . It refers to the ability of an organization to retain its employees. HRM Practices: A company to ground itself successfully in the chosen field of activity should adhere to sound human resource management practices, as it is firmly believed that human resource is an asset and investment in human capital paves way for comprehensive development. Many firms fail, in spite of being resourceful in terms of capital, infrastructure and technology. The reason shall be attributed to ineffective handling of human skills or misappropriation of human potential. Human resource management involves not only in recruiting and selecting the right people but also empowering them by suitable training to enhance their technical skills and expertise to perform tasks. The Purpose of Training: Training ultimately aims at converting theorists to performers and orients itself towards accomplishing the enterprise objectives. Big corporate companies concentrate on talent acquisition from the pool of fresh graduates and experienced hands in the IT industry as well. They create a lively corporate atmosphere with “an intelligence network” contributing to the success of the organization. Recruitment and Selection: If you have a feeling that, recruitment and selection are mere procedures to be followed for the sake of selection of human resource, kindly change that notion. These are the crucial steps which determine the fate of your organization. People from different disciplines form a team to achieve the goals and objectives of your organization. Leading a group with such diversity is a feat in itself. Selecting knowledge workers whom you believe will achieve your corporate mission and devising the human resource practices in accordance with their work-life balance will yield great results. Training Programmes: Training programs are developed for different spheres of activity by experienced trainers under the guidance of the top management. Proper training to the trainees ensures maximum work done in minimum time. Training not only makes individuals more informative and knowledgeable but also action buffs. Learning is a key process in training that brings about the desired change in behavior. Corporate companies are also concerned about the career prospects of employees working for them, as they are very well aware of the fact that providing lateral and vertical growth prospects for their workers is the only possible way to retain them. Another way for employee retention is to offer compensation on par or higher than industry standards and periodic review of their pay or compensation in accordance with the performance standards. This method of evaluation is suitable only for companies where workers are highly self motivated and have the capability to understand what it takes to reach the next level in their career ladder. Flexi-Timings: Flexibility is introduced in work life by some of the big corporates who try to visualize the practical problems faced by their employees, particularly women, who come to work. They offer “flexi-timings” in work and support by running “crèche” to nurture new borns. It has been proved that a small siesta after lunch improves the brain activity. The HR policies formulated by the management must encompass all the elements needed for a holistic vision, mission and business growth. This can be made possible by maximizing the efficiency of human capital that adds value to the organization. Note: Companies will also continue to remain generous with pay packages but the big change will be that they will invest a lot more in training and development. “Acquiring talent is much more expensive than grooming...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Training & Development
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
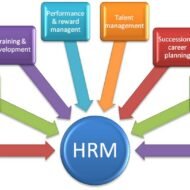
Definitions of Human Resource Management: 1. “A series of integrated decisions that govern employer-employee relations. Their quality contributes to the ability of organisations and employees to achieve their objectives.” (Milkovich & Boudreau, 1997). 2. “Concerned with the people dimension to management. Since every organisation comprises people, acquiring their services, developing their skills, motivating them to higher levels of performance and ensuring that they continue at the same level of commitment to the organisation are essential to achieving organisational goal. This is true, regardless of the type of organisation: viz. government, business, education, health, recreation, or social action.” (Decenzo & Robbins, 1989). 3.”The planning, organising directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, integration, and maintenance of human resource to the end those individual, organisational, and social objectives are accomplished.” (Flippo, 1984). 4. “The organisation function that focuses on the effective management, direction, and utilisation of people; both the people who manage produce and market and sell the products and services of an organisation and those who support organisational activities. It deals with the human element in the organisation, people as individuals and groups, their recruitment, selection, assignment, motivation, empowerment, compensation, utilisation, services, training, development, promotion, termination and retirement.”(Tracey,1994 ) Knowledge Workers Human resource management is therefore understood as the all significant art and science of managing people in an organisation. Increasing research output in behavioral sciences, new trends in managing ‘knowledge workers’ and advances in training methodology and practices have led to substantial expansion of the scope of human resource management function in recent years. HRM is not just an arena of personnel administration anymore but rather a central and pervasive general management function involving specialised staff as assistants to main line managers. Managing employee relationships is the role of the Human Resource department Human Resource Management is a process of valuing and developing people at work, this includes: Recruitment and selection Employee communication and engagement (participation) to increase employee retention Training and development Leadership WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST WEAKNESS Labour turnover & staff retention Labour turnover refers to the proportion of a workforce that leave during a period of time (usually one year) Labour turnover = number of staff leaving during the period x 100 average number of staff Staff retention refers to the ability of a firm to keep its workers. The disadvantages of having a large proportion of staff leaving each year include: The cost of recruiting replacement workers The cost of training the new workers Loss of productivity whilst replacements are found Loss of experienced workers Negative impact on reputation WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST STRENGTH Methods to control turnover: 1. Financial methods of motivation Bonuses Profit share Fringe benefits 2. Non financial methods of motivation Employee engagement and empowerment Training and development Promotion opportunities 3. Improved Human Resource Management procedures Four Fundamental Principles of HRM: Human Resource is the organisation’s most important asset; Personnel policies should be directed towards achievement of ENTERPRISE goals and strategic plans; Corporate culture exerts a major influence on achievement of excellence and must therefore be strengthened with consideration of employee welfare. Whilst integration of corporate resources is an important aim of HRM, it must also be recognised that all organisations are ‘pluralist societies’ in which people have differing interests and concerns, which they defend and at the same time function collectively as a cohesive group. →Evolution of...






