Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Human Resource, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategy implementation is the transformation of chosen strategy into organizational action so as to achieve strategic goals and objectives. The journey towards success is a saga or penance, where your effort and concentration is focused only on achieving the goal. It can be compared to the blinkers of a horse to give direction and avoid distractions. Proper resource planning is the key factor that gives a practical shape to your strategies. The available resources should be put into optimum use. Corporate Resource Planning: Resource planning at the corporate level comprehensively covers the planning for physical resources, human resources, financial and intangible or intellectual resources like patents, copyrights, technology, trademark etc., at the macro level of the firm. These are needed for the corporates to achieve their vision and also give direction to the departments at the functional level. These resources are allocated after giving due consideration to the industry’s cycle position, competitor strength, technological changes in the industry, market share and the type of competition in the industry. Economic Models with Value Additions: For instance, automobile owners have tapped the customer psychology and are concentrating more on producing bug cars that is very appealing to the upper middle class families, since a four wheeler is more comfortable and safe to drive, well within the budget range, ideal for a nuclear family and at the same time serves the purpose of a status symbol. So, these car manufacturers become direct competitors for two wheeler producers. Even if say, 25 to 30 percent of two wheeler population is shifted to four wheeler usage it is a huge success to the car manufacturers. Tata Nano car, a brain child of Ratan Tata is one of its kind. He has capitalized on the middle class Indian frame of mind to go for economic models with value additions. “Nothing is permanent except change”, so in this fast moving business arena all business persons are subjected to the necessity of thinking new, if not big. Corporates concentrate more on their strategic business units which serve as functional units and also a part of an organization, say a factory or a showroom. The resources for each of these business units have to be planned. The human resource department has to play its part in a promising way as human personnel are the critical success factors of an organization that manipulate other resources efficiently. Product and Process Innovations: Product and process innovations are the need of the hour and corporates are spending huge amounts on research and development of new products and processes. It has to be kept in mind that the innovations have to reach the markets quickly in order have an edge over your competitors. Identify your strength Tap the unidentified needs of the consumer Allocate management responsibility for each task Set your priorities by resource rationing Test your key assumptions Whether your product is acceptable in the market Whether the technology is updated All of these help you in forming a strategic platform upon which strategic implementation is done. Rational and realistic assumptions are the basic premises on which your decisions have to be based. Adequate finance, machinery and maintenance, labor force, marketing mix, your product strength, critical success factors of your organization, everything has to be thoroughly analyzed and put into action for successful strategic implementation. Related Videos… Alternative Competitive Advantage Introduction to Strategic...

Posted by Managementguru in Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
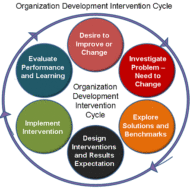
Organizational Development Training and development is an important aspect of human resource development. However the traditional methods and approach of T&D has its own limitations in that the focus is on individual development and behavior modification. This has seldom produced organizational development and hence in 1960’s an integrated approach called the ‘OD’ or organizational development was developed. Meaning and definition of organizational development (o.d.) “A process used to enhance both the effectiveness of an organization and the well being of its members through planned interventions.” OD is the systematic application of behavioral science knowledge for the purpose of improving productivity, efficiency, effectiveness and overall health of the total organization. The applied interventions attempt to modify the beliefs, assumptions, values, attitudes and standards of both the individuals and groups thereby transforming the organizational culture for the betterment of system as a whole. FEATURES OF ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT: HUMANISM: The focus is on the employees, their attitude and inter-personal relationships. An organization is a network of people whose emotions, outlook and cohesiveness are more important than monetary and other physical aspects because it is they who take the organization to the next higher level. This is made possible by open communication, free and frank discussions of problems with employees by the managers, inter-personal trust and above all, sense of belongingness, comradeship and team spirit. PROBLEM-SOLVING NATURE: The purpose of an OD intervention is to solve a problem. The employees themselves are given the opportunity to identify the problem by Survey Feedback and find a suitable solution through analysis. This is a cyclic process and also called as “Action Research”. SYSTEMS APPROACH: OD is concerned with not the structure or persons per se, but with the interplay of structure and persons. LEARNING THROUGH PARTICIPATION: The participants of the learning process are none other than the employees. They unlearn old things and learn new things by identifying, analyzing and finding the right solution to the bottlenecks. TOP MANAGEMENT SUPPORT AND INVOLVEMENT: OD intervention is successful only when top management involvement is full-fledged and ensures participation from all levels of managers and all departments in such an exercise. MULTIPLE INTERVENTIONS: Intervention takes place at various levels, individual as well as group and the purpose is molding desirable work culture and leadership styles suitable for the organization. ROLE OF CONSULTANT: Employing an external consultant will be more appropriate as he is less susceptible to influences and more objective. He acts as the change agent facilitating co-ordination and stimulation. CONTINGENCY PLANS: Alternate plans are also devised if in case the original plan fails; the idea is one that of trial and error, hence the need for contingency plans and approach to OD problem. RENSIS LIKERT’S OD FRAMEWORK: Rensis Likert’s 4 system OD framework aims at moving towards truly participative system. Care and caution must be adhered to steer the system gradually from where the organization now works. He also introduced diagnostic analysis to find what causes the current problem. His three part diagnostic analysis includes: A. OUTPUT CAUSES: Low productivity, absenteeism, declining profit B. INTERVENING CAUSES: Organization structure, control, policy and leadership C. ROOT CAUSES: Attitude, motivation level, empowerment and organization culture Tips for Organization Development OD CULTURE: “The OD paradigm values human and organizational growth, collaborative and participative processes and a spirit of enquiry.” Brown and Covey have made some attempts to identify OD values from the following: Norms and Values: Respect for people: People are the most important of all resources. So giving due respect and importance to people induces the creativity and innovation in them. Trust and Support: Trust, openness and supportive climate improve organization culture and empowerment. Power Equalization: This emphasizes hierarchical authority, control and centralization. Confrontation: Do not...




