Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting
on Apr 25th, 2015 | 0 comments
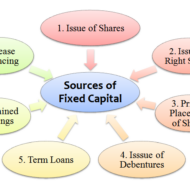
What is Long Term Financing? It is a form of financing that is provided for a period of more than a year to those business entities that face a shortage of capital. Before delving into the advantages of long term financing I would like to present you few fascinating facts on the economy that will blow your mind. Dell “has spent more money on share repurchases than it earned throughout its life as a public company,” writes Floyd Norris of The New York Times.According to Forbes, if a Google employee passes away, “their surviving spouse or domestic partner will receive a check for 50% of their salary every year for the next decade.”Start with a dollar. Double it every day. In 48 days you’ll own every financial asset that exists on the planet — about $200 trillion. Wow…According to Bloomberg, “Americans have missed out on almost $200 billion of stock gains as they drained money from the market in the past four years, haunted by the financial crisis.The “stock market” began in May 17th, 1792 when 24 stock brokers and merchants signed the Buttonwood Agreement.The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 creates the Securities and Exchange Commission, charged with the responsibility of preventing fraud and to require companies provide full disclosure to investors.Wall Street was laid out behind a 12-foot-high wood stockade across lower Manhattan in 1685. The stockade was built to protect the Dutch settlers from British and Native American attacks. Sources of Long Term Finance Long-term loans (External)Issue of shares or equitySale and leaseback (Internal)Retained profit Examples of long-term financing include – a 30 year mortgage or a 10-year Treasury note. Financial Markets and Securities Purpose of Long Term Finance To finance fixed assets.To finance the permanent part of working capital.Expansion of companies.Increasing facilities.Construction projects on a big scale.Provide capital for funding the operations. Factors determining Long-term Financial Requirements Nature of BusinessNature of Goods producedTechnology used Long term finance for businesses A Clear Perspective on Break Even Analysis Let us look at some of the Advantages of going for a Debt Financing Option Debt is the cheapest source of long-term financing. It is the least costly because interest on debt is tax-deductible, bondholders or creditors consider debt as a relatively less risky investment and require lower return.Debt financing provides sufficient flexibility in the financial/capital structure of the company. In case of over capitalization, the company can redeem the debt to balance its capitalization.Bondholders are creditors and have no interference in business operations because they are not entitled to vote.The company can enjoy tax saving on interest on debt. Disadvantages of Long Term Debt Financing Interest on debt is permanent burden to the company: Company has to pay the interest to bondholders or creditors at fixed rate whether it earns profit or not. It is legally liable to pay interest on debt.Debt usually has a fixed maturity date. Therefore, the financial officer must make provision for repayment of debt.Debt is the most risky source of long-term financing. Company must pay interest and principal at specified time. Non-payment of interest and principal on time take the company into bankruptcy.Debenture indentures may contain restrictive covenants which may limit the company’s operating flexibility in future.Only large scale, creditworthy firm, whose assets are good for collateral can raise capital from long-term debt. Financing through Debt Vs Equity There are a number of ways to finance a business using debt or equity. Though the first choice of many small-business owners would be equity, they may also prefer to utilize some type of debt to fund the business rather than take on additional investors. When done the right way, long-term debt financing provides a number of advantages to the business and its owner. Term Loans from Banks Most banks provide term loans,...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Financial Management, Project Management, Startups
on Jul 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is a Startup Cost? Non-recurring costs associated with setting up a business, such as accountant’s fees, legal fees, registration charges, as well as advertising, promotional activities, and employee training. Also called startup expenses, preliminary expenses, or pre-opening expenses. Let me clarify that this discussion pertains to small and medium size enterprise startup costs and not about capital budgeting. Any project that an entrepreneur wishes to undertake has four factors to be considered. Men Material Machine Money Finance is the lifeblood of any business and to be successful, one must, inject sufficient capital into it. Many businesses fail because of under-capitalization. Seed Money Requirements To determine how much seed money you need to start, you must estimate the costs of doing business at least for the first year. Expenses may be categorized as ‘one-time costs’ such as the fee for incorporating your business or the price of a sign for your building. Some will be ‘ongoing costs’, such as the cost of utilities, inventory, insurance, etc. There is a pressing need for you to bring enough working capital to run the day-to-day business affairs. Without a projected fund flow statement and proposal, no bank or financial institution shall offer you long term loans to run the business. First of all, you need to write the business plan and ask yourself the following questions. Ask yourself these 20 questions to make sure you’re thinking about the right key business decisions: Why am I starting a business? What kind of business do I want? Who is my ideal customer? What products or services will my business provide? Am I prepared to spend the time and money needed to get my business started? What differentiates my business idea and the products or services I will provide from others in the market? Where will my business be located? How many employees will I need? What types of suppliers do I need? How much money do I need to get started? Will I need to get a loan? How soon will it take before my products or services are available? How long do I have until I start making a profit? Who is my competition? How will I price my product compared to my competition? How will I set up the legal structure of my business? What taxes do I need to pay? What kind of insurance do I need? How will I manage my business? How will I advertise my business? Courtesy – http://www.sba.gov/ See ‘Short Term Financing’ to know more about financing your business. The term finance sanctioned in the form of ‘Term Loan’ is required for Land and site development Building and civil works Plant and Machinery Installation expenses and Miscellaneous fixed assets which comprise vehicles, furniture and fixtures, office equipment, workshop and laboratory equipment, distribution of power and water supply etc. Expenditure on infrastructure facilities like water supply, power connection, roads, transportation etc., has to be particularly considered if the units are located in economically backward areas. Startup...




