Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments
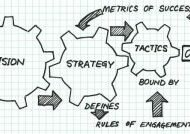
Tactics or Strategy – Ethical Considerations Give a man a fish everyday, his appetite is sated. Teach him how to fish; you have fulfilled his appetite for an entire life time. This is strategy. To make it work, to make the impossible, possible. There is no drawn out template for success or for that matter strategy. But both of them go together when the right strategy is used at the right time and you can bang on your target. Neither the same strategy fits the bill for everybody. Your smart approach to that particular situation backed up by your knowledge and experience does the magic. It cannot be taught, it comes from within when the situation warrants for action. It is more like “Survival of the fittest”, if you want to retain your niche in this business world you act fast and think wise. Tactics: How many of you are bold enough to think differently to make a difference, to make others feel your presence. Never implement tactics which is short lived and don’t make your presence felt either by imitation or by unethical competitor criticism. That will paint a greasy picture on your firm. That is of course strategy but cheap strategy. But always be on the run to know your competitors’ weaknesses and shortcomings which will make you improve your product or service. That is acceptable business practice where competitor spying gives us an edge in terms of identifying unexploited niches of the market. Resort to Constructive Strategies: Strategies must always be constructive and it assures success in the long run. Tactics or gimmicks will prove to be fruitful only for a short while and that is not your aim also. Will you be satisfied if you are able to sell your product or service as hot cakes only for a season! Is that going to cover your profit margin for the entire accounting year? True, strategies are always associated with making profits, boosting up the sales, for retaining the market share and maximizing the share value. But it should also make your business perennial and viable. Strategic Framework: Many of us forget that strategies are applicable in every activity of a firm that forms a compact framework which gives your business a solid foundation upon which you can build your empire of success without looking back. Right from framing your vision, mission, policies, procedures and programmes including recruitment, selection, training, evaluation and empowering your employees, strategies play their role in giving clarity and direction to the firm. Long-Term Planning: Although strategies are meant for long term planning, a periodic review and appraisal of the company’s strategies to all the employees concerned is a must to keep them informed. Strategies are secrets but not to the employees of your organization. Strategies are born out of compulsion, a compulsion to survive in the market and have an edge over others. So they must be meticulously planned after brain storming sessions and expert consultations. Sometimes even a small idea suggested by one of your employees might become the basis for a turnkey operation. So keep your eyes and ears open and also be open minded to accept ideas even from the lowest level as they are your pillars of strength and they know the pulse of the market and people better. Strategic Action Plans: Success is not a cake walk, it has to be achieved with great hardships and the taste of success will be sweeter. Strategies are formulated in every step of your business plan, remember it is an ongoing process; you have to revitalize your strategies every now and then to be in the scene, to make...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Product Forecasting – An Analogy What is Product Forecasting: It is the science of predicting the degree of success a new product will enjoy in the marketplace. Forecasting is said to be the first and foremost step in the planning process. One of the requirements for effective long-term planning by managers is to assess the changes in technology and environmental conditions that could affect the firm. This is termed as environmental scanning which facilitates the firm to benchmark its performance as against the top industry standards. Technological forecasting involves anticipating development of new products and processes and the time taken for such kind of innovations to be accepted and absorbed in the market. External Environmental Scanning: Environmental forecasts focus on factors such as population growth, availability of resources, social and political trends that may affect the firm’s future. Business firms become more informative on, The percentage of market share for existing products of the firm Future demand for its product range Decline in sales proportions Consumer feedback about product performance Customer satisfaction Sales team performance level Pitfalls in marketing strategies Need for new product development Unidentified customer needs and so on All predictive activity is subject to error, but technological and environmental forecasting is particularly different because they often involve assessing ideas and relationship that do not exist at the time the analysis is being performed. These forecasts are best suited for predicting performance a year or two in the future. Plan of Future Course of Action: Based on forecasting, the firm decides the future course of action. Sales forecasts help the firm to decide on the volume of production for the next few months and aid in aggregate capacity planning. Labor productivity is a crucial factor in determining the success of a business environment, especially a production environment. Manpower planning is purely based on production forecasts where in, the labor hour productivity is also taken into consideration. Forecasting Techniques: In the absence of empirical data, the forecasts must be based on expert opinions. Techniques like Delphi method can be used for this purpose. A group of experts is asked to assess a particular situation, presented with the judgments of others in the group, and then asked to reevaluate their individual positions based on what they have heard. The process continues until a consensus is arrived or until it is apparent that there will be no consensus. This helps the firm to consolidate its position with respect to specific problem situations. The Delphi method has been successfully used to forecast the nature and timing of technological change. Techniques like Delphi and Brain storming also help in the process of identification of bottlenecks, the current business trend, the firm’s future prospects, range of estimates for the desired breakthroughs etc. Although the pattern of a business cycle or a product cycle for the most part, follows a fairly predictable pattern, the firm cannot overlook probabilities, upon which the firm has to capitalize on. The firm has to become alert and employ some innovations at that point of time, when the market becomes saturated. Or else, the rate of growth declines and the firm has to decide whether to continue with the operations which calls for additional investment or close down the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Principles of Planning and Forecasting The guidelines of principles of planning are as follows: 1. Principle of primacy of planning: As discussed earlier planning is the prime function of management and precedes all the other functions. 2. Principle of verifiable objectives: The objectives set must be clear, achievable and verifiable in order to attain a feasible management model. 3. Principle of planning premises: The contributing factors in the external environment are government policies, economic factors, market standing, and consumer preferences etc. that decide the success of planning. Planning is done based on these assumptions but nevertheless, all the factors external to the business have to be thoroughly analyzed to ensure concrete planning. 4. Principle of limiting factor: Cost is one of the major limiting factor; production cost has to be factorized to ensure economy of scale and potential resources needed for a business in the likes of men, material and other physical resources have to be taken into consideration. 5. The commitment principle: Planning and decisions whether short term or long term is valid only for a particular period. The long term plan is nothing but the future impact of today’s decisions. Decisions concerning new product development by a company aims at creating an impact for the next 15 years or so while decisions concerning sales target has to be accomplished on a periodic basis- monthly or quarterly. 6. Principle of flexibility: A plan should be flexible and give room for contingencies like losses incurred through unexpected events. 7. Principle of navigational change: Plans while suggested to have built-in flexibility are also subjected to periodical review in the light of environmental fluctuations. A business can not stick to a long term plan devised originally since it is equally important to check on events and expectations periodically. FORECASTING AND PLANNING: Forecasting is a management technique that relies on both past experiences and present assumptions to predict the future. Again this serves as an important premise for the planning process. The conditions of the external environment though out of one’s control, if properly estimated, can lead an organization to produce wonderful results. TYPES OF FORECSATS: Economic forecast: To gauge the general economic scenario and its effect on sales. Technological forecast: To predict what new technologies can be developed, when and how to bring feasibility to the operations involved. Competition forecast: To look into the competitor strength and tactics and know where one stands. Social forecast: To predict the attitude of people and social conditions. Supplier’s forecast: Reveals the response of suppliers. FORECASTING TECHNIQUES: 1. Quantitative time series analysis: Monthly sales data is plotted in a chart and the past data helps in consolidating the sales volume and fluctuations in sales. Sales trend is determined and the assumption is that, the future will reflect the past and present trend and hence can be projected. If there is a lull in sales, reasons for the decline can be known by taking feedback from various quarters like, suppliers, consumers and employees. 2. Derived forecast: The forecast done for a specific purpose may be reused for another purpose. For example a census data can help you to determine the demography of a particular geographical area that might help you to reach your target customers. 3. Casual methods: If the underlying cause for the variable can be determined, the forecast can be arrived mathematically and produce quite accurate results. Social media marketing is very popular now a days and instantly you know how many hits are received for a particular product and the ratio of conversion into sales. 4. Brain storming: People with knowledge and expertise assemble in order to discuss the pros and cons of a particular idea, be it the launch of a new product, product promotion or withdrawal of a product line. 5. Delphi method: In this method, each and very expert is contacted independently and opinions are drawn...






