Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Dec 29th, 2014 | 0 comments

Scope of Financial Management Facebook Buys WhatsApp: Boneheaded or Brilliant? This was the title of a Forbes Article when Mark Zuckerberg acquired Whatsapp for $19 billion dollars, the price that may exceed the GNP of some of those countries. Mark is said to be an unconventional thinker and the WhatsApp acquisition shows Facebook’s determination to follow the road not yet paved. It is a bold move, yet filled with risks along the way. This is one of the finest examples of the big investment decisions of recent times and the right course of action, if you measure the number of potential users of the mobile messaging service rather than the cost of acquiring each user and the potential for selling ads to each user today. Follow these mind blowing tips to become prosperous Picture Courtesy : YoungHstlrs Financial management is one of the important aspects of overall management, which is directly asscoiated with various functional departments like personnel, marketing and production. Financial management embraces wide area with multidimensional approaches. The following are the important scope of financial management. Some of the major scope of financial management are as follows: 1. Investment Decision 2. Financing Decision 3. Dividend Decision 4. Working Capital Decision. 1. Investment Decision: The investment decision involves Risk EvaluationMeasurement of cost of capital andEstimation of expected benefits from a project. Capital budgeting and liquidity are the other two major components of investment decision. Capital budgeting takes care of the distribution of capital and commitment of funds in permanent assets to harvest revenue in future. Capital budgeting is a very focal decision as it impacts the long-term success and growth of a firm. All the same it is a very tough decision because it encompasses the estimation of costs and benefits which are uncertain and unknown. Picture Courtesy: Crowdfundingheroes 2. Financing Decision: Financing decision is related to financing mix or financial structure of the firm. The raising of funds requires decisions regarding Methods and sources of financeRelative proportion and choice between alternative sourcesTime of floatation of securities, etc. In order to meet its investment needs, a firm can raise funds from various sources. Long Term Sources of Finance: Share Capital or Equity SharesPreference Capital or Preference SharesRetained Earnings or Internal AccrualsDebenture / BondsTerm Loans from Financial Institutes, Government, and Commercial BanksVenture FundingAsset SecuritizationInternational Financing by way of Euro Issue, Foreign Currency Loans, ADR, GDR etc. Picture Courtesy: Cash & Treasury Management file Medium Term Sources of Finance: Preference Capital or Preference SharesDebenture / BondsMedium Term Loans fromFinancial InstitutesGovernment, andCommercial BanksLease FinanceHire Purchase Finance Short Term Sources of Finance: Trade CreditShort Term Loans like Working Capital Loans from Commercial BanksFixed Deposits for a period of 1 year or lessAdvances received from customersCreditorsPayablesFactoring ServicesBill Discounting etc. 3. Dividend Decision: In order to accomplish the goal of wealth maximization, a proper dividend policy must be established. One feature of dividend policy is to decide whether to distribute all the profits in the form of dividends or to plough back the profit into business. While deciding the optimum dividend payout ratio (proportion of net profits to be paid out to shareholders), the finance manager should consider the following: Investment opportunities available to the firmPlans for expansion and growth,Dividend stabilityForm of dividends, i.e., cash dividends or stock dividends, etc. 4. Working Capital Decision: Working capital decision is related to the FINANCING in current assets and current liabilities. Current assets include cash, receivables, inventory, short-term securities, etc. Current liabilities consist of creditors, bills payable, outstanding expenses, bank overdraft, etc. Current assets are those assets which are convertible into cash within a year. Similarly, current liabilities are those liabilities, which are likely to mature for payment within...

Posted by Managementguru in Management Accounting
on Oct 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments

Capital Budgeting and Capital Accounting Systems These internal accounting systems facilitate and support decision-makers in assessing potential investments with respect to cost effectiveness. The purpose of capital accounting systems support decision-makers in monitoring and planning liquidity. What is Capital Budgeting? Capital budgeting is the planning process used to determine whether an organization’s long term investments such as new machinery, replacement machinery, new plants, new products, and research development projects are worth the funding of cash through the firm’s capitalization structure. Capital budgeting systems is a framework that support management in making decisions in the context of capital investment decisions. In particular, capital budgeting systems help to determine whether or not a capital investment will earn back the original expenditure and in addition provide a reasonable return. This type of decisions usually entails large amounts of organizational resources at risk and, at the same time, affects the future development of the organization . Capital budgeting systems usually focus on capital investment decisions that cover many years. This discriminates capital budgeting systems from income determination and planning which usually focus on the current period. Capital investment decisions usually encompass cash inflows and outflows that accrue at different points in time which are usually answered by adding accrued interest of discounting of cash-flows. Capital budgeting process consists of six steps: Project Generation Estimation Of Cash-Flows Progress Through The Organization Analysis And Selection Of Projects Authorization Of Expenditures And Post-Audit Investigations. In the step of (1) project generation, potential investments are chosen for which in step (2) potential cash-flows are estimated. In step (3), i.e., progress through the organization, certain projects require approval of top-management. In step (4), analysis and selection of projects, the selected projects are assessed with respect to the fact that cash inflows and outflows usually realize at different points in time. In Step (5), authorization of expenditures, captures the final decision (usually made by top management) on whether or not to invest into the selected project. Finally, in step (6) captures a post-audit investigation, i.e., after a certain period of time actual results might be gained which potentially provide input for control purposes. Capital budgeting systems particularly support management in step (4), i.e., the analysis and selection of projects. Capital accounting systems support management in planning and controlling liquidity. Courtesy: S. Leitner, Information Quality and Management Accounting, Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments

Understanding Net Present Value One method of deciding or not a firm should accept an investment project is to determine the net present value of the project. The net present value (NPV) of a project is equal to the present value of the expected stream of net cash flows from the project, discounted at the firm’s cost of capital, minus the initial cost of the project. The value of the firm will increase if the NPV of the project is positive and decline if the NPV is negative. Thus, the firm should undertake the project if the net present value is positive and reject proposals whose values are negative. This method is considered the best, as it takes into account, the initial investment, and cost of capital and cash inflow over a period. Estimation of Future Cash Flow: One of the most important and difficult aspects of capital budgeting is the estimation of the net cash flow from the project. It is the difference between cash receipts and cash payments over the life of a project. Projected cash flow statement is an important criterion for banks to decide on sanctioning medium and long-term loans to prospective clients. Since cash receipts and expenditures occur in the future, a great deal of uncertainty is involved in their estimation. Some general guidelines are to be followed while estimating cash flows. First; cash flows should be measured on an incremental basis. That is, measurement of the firm’s cash flows with and without the project must be ascertained. Any increase in expenditure or reduction in the receipts of other divisions of the firm resulting from the adoption of a given project must be considered. Effect of Depreciation: Second thing is that, net cash inflow must be estimated on an after-tax basis, using the firm’s marginal tax rate.Third, as a non-cash expense, depreciation affects the firm’s cash flow only through its effect on taxes. The initial investment to add a new product line may include the cost of purchasing and installing new equipment, reorganizing the firm’s production process, providing additional working capital for inventory and accounts receivable and so on. The monetary flows generated by this kind of investment include, the incremental sales revenue form the project, salvage value of the equipment at the end of its economic life, if any and recovery of working capital at the end of the project. The outflow will be in the form of taxes, fixed costs and incremental variable costs. Internal Rate of Return or IRR: Another method of determining the acceptance rate of a project proposal is internal rate of return method (IRR).This is nothing but the discount rate that equates the present value of the net cash flow from the project to the initial cost of the project. The firm should undertake a project if the IRR on the project exceeds or is equal to the marginal cost of capital. Capital Rationing and Pay Back Period: More techniques are available for evaluating the feasibility of investment proposals, like, capital rationing, profitability index, pay back period and others. It is always a good thing to analyze the rate of return on investment before the start of the project. If it happens to be satisfactory, then the firm can take a step forward to finalize the proposal. The cost of capital climbs up when the investment return declines, and the firm is subjected to undue pressures of mounting interest rates and capital depletions....

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Management, Principles of Management, Project Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
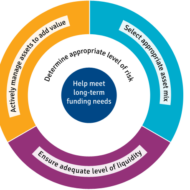
What is Business Risk? It is a term that explains the difference between the expectation of return on investment and actual realization. In CAPITAL BUDGETING, several alternatives of investments are examined before taking an investment decision and only then the Managing Director of the firm along with financial executives gear up for investing in a project that is sound and feasible. Even then the project may not become viable owing to the fluctuations in the economic environment. Money Manipulation So, the million dollar question arises, whether to invest and if invested, will it fetch me profit? See, you cannot have the cake and eat it too. Risk factor prevails in all kinds of environment and we try to over react in a business arena since it involves huge investments. But remember, MONEY WILL MULTIPLY IF YOU MANIPULATE IT WITH CARE. Business firms commit large sums of money each year for capital expenditure. It is therefore essential that a careful FINANCIAL APPRAISAL of each and every project which involves large investments is carried out before acceptance or execution of the project. These capital budgeting decisions generally fall under the consideration of highest level of management. Factors of risk to be considered before investing: Time value of money Pay back period Rate of return on investment(ROI) Uncertainties in the market Cost of debt Cost of equity Cost of retained earnings Factors to be monitored after investing: Maximising profit after taxes Maximizing earnings per share Maintaining the share prices Issue of dividends Ensuring management control Financial structuring Cost of capital refers to the opportunity cost of the funds to the firm I. e., the return on investment to the firm had it invested these funds elsewhere. Servicing the debt and Danger of Insolvency While making the decisions regarding investment and financing, the Finance Manager seeks to achieve the right balance between risk and return. If the firm borrows heavily to finance its operations, then the surplus generated out of operations should be sufficient to “SERVICE THE DEBT” in the form of interest and principal payments. The surplus would be greatly reduced to the owners as there would be heavy Debt Servicing. If things do not work out as planned, the situation becomes worse, as the firm will not be in a position to meet its obligations and is even exposed to the “DANGER OF INSOLVENCY“. Working Capital Management Considering all these factors, we have to come to the conclusion that FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT is like the BACKBONE of a business firm and WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT will be the blood flow infused into the body. Risks are inherent in a business environment whose management is quite possible with the right kind of farsightedness and planning. Luck does not favor anybody who is poor in planning and lack hard...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics
on Feb 17th, 2014 | 0 comments

Managerial Economics and Decision Making One has to observe the economic prospects of a particular #industry before venturing into it. Most of the people are not aware of the existence of some businesses with fantastic economic characteristics like high rate of return on invested capital, substantial profit margins and consistent growth. How do you think Bill Gates and Warren Buffet were able to make it on the Forbes top millionaires list? Successful leaders focus on the economics of a business for decision making. Economic Aspects of a Market Managerial economics is a #management science that gives you more idea about the economic aspects of a market and how they affect your decision making. This is very important because economic profits play a crucial role in a market based economy., While above normal profits are indicators of expansion and growth, below normal profits cautions you about tightening or retrenchment. Business economics is comprised of several tools of micro and macro economic analysis which are useful in management decision-making that act as facilitators to solve business problems. Micro economic instruments used in this context include demand analysis, production and cost analysis, breakeven analysis, theory of pricing, technical progress, location decisions and capital budgeting . Factors Influencing Management Decisions The macroeconomic concepts that are directly or indirectly related to management decisions include analysis of national income, business cycles, monetary policy, fiscal policy, central banking, public finance, economic growth, international trade, balance of payments, protectionism, free trade, exchange rates and international monetary system. The scope of management science is broad and is closely linked with economic theory, decision sciences and accounting. Traditional economics deals with theory and methodology of management, while managerial or business economics applies these theories to solve business problems. The tools and analytical techniques are useful in providing optimal solutions to business problems. Relationship with economics : Managerial economics borrows concepts from economics to idealize the strategic actions needed for decision making in a problem situation. The analysis of micro and macro economic concepts adds valuable information for the organization. Say, for example, national income forecasting is an important aid for the analysis of business conditions that in turn could be an invaluable contribution to forecast demand for specific product groups. Theories of market structure can be analyzed for market segmentation. Managers have the freedom to choose between the decision alternatives that best suits the objectives of the business enterprise. The challenge is to justify the alternative in terms of cost and benefit. Relationship with decision sciences : Decision models are created to format solutions for problem situations and the process uses techniques such as, optimization, differential calculus and mathematical programming. This also helps to analyze the impact of alternative courses of action and evaluate the results of the model. Economic models provide the organizations with the necessary insight concerning value maximization Relationship to Accounting The accounting data and statements constitute the language of business. The accounting profession has a significant impact on cost and revenue information and classification. A manager therefore must be familiar with the generation, interpretation and use of accounting data. Accounting is also seen as a decision management tool and not as a mere practice of book-keeping. The concepts and practices of accounting can be well applied to improve the economic scope of a project. Economic theory is all about allocating scarce resources between competing ends and managerial economics advocates rules for improving managerial decisions and for efficiently achieving the goals of an...










