Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
Executive Development – Options are Wide Open Who is an Executive: A person or group having administrative or managerial authority in an organization. While “executive” and “manager” and “leader” are often used interchangeably, “executive” is commonly used to signify the top 5% to 10% of the organization. Executive Development : aimed at developing the skills and competencies of those that (will) have executive positions in organisation. Capabilities of a Good Manager: A good manager can make an organization grow, survive and shine amidst tough competition, if he is bestowed with corporate competencies such as perseverance, capacity to put in hard work, sense of loyalty and responsibility, all of which may be inherited or acquired qualities. Loyalty stems from internalized morality that may be a result of his value system. Executive success is what the organizations should aim for, and firms should try to figure out the fundamental components that make up the success formula or equation. Road to Self-Development: In less developed countries, employees are more than satisfied if they are provided with a job that offers safety and security. Their thinking is restricted to mere physical and biological comforts and does not go beyond that point, where self development and self-actualization come into the picture. In developed countries, the situation is quite different, where the workers aim for empowerment and look for reasons that motivate them to do a job. Money also has its due role to play, and people whose wages are very meager cannot be expected to aim for empowerment, where their single motive is mere survival. Abraham Maslow’s Point of View: Abraham Maslow puts forward the hierarchical needs theory, arguing that, there are five levels of needs for people in general, right from physiological needs at the bottom of the pyramid and need for self actualization at the top, and safety, security and esteem needs coming in between. He points out that, once a need is satisfied, it ceases to be a motivator. This is so evident in our day to day lives, where wants and needs never cease to exist and once a want is satisfied, human mind wanders to catch hold of another. So, organizations should understand and analyze, what factors best motivate their employees, particularly their managers (who might serve as a source of inspiration to their subordinates).It should be remembered that non-availability of jobs leads to dissatisfaction whereas availability of jobs need not motivate employees. Some factors which have been proven to be real motivators are as following: Recognition Opportunities for self development Additional responsibilities(lateral expansion) Timely rewards(in terms of money and appreciation) Security Inculcating a sense of belongingness Conducive corporate atmosphere Corporate culture Good human relations Economic burden makes people less enthusiastic and anxious in developing countries and this hinders them from delivering to their fullest potential. Also the bureaucratic approach followed by conservative firms, autocratic leadership style and lack of supportive atmosphere make people work like automatons devoid of creativity. Such firms may show good results in terms of productivity initially, but in due course has to pay the price, in terms of absenteeism, high attrition rates and less efficiency. It has been proven that job satisfaction is directly proportional to efficiency. When people find a job tedious and monotonous, they tend to lose interest, which will be evident from their lack lustrous performance. Performance management has its bearing on executive success and by providing with ample scope for career advancement and autonomy; managers prove their mettle even within limited scope of resources. Acceleration of executive change implies the development of the executive mind for performing managerial activities in a better way. Note : A survey of CEOs in Fortune 500 enterprises indicated that executives spend little time with their...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategies to Tide Over Competition Distinctive Competence: is nothing but a set of unique capabilities that certain firms possess allowing them to make inroads into preferred markets and to gain advantage over the competition. Human brain is the greatest think tank and it evolves new methodologies of business management from time to time in order to sustain as well as win the race. Planning is the key factor that decides the rise or downfall of a business empire. “Where we are?” and “Where we want to be in the next few years?” is how every business leader’s basic thought process must be, without which he cannot proceed further in the competitive corporate environment. If we call planning as the basement of a building, then it should be very precise, clear cut and robust so that the business empire built on this basement will never collapse and it will also serve as a role-model for everyone who aspires to set his foot in the corporate business world. At the corporate level, strategic planning helps to establish the Purpose Mission and Objective for the firm as a whole and “outlines the overall plan to attain them.” Strategy is nothing but a unique set of action plan that will distinguish you from your competitors and make you have an edge over them. Likewise strategic planning is nothing but thinking out of the box to” CREATE YOUR OWN NICHE MARKET” in the business environment. STRATEGIC COMPETENCE takes you to the top of the ladder; but to withhold your position you need to formulate innovative ideas to tide over the challenges in the market. Strategic planning facilitates this process by giving you time frame to complete your short term objectives and long term goals. Infographic Courtesy: The 4 key sources to seek insights for marketing planning Planning for SBU’s: Business level planning is done for the enterprise’s STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNITS or SBU’S. These are individual” cash cows” that makes your business noteworthy and also brings in constant revenue to run your other units successfully even in periods of recession or if a particular product is not that successful as you might have expected it to be. I shall compare a business plan to a travel plan. Both involve planning, resources, capital, marketing and so on. . . Both have starting points but a business plan and its objectives never end and you can never come back to the starting point in a business as that of a travel, because you only expand and grow to greater heights in a business provided your plan is pucca. And also the strategy seeks the integration and control of marketing, finance, production and human resources at the functional level. Strategic Plans at different functional levels: Strategic plans at different levels must be integrated to ensure that they work in tandem and reinforce each other, thereby contributing to the corporate level strategy adopted for the entire corporate group. I would call strategic planning as” INTELLIGENCE DESIGN CHOICE ACTIVITY “adopted by a corporate and it has become an inevitable feature in the directory of the business world....

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments
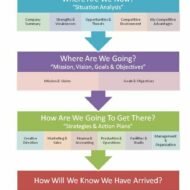
The Management Planning Process We have heard of “Master Plans” being structured and engineered to give astounding results that is purely systematic in approach and masterly in execution. Planning facilitates to make use of the opportunities that are available in the environment to make it to the top. Opportunity Analysis is nothing but, an awareness of the factors in the external environment; understanding of the strength and weaknesses of the organization. This is the first step of planning where we have to scrutinize the market, competition, customers’ preferences, tastes, our strengths and weaknesses. Establishing Objectives is another criterion that ensures “Where we want to be, and what we want to accomplish and when”. What are Objectives? Objectives are set for the organization and each subordinate is also entrusted with them. Objectives lay emphasis on goal setting which normally emanates from the top, but it may also originate from the bottom. Management by objectives is a great concept that involves all the employees working for the organization to be a part of goal setting and decision making. Planning Premises: Premises are “Assumptions” about the ‘environment.’ It involves identification of critical factors of the environment that affect the planning. Examples of critical factors are government policies, tax rates, business cycle development, economic indicators, economic forecasts etc. No body can precisely predict the environment factors precisely and make an accurate forecast. However one can fairly predict the critical factors required for the plan. Identifying Alternatives is very significant in a corporate business environment as every plan has got a set of alternative course of action. A reasonable number of alternatives can be developed for a plan. Evaluating Alternatives and Selecting the Best: A reasonable number of alternatives can be evaluated on the basis of the principle of limiting factor. The limiting factors may be costs, time, manpower and other resources. By applying techniques of operations research, every alternative can be evaluated. For e. g. alternative ‘A’ may benefit the organization in the short term but may be more expensive and alternative ‘B’ may benefit in the long run but may be less expensive. If one wants to earn immediate profits by spending more money he can choose alternative ‘A’. If the limiting factor is cost, he is forced to choose alternate plan ‘B’. Planning is not complete with selecting the best alternative; a set of derivative plans are developed to support the basic plan. For example an educational institution might like to own a fleet of buses, for which derivative plans for selection has to be made- training of drivers and maintenance staff are supportive plans for the main plan-procurement of buses. Developing budgets completes the planning course of action and budget is referred in financial terms and they are required to control the plans. Planning is the Prime Function: Planning is the prime function of all as it precedes all functions. 1. The objectives must be clear, verifiable and attainable. 2. Planning premises are vital to the success of planning as they supply information related to future like probable competitive behavior, general economic conditions, capital and material availability, government control etc. 3. All the critical factors are clearly and thoroughly analyzed and taken into consideration. One should be able to identify clearly the critical factors that limit the attainment of the goal. It could be costs, time, manpower or any other resources. 4. In a practical business situation, one should be clearer in identifying these factors, only then the selection of the best alternative is possible. 5. Any decision taken in a plan is valid for a particular period i.e., the plan may be short term or long-term, the commitment principle...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Group Dynamics Any effective group has three core activities: 1. Accomplishing its goals 2. Maintaining itself internally 3. Developing and changing in ways that improves its effectiveness. Let us now try to understand the various dimensions of an effective group that facilitate the above mentioned three core elements to function properly which provide a sense of direction to the productive group. a) Group goals: Must be clearly understood. Be relevant to the needs of the group members. Highlight the positive inter dependence of members. Evoke from every member a high level of commitment to their accomplishment. b) Communication: Must communicate their ideas and feelings accurately and clearly. Effective two way communication is mandatory for interaction c) Participation and Leadership: All should participate and all should be listened to. Share responsibilities that eases the burden. Increases the cohesiveness of the group. d) Appropriate decision making procedure: Balance between time and member resources. Flexible decision making to suit the needs of the situation. e) Power and Influence: · Should be equal · Based on expertise, ability and access to information and not on authority · Coalitions must be formed between group members on the basis of mutual influence and interdependence. f) Conflicts: · Are to be encouraged as they promote involvement in the group’s work, improve quality and creativity in decision making. · Minority opinions should be accepted and used g) Group Cohesion: · Needs to be high · Level of acceptance, support, and trust among the members decide how cohesive the group is h) Problem Solving: · Problems should be resolved with minimal energy and permanently · Existence of problems must be found out quickly and solutions should improve the effectiveness of group behavior i) Inter-personal effectiveness: · Needs to be high · It is a measure of how all the consequences of your behavior match your intention. ⇓ Picture Courtesy: 6 WAYS TO DEVELOP A WINNING TEAM CULTURE Group Cohesiveness: This is defined as the average resultant force acting on members to remain in a group. The characteristics or criteria that determine group cohesiveness are as follows: 1. Degree of dependency on the group: The greater the number of individual needs are satisfied, the greater the cohesiveness. 2. Size: If the size of the group interaction is low, it results in low cohesiveness. If the size of the group is small, the members tend to have free and more interaction, leading to high level of cohesiveness and vice versa. 3. Homogeneity: Where the interests and background of the group is similar, you find greater cohesiveness. 4. Outside pressure: Outside pressure minimizes internal conflicts leading to high cohesiveness. You find people responding with greater cohesiveness during times of natural disaster and calamities. 5. Competition: Competition between the members of the same group or intra group competition reduces cohesiveness but competition members of different groups or inter-group competition increases cohesiveness. Group Cohesiveness can be encouraged by the following ways: · Make the group smaller · Encourage agreement with group goals · Increase the time members spend together · Stimulate competition with other groups · Give rewards to groups rather than to a single member · Physically, isolate the group. ...

Posted by Managementguru in Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Feb 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Organizational change is concerned with making things different and change agent is a person or group of persons who act as catalysts to bring about change. Say, managers and outside expert consultants can be called as change agents. What is Organizational Change? This is how you have to Strategise in order to Win Organizational development refers to the overall development of an organization in terms of improving the ability of that organization in tandem with the needs of the external environment and involves a system oriented approach to change. Recommended: Resourceful Guide on Organizational Development from Maryville University titled ” Organizational Development Guide: Definition, Process & Development Models “ Organizational change: All the elements of a social system like people, formal organization, informal organization, operational environment, communication, decision making and patterns of co-operation are bound to change when there is change in the external environment but this gives rise to a positive pressure which acts like a self-correcting mechanism to modify and set right the bottle-necks or loop-holes in the working system. Causes For Change Work force: The increasing awareness and educational qualification among the workforce is responsible for the attitude change. You can expect loyalty from workers above fifty but not workers who fall under the age category thirty. This is because their loyalty is oriented towards their career and not to the employer. Technology change: Internet, telecommunication systems, computers, robotics, flexible manufacturing operations have created a great impact on the working style of firms and necessitated the work force to be tech-savvy in order to survive in the job market. Economic, social, political, and physical environmental changes: Economic– Business cycles, inflation, recession, stock market crashSocial– Changing life styles and preferences of customers is the keyPhysical– Consumers, suppliers, employees, union, shareholders and the governmentPolitical– Political decisions affecting the market, pressure, legal hassles:- all these affect the working of a firm. Changes in competition: Global economy has brought big players from countries like USA, Japan, Germany and the like to compete in the same market and successful organizational are those who have adapted to competitive environment. When we talk about organizational change, we emphasize on “PLANNED CHANGE OR DELIBERATE CHANGE” in order to suit ourselves to the changing environment. Otherwise, according to Darwin’s theory of “Survival of the fittest” you will fade away in due course of evolution. This Infographic clearly reveals the fact that “It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to...










