Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
Organizational Discipline – A Way of Life Organizational Discipline: Discipline is the force that prompts individuals or groups to observe rules, regulations, standards and procedures deemed necessary for an organization. Discipline is one word that instills fear in the minds of individuals. The very word sounds autocratic when uttered by your boss and creates a feeling that you are being forcibly controlled. If you do not live up to the expectations of the management, definitely you are going to get listed for disciplinary action. Why is that discipline always gets enforced to gain obedience?Why people get intimidated when subjected to disciplinary action?Why streamlining your behavior becomes so difficult some times? Have you ever given a thought on how we always try to put the blame on management for being a father figure? We have to see things from a broader perspective. When you work for somebody, it is their prerogative to develop some rules and standardize some norms which they think is suitable for the mode of operations. Policies and procedures are formulated for the effective functioning of the organization. It is your responsibility to make them satisfied with your conduct to gain trust and confidence. Organizations are real time schools where you can learn a lot about proper social behavior and develop high standards of discipline. Learning Induces Change in Behavior Learning, an ongoing process is a wonderful experience and individuals must use the opportunity to fit themselves well in the human network when they work for big corporates. The objective of discipline is “orderly behavior”. How many of you maintain a cordial relationship with your peers in the organization?Are you sure they are not talking behind your back for some unpleasant quality of yours?Are you alienating yourself from the rest of the group? Self appraisal is the best way to rank yourself against various critical factors of interpersonal relationship with your team members. Things which we have to consider that might be the causes for indiscipline and misconduct stems from psychological, social and personality oriented factors. Absenteeism Pic Source: Dominion Systems Absenteeism is one thing that no superior can withstand as it directly affects the productivity and vitality of the company. The reasons if presented are weird, he becomes more agitated. Dishonesty is not a thing to be tolerated by the management. Insubordination also causes clashes between the executives and the employees as their “egos are battered.” Carrot and Stick Policy Considering from the employees’ point of view, the carrot and stick policy of the management alone do not make them committed to the firm. Challenging tasks, sense of participation, favorable work climate etc. makes them more responsible and faithful. Immediate rewards and recognitions are more appealing than deferred benefits like pension or gratuity. The emotional aspects of the employees must not be handled in a conservative but in a flexible manner by the management. This will create a feeling of trust and openness between the two. Democracy Hard and fast rules may not solve the purpose when there is no room for any humanism or democracy. This might even be the cause for employees to work against the interests of the company. This leads to disciplinary actions which prove hectic to both the parties. The management on its part has to definitely shed its autocratic attitude and adapt to more participative style of leadership. Personnel department has to play their administrative role in acting as a link factor between the employees and their superiors. Although managers exercise the authority of punishment, it is the HR department’s duty to develop proper procedures of administration of discipline and assist the management in conducting enquiries and solicit the cooperation...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 16th, 2014 | 0 comments
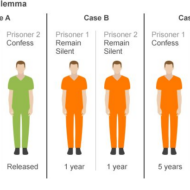
Game theory and strategy What is Game Theory: Set of concepts designed for decision making in situations of competition and conflict under specified rules. The prisoner’s dilemma: The prisoner’s dilemma is a canonical example of a game, analyzed in game theory that explains why two individuals might not cooperate, even if it appears that it is in their best interest to do so; Albert W. Tucker formalized the game with prison sentence payoffs and gave it the “prisoner’s dilemma” name. To solve many practical problems that are encountered in economic, military or other disciplines, one has to deal with situations in which there are two or more conflicting parties striving for the same objective and the outcome of each action of one party depends solely on the opposite parties choice of a course of action. As we all know only one horse can win the race ultimately and the other parties only can prolong the race or see to that they make every possible move to delay the opponent’s success. So, what’s this game theory all about? This is a special mathematical method that was evolved mainly to analyze conflict situations where the number of competitors is finite, each participant has a definite set of actions to choose and there is a conflict of interest between the competitors. So it helped the participants to reach a decision that would put them in the winning post. This theory has spilled its implications on business situations where success is the motto and conflict and competition the order of the day. Only the best among the best survive. Darwin’s theory, “Survival of the fittest” applies not only to biological organisms but also to business organizations which are also abuzz with activity. Chance Moves: Games like chess, checkers are played according to a definite set of rules laid down and these game patterns has inspired business persons to introduce strategies in business, where the concentration is mainly focused on the chance moves that defeats the opponent. Big business corporates mainly concentrate on the strengths and weaknesses of their competitors to have an edge over them. A real game is controlled and regulated by the statutory rules to be followed but a business game involves lot of killer instincts and intuitions combined with rational thinking and logic. Optimal Strategy: The first party always puts himself in the shoes of the other party and tries to perceive how the other party would react in a particular situation. Although the aim is to win, choosing the optimal strategy is what matters. It will at least keep you in bay. Precise solutions can be arrived at if you plan your game fittingly. The anticipation and thrill that is involved in a strategic game is matchless. We witness a lot of firms imitating what the leader of the market does. The risk is borne solely by the firm introducing the change and the firm takes the major share of profit as it is the pioneer and if it loses the next strategic move is planned for. For a company with sound financial position, the chance move is worth giving a try, head or tail doesn’t matter. The stalkers are benefited by the waiting period during which they come to know of the pros and cons of the strategy employed by the leader. Games are played in the true spirit of sportsmanship, but a business faces cut throat competition. There is no space for any courtesy or liberal approach. If you are quick enough to pick the pulse of the people by gauging their preferences, analyzing the market conditions and employing timely strategies you will at...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, CSR, Human Resource, Principles of Management
on Mar 12th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is the relationship between Corporate Social Responsibility and Business Ethics Business ethics can be defined as the principles and standards that establish acceptable conduct in business organizations. The acceptability of behaviour in business is determined by customers, competitors, government regulators, interest groups, and the public, as well as each individual’s personal moral principles and values. Can Ethics be Taught? I feel that ethics cannot be taught: it is an inbuilt entity and in countries like India where religion is all pervasive in business or any other discipline, this quality is imbibed in every individual right from his birth. The power of money and authority plays a major role in changing a man’s perspective and bureaucratic hurdles and red tapism mar the pace of business development. Businessmen should never compromise ethical principles with short-sighted objectives of amassing material wealth but should develop a spirit of altruism. Management education should focus also on training the individuals to be ethic-savvy apart from being mere decision making authorities satisfied with their designation and power of authority. Employees have the same kind of ethical responsibility towards their organisation and should not misuse time and property and should not place their interests before the enterprise objectives. What is Corporate Social Responsibility? Many consumers and social advocates reckon that businesses should not only make a profit but also consider the social implications of their activities. We define social responsibility as a business’s obligation to maximize its positive impact and minimize its negative impact on society. Although many people use the terms social responsibility and ethics interchangeably, they do not mean the same thing. Business ethics relates to an individual’s or a work group’s decisions that society evaluates as right or wrong, whereas social responsibility is a broader concept that concerns the impact of the entire business’s activities on society. There are good business reasons for a strong commitment to ethical values: 1. Ethical companies have been shown to be more profitable. 2. Making ethical choices results in lower stress for corporate managers and other employees. 3. Our reputation, good or bad, endures. 4. Ethical behaviour enhances leadership. 5. The alternative to voluntary ethical behaviour is demanding and costly regulation. Points to Ponder relating to behavioral ethics. 1. What conflicts of interest have you personally experienced in personal or professional roles? 2. If you perceive a potential conflict for yourself, what are some ways you might ensure that this conflict doesn’t lead to unethical behavior for you and others? 3. When have others’ conflicts of interest impacted how you or those you know were treated? 4. What types of policies can or do organizations implement to try to reduce conflicts of interest or their costs? 5. Why do you believe conflicts of interest are so pervasive in society? Why don’t we take more steps to avoid them? 6. Why is it so hard for individuals to recognize their own conflicts of interest, and how is this impacted by behavioral biases? Unethical behavior,conflicts,personal interests,responsibility What is Conflict of Interest? Conflict of interest arises when there is a clash between responsibility and reward. Say, if a doctor decides to be more business-like, if a judge decides to favor one party, if a ruling party favors a decision not good for the masses, what will happen? A conflict of interest exists when a person must choose whether to advance his or her own personal interests or those of others. Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., may have the toughest policy against conflict of interest in the retail industry. Sam Walton, the late founder of Wal-Mart, disallowed company buyers from accepting so much as a cup of coffee from suppliers. The Wal-Mart policy is black...






