Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
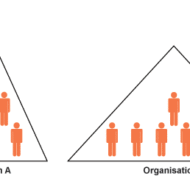
Levels of Organization An organization is a network consisting of people interacting to accomplish the enterprise objectives. The inter relationship is always complex as groups tend to develop conflicts and difference of opinion among themselves and in between. Hence the structure of an organization should be designed to clarify who is to do what task and who is responsible for what results and to furnish decision-making devoid of uncertainty. Organization implies to Recognizing and classifying the required activities Grouping of activities in order to achieve the objectives Appointing a manager and assigning him with the necessary authority to lead each group The provision for co-ordination vertically and horizontally “Organization is the establishment of authority and relationships with provision for coordination between them, both vertically and horizontally in the enterprise structure,” According to Koontz. FORMAL ORGANISATION It implies a formalized intentional structure of roles or positions. Formal organization must be flexible. The formal structure is laid down by the top management The levels are designed on the basis of specialization Purely task oriented and not people oriented Rules are very stringent and everyone is expected to follow them without fail INFORMAL ORGANISATION A network of personal and social relations arising spontaneously as people associate with one another and not restricted by the formal rules or structure. One important aspect of organizing is the establishment of department. Department designates a distinct area, division, or branch of an organization over which a manager has authority for the performance of specified activities. Spontaneous in nature More people oriented Based on religion, culture, common problems faced by the workforce etc., Membership is voluntary and the same person can be a member of many groups. ORGANISATION LEVELS AND SPAN OF MANAGEMENT Why there is a need to organize? To co-ordinate the activities of the people involved in the organization’s functions for which there needs to be certain levels established to facilitate the co-operation effective. There are two types of spans, 1. Wide span 2. Narrow span Pic Courtesy: LumenLearning WIDE SPAN: Wide span of management has fewer organizational levels with more number of sub-ordinates reporting to a superior. Though it proves advantageous for the superior as delegation becomes part of the process and hence work is shared, care must be taken in selecting the right people for completion of tasks and clear policies must be made to avoid confusion. There is this tendency of overloaded superiors to become decision bottlenecks and there exists the danger of superior’s loss of control too. This kind of management needs exceptionally qualified managers to lead the respective groups. NARROW SPAN: Narrow span of management involves many organizational levels with fewer number of employees reporting to a superior. This facilitates close supervision, close control and fast communication between superiors and subordinates. On the contrary, superiors tend to get too involved in subordinates’ work and this kind of management incurs higher costs due to many levels in the organization and there is excessive distance between the lowest and top most levels. FACTORS DETERMINING AN EFFECTIVE SPAN: 1. Training of Subordinates: Well trained subordinates save much time and energy of the superiors and training has to be a continuous process as the technological policies and procedures are subjected to change periodically. 2. Clarity of Delegation of Authority: Clarity implies direction and guidance from the manager’s end to the subordinate. A manager has the responsibility of clearly explaining the task and the methods involved to complete the task in a suitable manner to his subordinates. In cases of machine handling, “On the Job Training” becomes inevitable. If not, the work will not be completed as per the schedule due to lack of clarity. 3. Clarity of Plans: In a production environment, the workers have to be...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Group Dynamics Any effective group has three core activities: 1. Accomplishing its goals 2. Maintaining itself internally 3. Developing and changing in ways that improves its effectiveness. Let us now try to understand the various dimensions of an effective group that facilitate the above mentioned three core elements to function properly which provide a sense of direction to the productive group. a) Group goals: Must be clearly understood. Be relevant to the needs of the group members. Highlight the positive inter dependence of members. Evoke from every member a high level of commitment to their accomplishment. b) Communication: Must communicate their ideas and feelings accurately and clearly. Effective two way communication is mandatory for interaction c) Participation and Leadership: All should participate and all should be listened to. Share responsibilities that eases the burden. Increases the cohesiveness of the group. d) Appropriate decision making procedure: Balance between time and member resources. Flexible decision making to suit the needs of the situation. e) Power and Influence: · Should be equal · Based on expertise, ability and access to information and not on authority · Coalitions must be formed between group members on the basis of mutual influence and interdependence. f) Conflicts: · Are to be encouraged as they promote involvement in the group’s work, improve quality and creativity in decision making. · Minority opinions should be accepted and used g) Group Cohesion: · Needs to be high · Level of acceptance, support, and trust among the members decide how cohesive the group is h) Problem Solving: · Problems should be resolved with minimal energy and permanently · Existence of problems must be found out quickly and solutions should improve the effectiveness of group behavior i) Inter-personal effectiveness: · Needs to be high · It is a measure of how all the consequences of your behavior match your intention. ⇓ Picture Courtesy: 6 WAYS TO DEVELOP A WINNING TEAM CULTURE Group Cohesiveness: This is defined as the average resultant force acting on members to remain in a group. The characteristics or criteria that determine group cohesiveness are as follows: 1. Degree of dependency on the group: The greater the number of individual needs are satisfied, the greater the cohesiveness. 2. Size: If the size of the group interaction is low, it results in low cohesiveness. If the size of the group is small, the members tend to have free and more interaction, leading to high level of cohesiveness and vice versa. 3. Homogeneity: Where the interests and background of the group is similar, you find greater cohesiveness. 4. Outside pressure: Outside pressure minimizes internal conflicts leading to high cohesiveness. You find people responding with greater cohesiveness during times of natural disaster and calamities. 5. Competition: Competition between the members of the same group or intra group competition reduces cohesiveness but competition members of different groups or inter-group competition increases cohesiveness. Group Cohesiveness can be encouraged by the following ways: · Make the group smaller · Encourage agreement with group goals · Increase the time members spend together · Stimulate competition with other groups · Give rewards to groups rather than to a single member · Physically, isolate the group. ...

Posted by Managementguru in Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
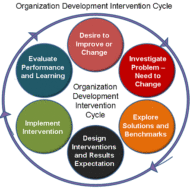
Organizational Development Training and development is an important aspect of human resource development. However the traditional methods and approach of T&D has its own limitations in that the focus is on individual development and behavior modification. This has seldom produced organizational development and hence in 1960’s an integrated approach called the ‘OD’ or organizational development was developed. Meaning and definition of organizational development (o.d.) “A process used to enhance both the effectiveness of an organization and the well being of its members through planned interventions.” OD is the systematic application of behavioral science knowledge for the purpose of improving productivity, efficiency, effectiveness and overall health of the total organization. The applied interventions attempt to modify the beliefs, assumptions, values, attitudes and standards of both the individuals and groups thereby transforming the organizational culture for the betterment of system as a whole. FEATURES OF ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT: HUMANISM: The focus is on the employees, their attitude and inter-personal relationships. An organization is a network of people whose emotions, outlook and cohesiveness are more important than monetary and other physical aspects because it is they who take the organization to the next higher level. This is made possible by open communication, free and frank discussions of problems with employees by the managers, inter-personal trust and above all, sense of belongingness, comradeship and team spirit. PROBLEM-SOLVING NATURE: The purpose of an OD intervention is to solve a problem. The employees themselves are given the opportunity to identify the problem by Survey Feedback and find a suitable solution through analysis. This is a cyclic process and also called as “Action Research”. SYSTEMS APPROACH: OD is concerned with not the structure or persons per se, but with the interplay of structure and persons. LEARNING THROUGH PARTICIPATION: The participants of the learning process are none other than the employees. They unlearn old things and learn new things by identifying, analyzing and finding the right solution to the bottlenecks. TOP MANAGEMENT SUPPORT AND INVOLVEMENT: OD intervention is successful only when top management involvement is full-fledged and ensures participation from all levels of managers and all departments in such an exercise. MULTIPLE INTERVENTIONS: Intervention takes place at various levels, individual as well as group and the purpose is molding desirable work culture and leadership styles suitable for the organization. ROLE OF CONSULTANT: Employing an external consultant will be more appropriate as he is less susceptible to influences and more objective. He acts as the change agent facilitating co-ordination and stimulation. CONTINGENCY PLANS: Alternate plans are also devised if in case the original plan fails; the idea is one that of trial and error, hence the need for contingency plans and approach to OD problem. RENSIS LIKERT’S OD FRAMEWORK: Rensis Likert’s 4 system OD framework aims at moving towards truly participative system. Care and caution must be adhered to steer the system gradually from where the organization now works. He also introduced diagnostic analysis to find what causes the current problem. His three part diagnostic analysis includes: A. OUTPUT CAUSES: Low productivity, absenteeism, declining profit B. INTERVENING CAUSES: Organization structure, control, policy and leadership C. ROOT CAUSES: Attitude, motivation level, empowerment and organization culture Tips for Organization Development OD CULTURE: “The OD paradigm values human and organizational growth, collaborative and participative processes and a spirit of enquiry.” Brown and Covey have made some attempts to identify OD values from the following: Norms and Values: Respect for people: People are the most important of all resources. So giving due respect and importance to people induces the creativity and innovation in them. Trust and Support: Trust, openness and supportive climate improve organization culture and empowerment. Power Equalization: This emphasizes hierarchical authority, control and centralization. Confrontation: Do not...






