Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Oct 24th, 2016 | 0 comments

Types of accounting information may be classified into four categories: Operating informationFinancial accounting informationManagement accounting information andCost accounting information 1. Operating Information: This is the kind of information which is required to conduct the day-to-day activities. Examples of operating information are: Amount of wages paid and payable to employeesInformation about the stock of finished goods available for sale andEach one’s cost and selling priceInformation about amounts owed to and owing by the business enterpriseInformation about stock of raw materials, spare parts and accessories and so on. By far, the largest quantity of accounting information provides the raw data (input) for financial accounting, management accounting and cost accounting. Spend Wisely 2. Financial Accounting: Financial accounting information is meant both for owners and managers and also for the use of individuals and agencies external to the business. This accounting is concerned with the recording of transactions for a business enterprise and the periodic preparation of various reports from such records. The records may be for general purpose or for a special purpose. Focus on the Long Term 3. Management Accounting: Management accounting makes use of both historical and estimated data in assisting management in daily operations and in planning for future operations. It deals with specific problems that is faced by enterprise managers at various organizational levels. The management accountant is often concerned with finding alternative courses of action and then helping to select the best one. For e.g. The accountant may help the finance manager in preparing plans for future financing or may help the sales manager in deciding the selling price to be fixed on a new product by providing suitable data. Generally management accounting information is used in three important management functions: ControlCo-ordination andPlanning 4. Marginal costing This is an important technique of management accounting which provides multi dimensional information that helps in decision making. Specialised Accounting Fields A number of specialized fields in accounting also have evolved besides financial accounting. Management accounting and cost accounting are the result of rapid technological advances and enhanced economic growth. The most important among them are explained below: 1. Tax Accounting: Tax accounting is all about the filing of tax returns and the consideration of the tax implications of proposed business transactions or alternative courses of action. Accountants specializing in this branch of accounting are familiar with the tax laws affecting their employer or clients and are up to date on administrative regulations and court decisions on tax cases. 2. International Accounting: This accounting is concerned with the special issues associated with the international trade of multinational business organizations or MNC’s. Accountants specializing in this area must be familiar with the influences that custom, law and taxation of various countries bring to bear on international operations and accounting principles. 3. Social Responsibility Accounting: This branch is the newest field of accounting and is the most difficult to describe. Social responsibility accounting is so called because it not only measures the economic effects of business decisions but also their social effects, which have previously been considered to be immeasurable. Social accounting is also known as social accounting and auditing, social and environmental accounting, corporate social reporting, corporate social responsibility reporting, non-financial reporting or accounting. Benefits of Social Accounting 4. Inflation Accounting: Inflation accounting is a term describing a range of accounting models designed to correct problems arising from historical cost accounting in the presence of highinflation and hyperinflation. Inflation accounting is used in countries experiencing high inflation or hyperinflation. 5. Human Resources Accounting: Human resource accounting is the process of identifying and reporting investments made in the human resources of an organization that are presently unaccounted for in the conventional accounting practices. It is an extension of standard accounting principles. This system of accounting...

Posted by Managementguru in Decision Making, Project Management, Strategy
on May 4th, 2014 | 0 comments
In many segments that rely on a culture of project management, the project officially begins with the official approval of the project, which is not so in the development sector, where the project life more commonly begins with a Project Identification and Screening Phase. The seed of a project arises merely as an idea – a need or opportunity that is weighed, scrutinized, and eventually developed into a project which is managed through the project life cycle. The most critical question one has to ask would be ‘Are we doing the right project?’ Because a problem well understood is half done. Let us Cruise Through the Ideas in Project Identification and Screening Search for New Ideas What are the objectives? *Brainstorm to generate alternative solutions. -Emerging market trends. –SWOT analysis. -Other constraints *Shortlist candidate ideas for detailed scrutiny. Motivation Projects are a means to accomplish -Individual or family objectives -Organizational objectives -National or global objectives Project Identification begins in response to the specific need or the objectives Objectives To increase profitsTo minimize threats of lossesTo become more competitiveTo provide help after a disasterTo train people in a new areaTo reduce pollution in DelhiTo become a successful entrepreneur Download this project planner template to effectively conduct your projects 👇 Minimal-and-Elegant-Project-Planner-TemplateDownload Swot Analysis A tool that detects the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of an organization. In particular, SWOT is a basic, straightforward model that measures what an organization can and cannot do as well as its probable opportunities and threats. The method of SWOT analysis is to take the information from an environmental analysis and distinguish it into internal (strengths and weaknesses) and external issues (opportunities and threats). Once this is over, SWOT analysis determines what may assist the firm in accomplishing its objectives, and what obstacles must be overcome or minimized to achieve desired results. • Objectives • Experience • Resources • Environment pressures -Keeping these factors in mind an analysis of strengths, weaknesses , opportunities and threats is made to identify and select suitable projects. STRENGTHS • Experience and expertise • Financial position • Capital raising capability • Industrial contacts • Foreign collaborations WEAKNESSES • Newer unfamiliar technologies • Inability to raise huge investments • Lack of experience • Lack of trained personnel • Inability to forecast market trends OPPORTUNITIES • Emerging technologies • New products with new markets • New processes with better features • Special financing schemes • Government and other incentives THREATS • Competitors • Poor state of the economy • Outdated technology • Unprofessional management skills • New products and services BRAINSTORMING • A good means to generate new project ideas • Focus on uninhibited participation by a group • Listing of ideas without suppressing creativity at source • List of ideas subjected to screening and evaluation subsequently Download this meeting notes planner template to effectively conduct your project meetings 👇 Pink-Yellow-Gradient-Project-Meeting-Notes-PlannerDownload SCREENING OF IDEAS Poor Fair Good Vgood Excellent (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Weight •Cost * 20% •Risk * 30% •Return * 40% •Hazard * 10% •(score = 2×0.2+3×0.3+4×0.4+2×0.1= 3.1) CRITERIA IN SCREENING PROJECTS • Investment • Rate of return • Risk • Likely profit • Payback • Similarity to existing business • Expected life • Flexibility • Environment impact • Competition Let us look at the following example – Reducing Vehicular Pollution in Delhi Ideas Generated in Brain Storming Restrict registration of new vehiclesEnforce strict emission regulations for vehiclesBan diesel run vehicles on roadIntroduce MRTS – Mass Rapid Transport System for the cityEncourage use of car poolsGrow more trees/ green belts in the cityDeclaring no traffic zones in the cityBan vehicles with an age of ten or more years from plying on the roads These and...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments
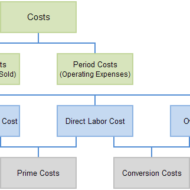
Costing is the technique and process of ascertaining cost whereas cost accounting is the application of costing and cost accounting principles, methods and techniques to the science, art and practice of cost control and ascertainment of profitability.

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
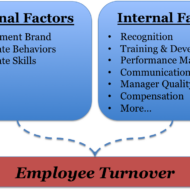
Smart Retention Strategies: Before going into the details of how to handle attrition, the first thing you must understand and realize is this. Each person working for you will have different expectations, perspectives and demands about his job, work environment and compensation respectively. Right at the time of recruiting and selecting the employee, his ideas must be taken into consideration and then it becomes the prerogative of the management whether to hire the person for that particular job. So the first step will be the right person for the right job, giving due importance to the anticipation of the employee who is going to become a member of your business family. Udemy Best Sellers:New Manager Training in Essential SkillsLeadership: Practical Leadership Skills Need for Open Conversation: In case of a small firm or company, it is easy for the manager to have a one on one conversation with each employee to settle his score of grievances then and there. Managers must have an open conversation without room for any ambiguity in the minds of his workers. The manager should try to protect the interest of the employees by representing their demands to the management at the right time. Many employees quit their positions because they have a nagging feeling at the back of their minds that their immediate boss is not the right kind of person to whom they can look up to and ask for support. In big corporates it is not easy to go for a one on one approach. A unique corporate culture that Trains the employees to have an uniform approach to all the systems of routineLed by an effective leader who controls and monitors the behavior and attitude of the workersPossesses sound management practices that make the employees come out with their suggestions freely and induce them to participateProvides satisfactory compensationIncorporates an open door policy catering to the different needs of people and also to the different levels of management, will help the managers to have a healthy relationship with the employees. Human Wants and Needs: Human wants are unlimited and when one want is satisfied, we want more of the same or yet another of a higher order. Approach your workforce to satisfy their craving either in terms of compensation or recognition which will also help to retain your workforce to a greater extent. There should be room for growth, especially for entrepreneurial minds and minds that have parallel thinking. Pic Courtesy: CuteHR Self-Motivation is the Key: Although motivation brings cheer amongst your workforce, self-motivated employees produce better results. Job satisfaction is a relative term; it differs with individuals, some like challenges and some are easily satisfied with an increase in salary quotient. A comprehensive appraisal on the personality of your workforce will give you a clear picture of the IQ (Intelligence Quotient) and EI (Emotional Intelligence) range of your employees which helps in designating employees in the appropriate slots. Such human rationing saves you a lot of time, energy and money as the employees are guaranteed satisfaction in their jobs. Contracts and Agreements: Contracts and agreements bind the employees to the firm only legally. How is that going to help you in terms of productivity? If one of your employees is going to work with discontent, he becomes a problem source spreading the same kind of feeling to others working with him. So it is also necessary for the management to spot out these problem persons either to bring them back into the groove or fire them without any further delay. Rising costs of living and unemployment ratios are really of economic concern, but still we find employees just like that quitting...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

A Process of Intelligence Effective Decision making is a process of Intelligence, Design and choice activities and “is a central part of the management process”. Decisions are hard to make but once decided there should be no second take. The following steps are involved in the process of Decision-making: 1. Recognizing the problem 2. Deciding priorities among problems 3. Diagnosing the problem 4. Developing alternative courses of action 5. Evaluating alternatives 6. Selecting the best alternative 7. Effective implementation and follow-up action. Recognizing the Problem– Herbert A Simon calls this step as an “intelligent activity“. It is important to find out whether there is any deviation from the past experience. For e.g. Sales might decrease, expense might decrease, sometimes there might be deviations from the plan, sales budget, and competitors may outperform by improved systems. Deciding priorities among the problems: A manager would face many problems at the same time. He should not be bogged down with small and unimportant problems. Some problems can be easily solved by the sub-ordinates. Some may not be important. A manager must see that – he selects carefully the most important problem. Peter Drucker says that “once the right problem is perceived then half of the problem is solved”. A manager must diagnose carefully by asking the following questions. a. What is the real problem? b. What are the causes and effects of the problem? c. Is this problem very important? d. Can they be solved by sub-ordinates? e. Which is the right and most important problem to be solved? Diagnosing the Problem: After choosing the right problem the manager must now start diagnosing the problem. There is no simple answer to the question of how to diagnose the problem, because every individual differs in his or her own way of diagnosing the problem depending on the different background orientations and training. A manager must systematically analyze the problem for identifying the alternative causes of action. Developing Alternative Courses of Action: This step is creative and innovative where a manager analyzes from all perspectives Sometimes a manager can also use a technique called “brainstorming” where a few individuals discuss at length the various possible available alternatives. First of all, a manager must be thoroughly familiar with the problem. This is called saturation. Later, he must think about the problem from several view-points which is called deliberation. Sometimes the manager may not get into the crux of the problem, i.e. there may not be any fruitful result of deliberation, and then the manager might temporarily switch off his conscious search and relax. This process of realization is called incubation. Then after sometime, a flash of light may occur, and the manager may get some insights and ideas. This stage is called illumination. In the last stage, which is called accommodation, the manager resynthesises his ideas into a usable proposal. Evaluating the Alternatives: The manager must now give proper weightage to the positive and negative aspects of the alternatives and evaluate by using some criteria like (a) time; (b) cost; (c) risk; (d) results expected; (e) deviations anticipated; (f) resources available for implementation. Selecting the Best Alternative: This is the most important step where the manager selects the best alternative that will yield maximum profits or results with minimum cost, input or resources. To put it in simple terms, the solution should be able to solve the problem in the best possible way. Effective Implementation and Follow-up Action: Any decision without proper implementation becomes futile and hence proper care must be taken by the manager to pool resources and start implementing the decision taken. In large organizations, follow-up procedures are available in the system...










